ANSARI - Artificial Neural Network: Learn About Electronics (Learn Electronics)
Here you can read online ANSARI - Artificial Neural Network: Learn About Electronics (Learn Electronics) full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2020, genre: Children. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.

Artificial Neural Network: Learn About Electronics (Learn Electronics): summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Artificial Neural Network: Learn About Electronics (Learn Electronics)" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
ANSARI: author's other books
Who wrote Artificial Neural Network: Learn About Electronics (Learn Electronics)? Find out the surname, the name of the author of the book and a list of all author's works by series.
Artificial Neural Network: Learn About Electronics (Learn Electronics) — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Artificial Neural Network: Learn About Electronics (Learn Electronics)" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:

- 1943 It has been assumed that the concept of neural network started with the work of physiologist, Warren McCulloch, and mathematician, Walter Pitts, when in 1943 they modeled a simple neural network using electrical circuits in order to describe how neurons in the brain might work.
- 1949 Donald Hebbs book, The Organization of Behavior , put forth the fact that repeated activation of one neuron by another increases its strength each time they are used.
- 1956 An associative memory network was introduced by Taylor.
- 1958 A learning method for McCulloch and Pitts neuron model named Perceptron was invented by Rosenblatt.
- 1960 Bernard Widrow and Marcian Hoff developed models called "ADALINE" and MADALINE.
- 1961 Rosenblatt made an unsuccessful attempt but proposed the backpropagation scheme for multilayer networks.
- 1964 Taylor constructed a winner-take-all circuit with inhibitions among output units.
- 1969 Multilayer perceptron MLP MLP was invented by Minsky and Papert.
- 1971 Kohonen developed Associative memories.
- 1976 Stephen Grossberg and Gail Carpenter developed Adaptive resonance theory.
- 1982 The major development was Hopfields Energy approach.
- 1985 Boltzmann machine was developed by Ackley, Hinton, and Sejnowski.
- 1986 Rumelhart, Hinton, and Williams introduced Generalised Delta Rule.
- 1988 Kosko developed Binary Associative Memory BAM BAM and also gave the concept of Fuzzy Logic in ANN.
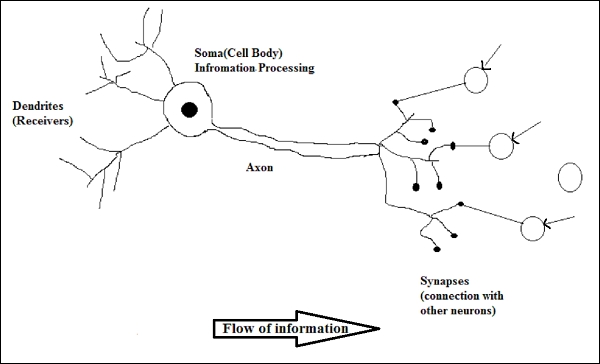
- Dendrites They are tree-like branches, responsible for receiving the information from other neurons it is connected to. In other sense, we can say that they are like the ears of neuron.
- Soma It is the cell body of the neuron and is responsible for processing of information, they have received from dendrites.
- Axon It is just like a cable through which neurons send the information.
- Synapses It is the connection between the axon and other neuron dendrites.
Biological Neural Network BNN BNN | Artificial Neural Network ANN ANN |
Soma | Node |
Dendrites | Input |
Synapse | Weights or Interconnections |
Axon | Output |
Criteria | BNN | ANN |
Processing | Massively parallel, slow but superior than ANN | Massively parallel, fast but inferior than BNN |
Size | 10 neurons and 10 interconnections | 10 to 10 nodes mainlydependsonthetypeofapplicationandnetworkdesigner mainlydependsonthetypeofapplicationandnetworkdesigner |
Learning | They can tolerate ambiguity | Very precise, structured and formatted data is required to tolerate ambiguity |
Fault tolerance | Performance degrades with even partial damage | It is capable of robust performance, hence has the potential to be fault tolerant |
Storage capacity | Stores the information in the synapse | Stores the information in continuous memory locations |
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Artificial Neural Network: Learn About Electronics (Learn Electronics)»
Look at similar books to Artificial Neural Network: Learn About Electronics (Learn Electronics). We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Artificial Neural Network: Learn About Electronics (Learn Electronics) and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.














