This workbook is designed to help students practice writinggeometry proofs. The early chapters review terminology, notation, and theunderlying principles. Another chapter outlines the strategy and offers tips.Nine fully-solved examples are provided to help serve as a guide. Each of theexercises is fully solved in the back of the book. This book focuses on plane Euclidean geometry.
Standardtopics are included, such as: parallel lines and transversals alternate interior angles similar and congruent triangles circles, chords, and tangents quadrilaterals the Pythagorean theorem regular polygons interior and exterior angles complements and supplements area of plane figures inscribed and circumscribed the centroid of a triangle May you (or your students) find this workbookhelpful and improve your fluency in writing geometry proofs.
1 TERMINOLOGY
A straight
line extends infinitely ineach direction. A
line segment is a portion of astraight line: it connects two points. The line segment is finite. It doesntextend beyond its endpoints.
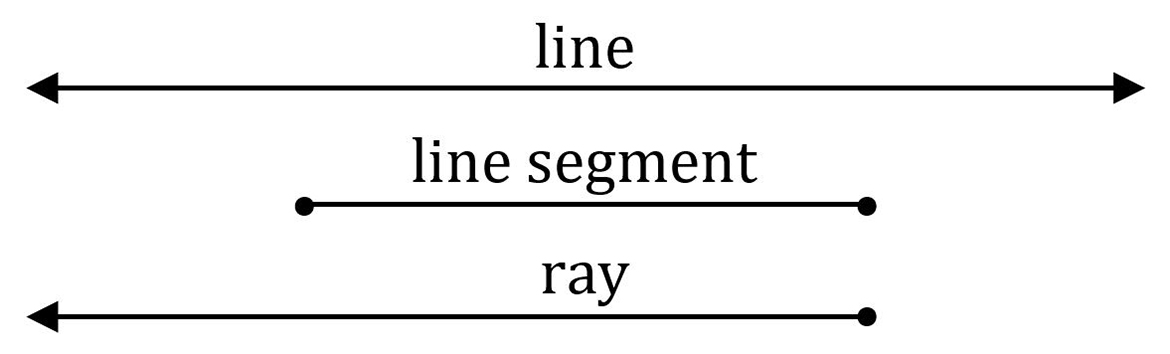
An
angle forms when two linesintersect. (In this case, it doesnt matter if they are lines, line segments,or rays. (In this case, it doesnt matter if they are lines, line segments,or rays.
Although if they are both lines, they technically form four angles.) Angular measure refers to thenumerical value that you would obtain (in degrees or radians) if you measuredthe angle with a protractor. Angular measure represents a number, whereas anglerefers to a geometric figure (it is a visual representation). A vertex is the point where two linesintersect. (In this case, it doesnt matter if they are lines, line segments,or rays.) The plural form of this term is vertices .  One degree is an angular measurecorresponding to 1/360 of a complete circle. One radian is an angular measuredefined such that
One degree is an angular measurecorresponding to 1/360 of a complete circle. One radian is an angular measuredefined such that  radians corresponds to 180.
radians corresponds to 180.
A right angle has an angular measureof 90. One way to form a right angle is to draw one quarter of a circle. An acute angle has an angular measurethat is less than 90. An obtuse angle has an angularmeasure that is greater than 90. 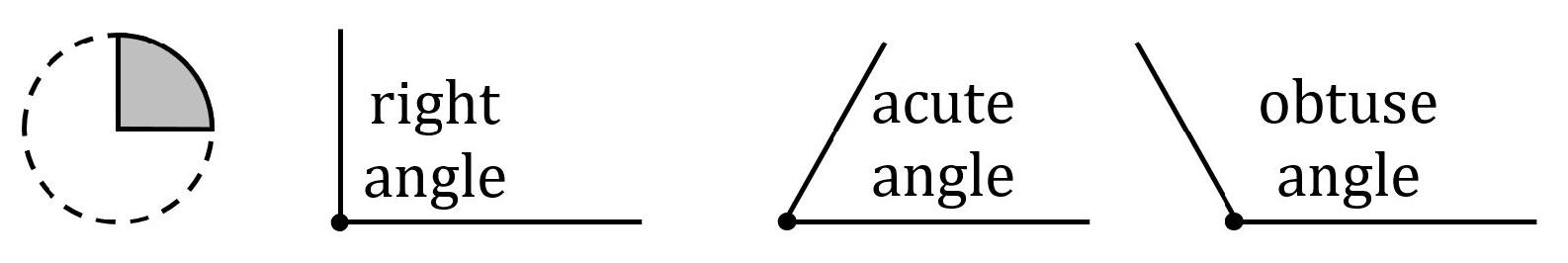 Parallel lines extend in the samedirection and are the same distance apart at any position (such that they willnever intersect). Intersecting lines meet at somepoint.
Parallel lines extend in the samedirection and are the same distance apart at any position (such that they willnever intersect). Intersecting lines meet at somepoint.
When only a portion of each line is drawn, you may need to imagineextending the lines in order to visualize the point of intersection. Perpendicular lines intersect at aright angle. They form a 90 angular measure. Two lines are askew if they areneither parallel nor intersecting. Two lines that lie in the same plane cantbe askew, but it is possible for two nonplanar lines in space to be askew.(However, it is possible for two coplanar line segments to be askew. Recallthat a line segment is finite, whereas a line extends infinitely.) 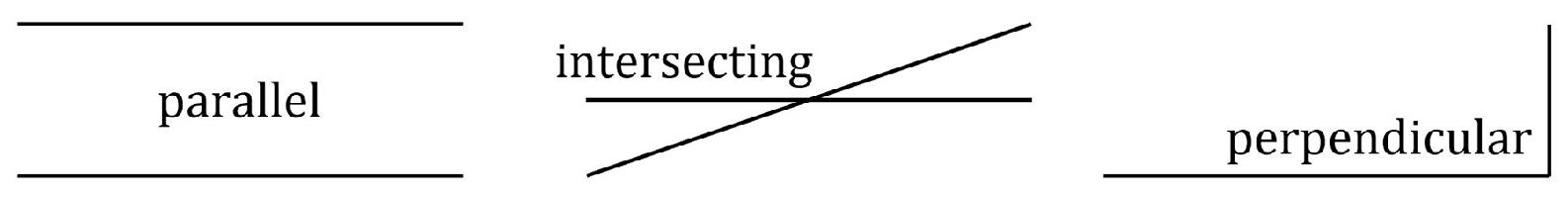 Complementary angles form a rightangle.
Complementary angles form a rightangle.
Their angular measures add up to 90. Supplementary angles form straightline. Their angular measures add up to 180. Vertical angles form on oppositesides of a vertex when lines intersect. Vertical angles are congruent. 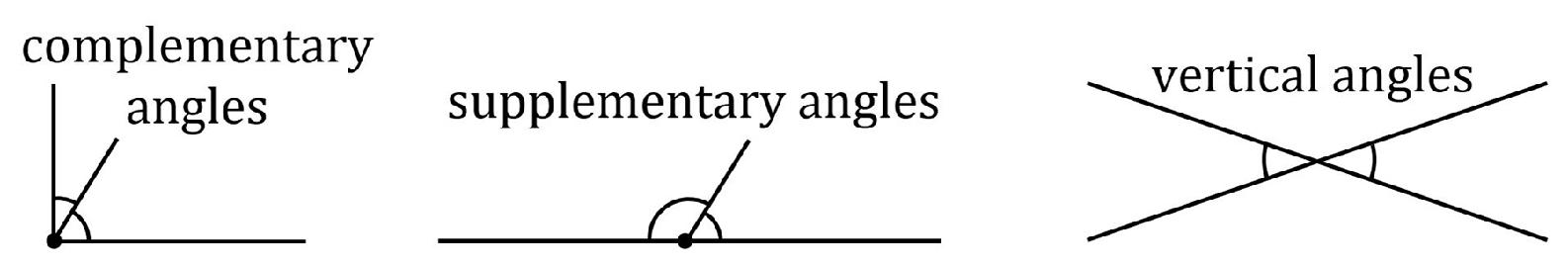 A plane is an infinitely large, flat,two-dimensional shape.
A plane is an infinitely large, flat,two-dimensional shape.
Imagine an infinitely large rectangle (or even a circle)as that would form a plane. A polygon is a closed plane figurewith straight edges. An equilateral polygon has sides withthe same length. An equiangular polygon has interiorangles with the same angular measure. A regular polygon is both equilateraland equiangular. An interior angle forms at the vertexof a polygon and lies inside of the polygon.
An exterior angle is formed by oneedge of a polygon and a line that extends from an adjacent edge. 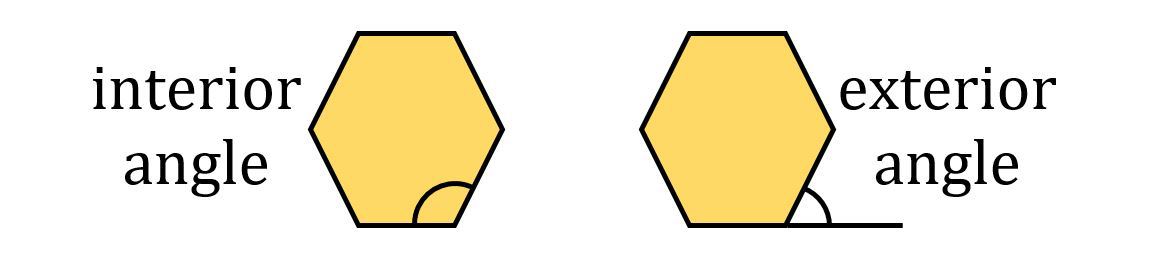 For a convex polygon, the measure ofall of the interior angles is less than 180. For a concave polygon, at least oneinterior angle is greater than 180.
For a convex polygon, the measure ofall of the interior angles is less than 180. For a concave polygon, at least oneinterior angle is greater than 180. 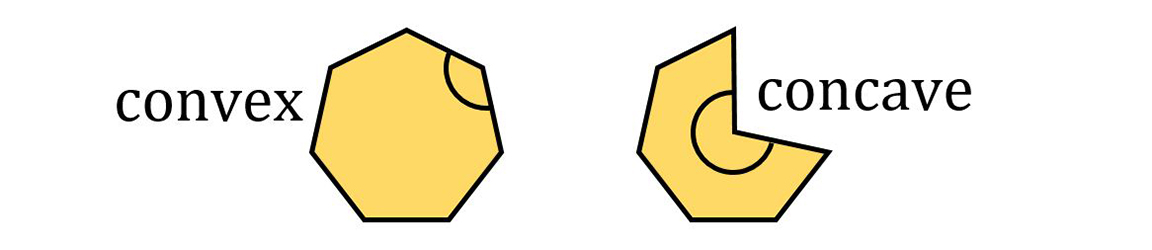 Some common polygons include thetriangle (3 sides), quadrilateral (4 sides), pentagon (5 sides), hexagon (6sides), heptagon (7 sides), and octagon (8 sides).
Some common polygons include thetriangle (3 sides), quadrilateral (4 sides), pentagon (5 sides), hexagon (6sides), heptagon (7 sides), and octagon (8 sides). 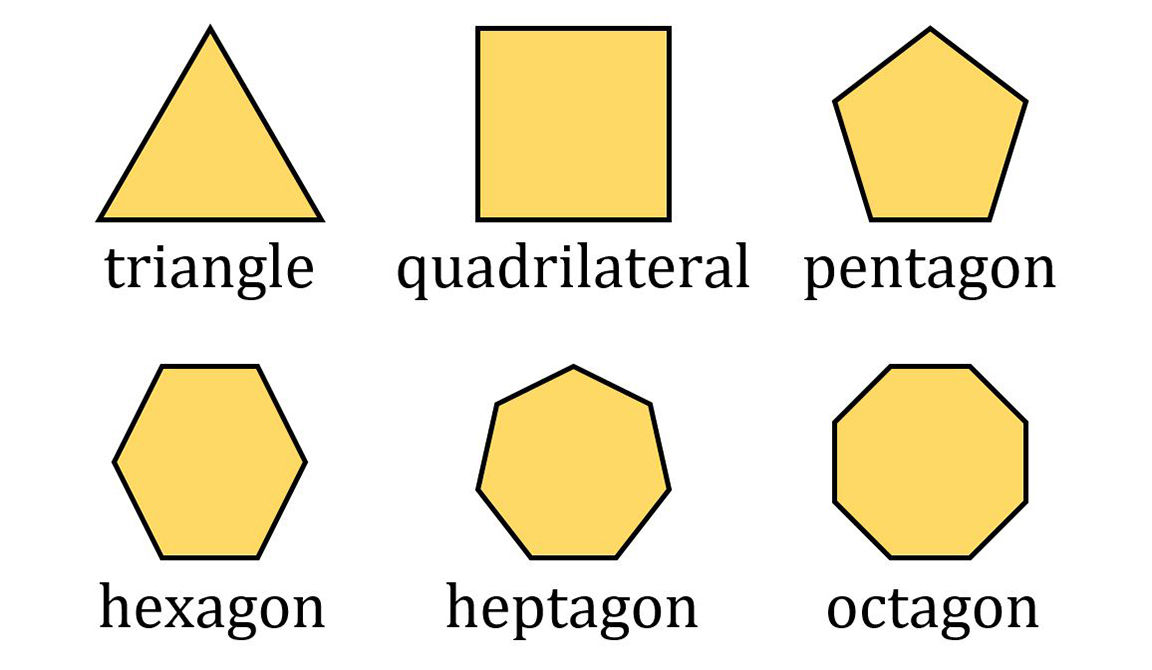 An isosceles triangle has two sideswith the same length. An equilateral triangle has threesides with the same length.
An isosceles triangle has two sideswith the same length. An equilateral triangle has threesides with the same length.
An equilateral triangle is also equiangular (butthis isnt necessarily true for other types of polygons). A scalene triangle has sides with alllengths different.  A quadrilateral is a polygon withfour sides. Special quadrilaterals include the square (regular), rectangle(equiangular), rhombus (equilateral), parallelogram (two pairs of paralleledges), and the trapezoid (one pair of parallel edges).
A quadrilateral is a polygon withfour sides. Special quadrilaterals include the square (regular), rectangle(equiangular), rhombus (equilateral), parallelogram (two pairs of paralleledges), and the trapezoid (one pair of parallel edges). 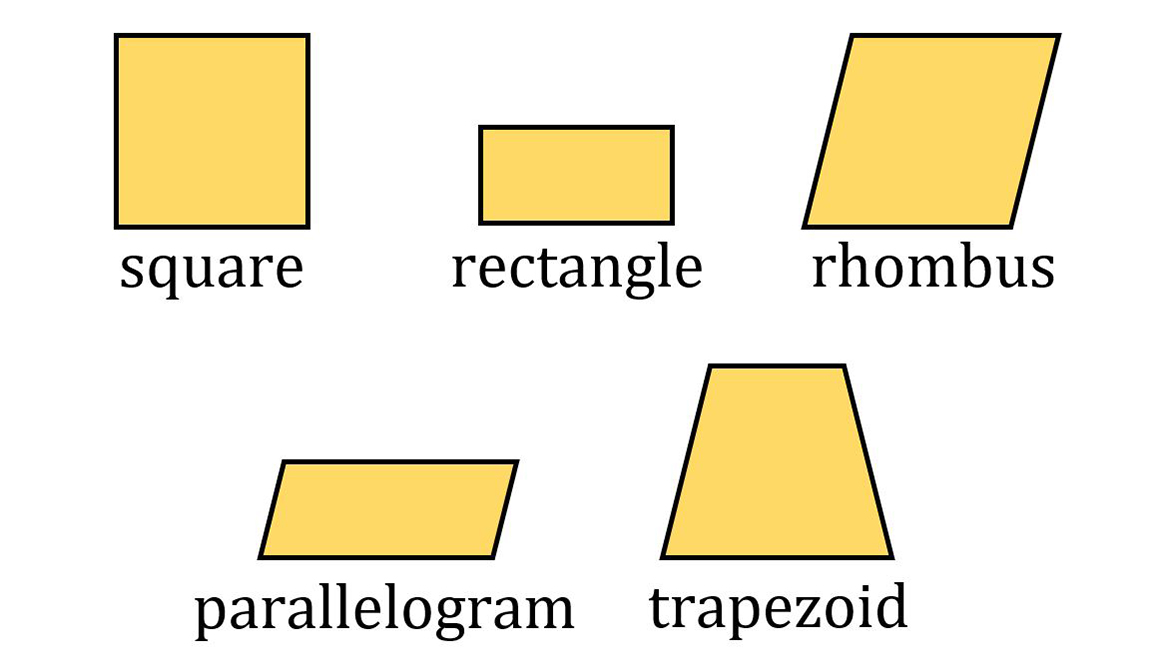 The term equidistant means equallydistant. The midpoint of a line segment isequidistant from the endpoints.
The term equidistant means equallydistant. The midpoint of a line segment isequidistant from the endpoints.
A median joins the vertex of atriangle to the midpoint of the opposite side. A bisector cuts something into twoequal parts. When the term bisector is applied to a line segment, it cuts theline segment in half. When the term bisector is applied to an angle, it cutsthe angle in half. For a general triangle, note that the angle bisector isntthe same as the median. 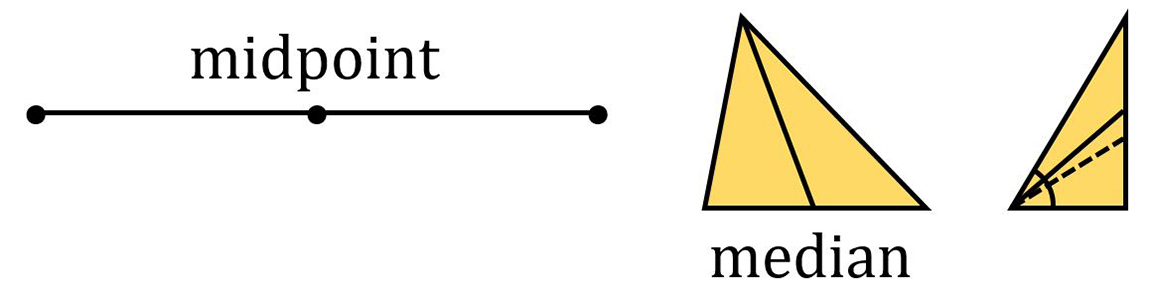









 Essential Practice Problems Workbook with Full Solutions
Essential Practice Problems Workbook with Full Solutions  Chris McMullen, Ph.D.
Chris McMullen, Ph.D.  monkeyphysicsblog.wordpress.com improveyourmathfluency.com chrismcmullen.com
monkeyphysicsblog.wordpress.com improveyourmathfluency.com chrismcmullen.com 

 An angle forms when two linesintersect. (In this case, it doesnt matter if they are lines, line segments,or rays. (In this case, it doesnt matter if they are lines, line segments,or rays.
An angle forms when two linesintersect. (In this case, it doesnt matter if they are lines, line segments,or rays. (In this case, it doesnt matter if they are lines, line segments,or rays.  One degree is an angular measurecorresponding to 1/360 of a complete circle. One radian is an angular measuredefined such that
One degree is an angular measurecorresponding to 1/360 of a complete circle. One radian is an angular measuredefined such that  radians corresponds to 180.
radians corresponds to 180.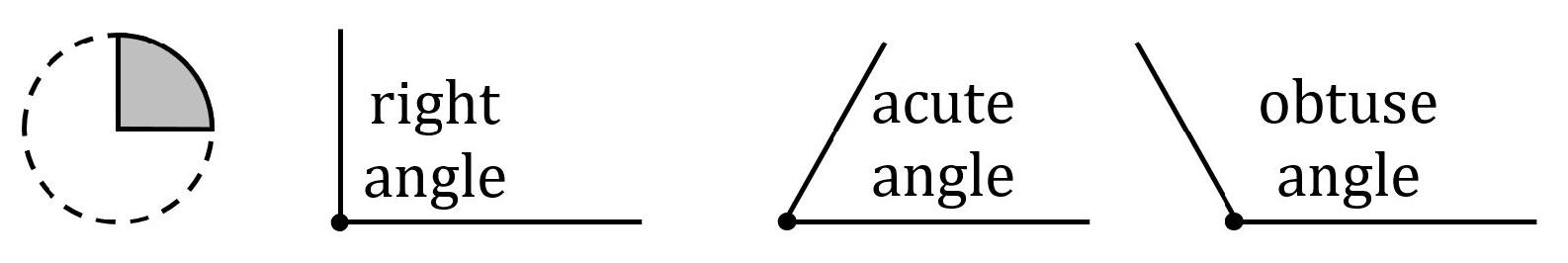 Parallel lines extend in the samedirection and are the same distance apart at any position (such that they willnever intersect). Intersecting lines meet at somepoint.
Parallel lines extend in the samedirection and are the same distance apart at any position (such that they willnever intersect). Intersecting lines meet at somepoint. Complementary angles form a rightangle.
Complementary angles form a rightangle. A plane is an infinitely large, flat,two-dimensional shape.
A plane is an infinitely large, flat,two-dimensional shape. For a convex polygon, the measure ofall of the interior angles is less than 180. For a concave polygon, at least oneinterior angle is greater than 180.
For a convex polygon, the measure ofall of the interior angles is less than 180. For a concave polygon, at least oneinterior angle is greater than 180.  Some common polygons include thetriangle (3 sides), quadrilateral (4 sides), pentagon (5 sides), hexagon (6sides), heptagon (7 sides), and octagon (8 sides).
Some common polygons include thetriangle (3 sides), quadrilateral (4 sides), pentagon (5 sides), hexagon (6sides), heptagon (7 sides), and octagon (8 sides).  An isosceles triangle has two sideswith the same length. An equilateral triangle has threesides with the same length.
An isosceles triangle has two sideswith the same length. An equilateral triangle has threesides with the same length. A quadrilateral is a polygon withfour sides. Special quadrilaterals include the square (regular), rectangle(equiangular), rhombus (equilateral), parallelogram (two pairs of paralleledges), and the trapezoid (one pair of parallel edges).
A quadrilateral is a polygon withfour sides. Special quadrilaterals include the square (regular), rectangle(equiangular), rhombus (equilateral), parallelogram (two pairs of paralleledges), and the trapezoid (one pair of parallel edges).  The term equidistant means equallydistant. The midpoint of a line segment isequidistant from the endpoints.
The term equidistant means equallydistant. The midpoint of a line segment isequidistant from the endpoints.