Contents
Words in the glossary appear in bold type the first time they are used in the text.
Please visit our website, www.garethstevens.com. For a free color catalog of all our high-quality books, call toll free 1-800-542-2595 or fax 1-877-542-2596.
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Names: Jacobson, Bray, author.
Title: Food chains and webs / Bray Jacobson.
Description: New York : Gareth Stevens Publishing, [2020] | Series: A look at nature's cycles | Includes index.
Identifiers: LCCN 2018039603| ISBN 9781538241066 (paperback) | ISBN 9781538241080 (library bound) | ISBN 9781538241073 (6 pack)
Subjects: LCSH: Food chains (Ecology)--Juvenile literature.
Classification: LCC QH541.15.F66 J34 2020 | DDC 577/.16--dc23
LC record available at https://lccn.loc.gov/2018039603
First Edition
Published in 2020 by
Gareth Stevens Publishing
111 East 14th Street, Suite 349
New York, NY 10003
Copyright 2020 Gareth Stevens Publishing
Designer: Sarah Liddell
Editor: Kristen Nelson
Photo credits: Cover, p. 1 (main) MZPHOTO.CZ/Shutterstock.com; cover, p. 1 (inset) Rudmer Zwerver/Shutterstock.com; arrow background used throughout Inka1/Shutterstock.com; p. 5 Igorsky/Shutterstock.com; p. 7 irin-k/Shutterstock.com; p. 9 Paul Reeves Photography/ Shutterstock.com; p. 11 (background) Rich Carey/Shutterstock.com; pp. 11 (food chain), 25 NoPainNoGain/Shutterstock.com; p. 13 Tony Baggett/Shutterstock.com; pp. 15, 21, 25, 30 (background) ismed_photography_SS/Shutterstock.com; p. 15 (food chain) Colin Hayes/ Shutterstock.com; p. 17 Andrew Astbury/Shutterstock.com; p. 19 alinabel/Shutterstock.com; p. 21 (food web) snapgalleria/Shutterstock.com; p. 23 Derrick Hamrick/imageBROKER/ Getty Images; p. 27 Warut Prathaksithorn/Shutterstock.com; p. 29 ugurhan/E+/Getty Images; p. 30 (food web) Vecton/Shutterstock.com.
All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced in any form without permission in writing from the publisher, except by a reviewer.
Printed in the United States of America
CPSIA compliance information: Batch #CS19GS: For further information contact Gareth Stevens, New York, New York at 1-800-542-2595.
ITS ALL CONNECTED!
All the living things, or organisms, in an ecosystem are connected. Organisms have feeding relationships with one another, whether predator, prey, or plant. Food chains and food webs are the ways scientists show these relationships.

MAKE THE GRADE
An ecosystem is every living and nonliving thing found in a place, including animals, plants, and even the water and rocks there.
ON THE LEVEL
In food chains and food webs, organisms are grouped into trophic, or feeding, levels. Producers are often the first trophic level. They dont eat other organisms. Instead, producers make their own food. Most producers are autotrophs, which means they make their own food using photosynthesis.

MAKE THE GRADE
Common producers include grasses, flowering plants, algae, and some kinds of bacteria.
Consumers eat other organisms. The animals on the second feeding level are often called primary consumers because they eat producers. Primary consumers are commonly herbivores, which means they only eat plants. Others may eat algae or bacteria.

MAKE THE GRADE
Consumers are also called heterotrophs.
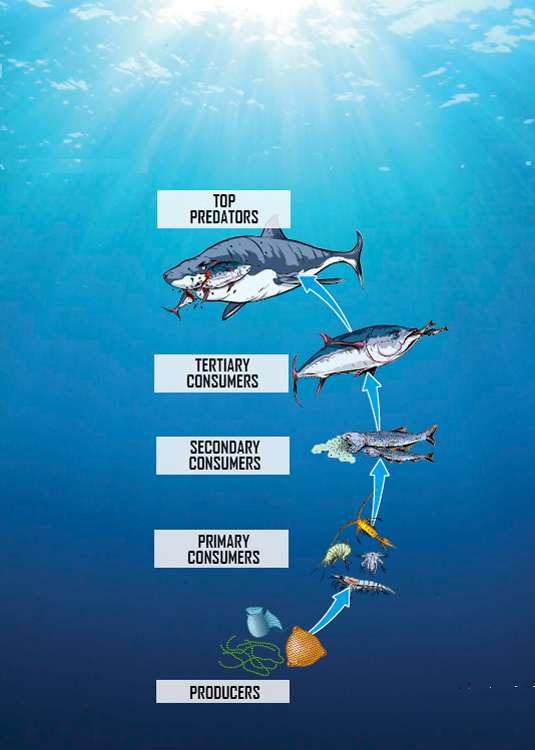
Secondary consumers are the animals that eat primary consumers! Theyre commonly carnivores, or meat eaters. Tertiary consumers eat secondary consumers and may eat primary consumers, too. There are also higher levels of consumers that eat the animals below them on the food chain!
MAKE THE GRADE
Top predators are animals that dont have any natural enemies. Theyre found in the highest levels of an ecosystems food chain or web.
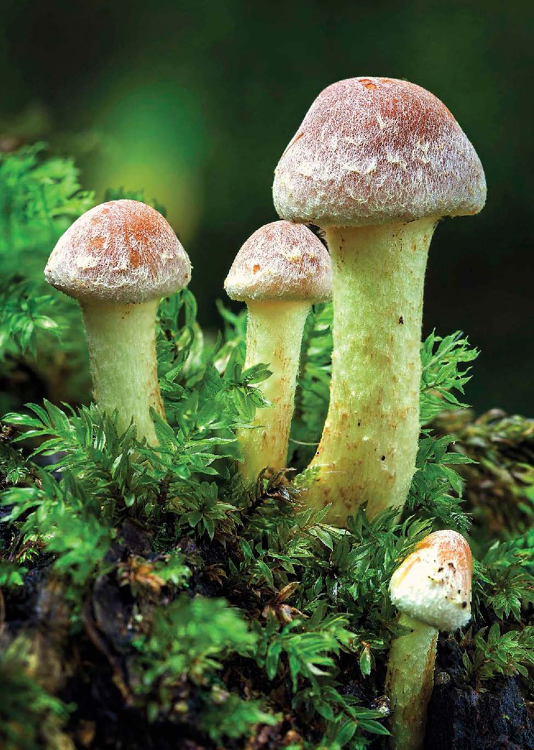
Decomposers are an important part of all ecosystems, but they arent often shown in food chains or webs. Decomposers eat the matter from dead producers and consumers. They break it down into nutrients. These nutrients go back into the soil for producers to use!

MAKE THE GRADE
Common decomposers are bacteria and fungi, as well as some bugs, slugs, and worms. They naturally recycle matter in an ecosystem!
THE MAIN CHAIN
Food chains show how energy and nutrients move through living things as they eat and are eaten by other living things. Arrows between pictures of each organism show the direction the energy and nutrients are moving. Most food chains start with producers.
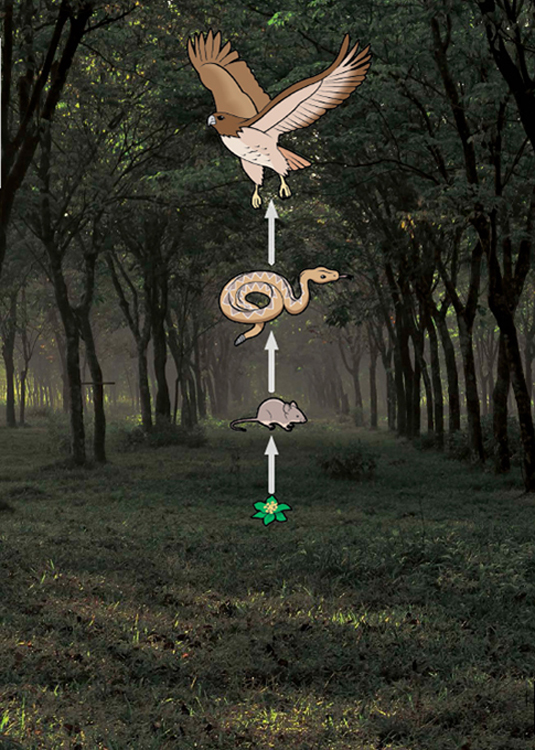

MAKE THE GRADE
Some food chains start with the dead matter of producers and consumers. They then show decomposers and detritivores, or consumers that eat dead matter.
ENERGY LOSS
Food chains and webs can only get so large. Thats because living things use most of the energy they get from eating to stay alive. Not much of this energy is kept in their biomass, or body. And their body is what the next consumer eats!

MAKE THE GRADE
Some of what organisms eat cannot be digested and leaves the body as waste. That matters energy is lost. Its not used or stored in the body.
Only about 10 percent of the energy that moves into a trophic level makes it to the consumers above it! So, the size of food chains and webs reach a limit. Thats also why there are fewer consumers at the top of a food chain or web.
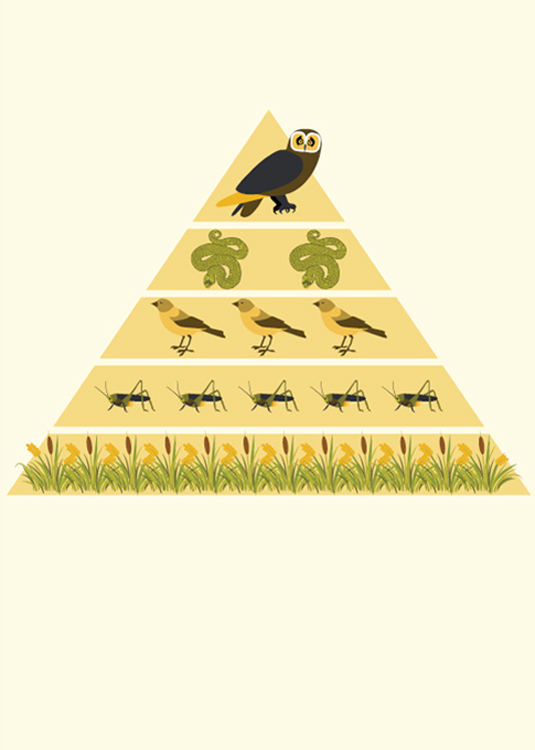

MAKE THE GRADE
Most food chains or webs can only reach about four trophic levels.
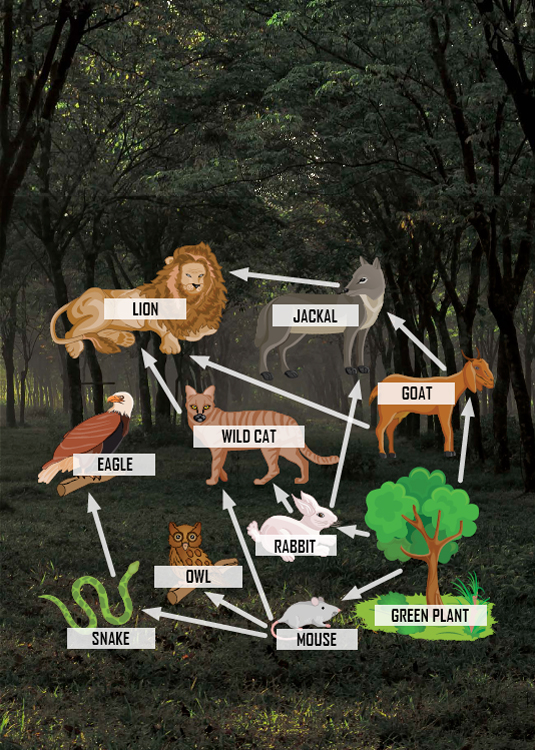
INTO THE WEB
The feeding relationships in an ecosystem arent linear like a food chain shows. Theyre interconnected! One animal can be part of many food chains. A food web shows the feeding relationships between all the organisms in an ecosystem.