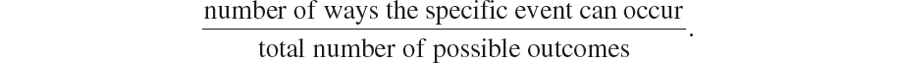ATTACKING PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS PROBLEMS
David S. Kahn
Dover Publications, Inc., Mineola, New York
Copyright
Copyright 2016 by David S. Kahn
All rights reserved.
Bibliographical Note
Attacking Probability and Statistics Problems is a new work, first published by Dover Publications, Inc., in 2016.
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Names: Kahn, David S.
Title: Attacking probability and statistics problems / David S. Kahn.
Description: Mineola, New York : Dover Publications, Inc., 2016.
Identifiers: LCCN 2015047548| ISBN 9780486801445 | ISBN 0486801446
Subjects: LCSH: Mathematical statisticsStudy and teaching. |
ProbabilitiesStudy and teaching.
Classification: LCC QA276.18. K34 2016 | DDC 519.5dc23 LC record available at http://lccn.loc.gov/2015047548
Manufactured in the United States
80144601 2016
www.doverpublications.com
To the Reader:
Welcome to Probability and Statistics! In most of the mathematics that you have probably studied before this, you usually are given a problem for which you try to find the exact answer. One of the challenging aspects of Probability and Statistics is that there often is not necessarily an exact answer to a given problem. Instead, you may have to find a range of numbers for an answer or you may have to look at some data and decide that your data is not good enough for you to draw a definite conclusion. In Probability and Statistics, we study what might occur or what the data is probably trying to tell us. This can be challenging, but this book will teach you how to attack Probability and Statistics problems and successfully conquer them.
This book is not meant to be an exhaustive study of Probability or Statistics. We will first look at Probability in the first four chapters, focusing on the kind of problems that we will need to be able to solve in order to learn Statistics. While Probability is a fascinating and complex topic, we do not have the space to cover all of the various aspects of the field. Instead, we will look at the basics of Probability, so that we can understand the Statistics portion of the book.
The remaining chapters are devoted to Statistics. They are intended to help you learn to attack the kinds of problems that you will encounter in an elementary Statistics course. Also, much of what is taught in a Statistics course can be calculated using a statistical software program, a spreadsheet program, or even a calculator. Although we will show you how to calculate a variety of statistics, we leave the more cumbersome and obscure calculations for you to carry out with your computer. Instead, it is more important to understand what the statistics mean than to be able to do the calculations themselves (which can be tedious).
We have organized this book so that you can proceed from one topic to another, or you can jump to the topics that you want to work on. To be truthful, you will probably find that you need to go through all of the units if you truly wish to be able to attack Probability and Statistics. The book is divided into 12 units, each of which will teach you what you need to know to do well in that topic. This book focuses on the essentials and how to master the problems. We suggest that you read through each unit completely, do all of the exercises, and complete all of the practice problems. Each example and problem has a complete explanation to help you understand how to solve the problem correctly. There are many good textbooks on Probability and Statistics, and after you have worked through a unit, you may want to refer to a textbook for further practice on that units topic.
Probability and Statistics is a fascinating area of mathematics. So much of what you will encounter in your daily lives involves both topics. After you have gone through this book, you will be able to do well in your Statistics course. You will also have a better understanding of the statistics that you will read and hear about. Are you ready? Then its time to Attack Probability and Statistics!
Acknowledgments
First of all, I would like to thank my editor, Janet Kopito, for her patience and meticulousness. Next, I would like to thank Marisa Bruno for working through all of the problems and double-checking my calculations. I would also like to thank the copy editor, Louise Jarvis, and the proofreader, Lynze Greathouse, for finding the many typos that one makes when writing a mathematics book. I owe a lifetime debt to my father, Peter Kahn, and to my dear friend, Arnold Feingold, who encouraged my interest in mathematics and have always been there to guide me through the rough spots. And finally, I would like to thank the very many students whom I have taught and tutored, who never hesitate to correct me when I am wrong, and who provide the fulfillment that I so deeply derive from teaching math.
ATTACKING PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS PROBLEMS
UNIT ONE
Basic Probability
In this unit, we are going to learn some of the basics of probability. Statistics, as we will learn, is a way of describing and analyzing events that have already occurred. Probability, on the other hand, is a way of predicting events that might occur. In order to understand the probability that a specific event might occur, we need to know about how often that event might occur relative to how often related events might occur. For example, if we roll a die, how often will the number 1 occur compared to how often any of the numbers from 1 to 6 might occur. Given that there are six numbers on a die and, assuming that it is an honest die, any of those numbers could occur when we roll the die, we expect the number 1 to occur  of the time. Suppose, instead, that we had a 10-sided die, with the numbers 1 to 10 on it. If we roll that die, we would expect the number 1 to occur
of the time. Suppose, instead, that we had a 10-sided die, with the numbers 1 to 10 on it. If we roll that die, we would expect the number 1 to occur 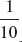 of the time. Going back to our regular die, how often would we expect an even number to occur? Well, there are 3 even numbers, {2, 4, 6}, and 3 odd numbers, {1, 3, 5}. When we roll the die, we would expect an even number to occur
of the time. Going back to our regular die, how often would we expect an even number to occur? Well, there are 3 even numbers, {2, 4, 6}, and 3 odd numbers, {1, 3, 5}. When we roll the die, we would expect an even number to occur  or
or  of the time.
of the time.
This leads us to our first rule:
Rule #1: The probability that an event will occur is
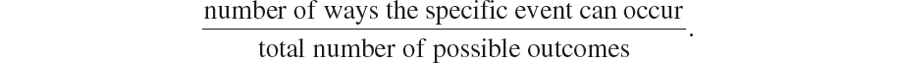
Note that when we use the term event, what we mean is a roll of the die, a toss of the coin, etc. The denominator, or total number of possible outcomes is referred to as the sample space. For example, if we roll a 6-sided die, the sample space is the set of numbers that we can roll, namely {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. If we toss a coin twice, the sample space is {HH, HT, TH, TT}, where H represents the head side of a coin (heads) and T represents the tail side of a coin (tails). A sample space is very useful for enumerating the possible outcomes when that number is relatively small. We would not want to write out the sample space for tossing 10 coins. There would be 210 = 1024 elements!
Lets look at some more examples.
Example 1: We roll a 6-sided die. What is the probability that a multiple of 3 will occur?
There are two multiples of 3, namely 3 and 6. There are 6 possible outcomes. Thus, the probability that a multiple of 3 will occur is 
Next page











 of the time. Suppose, instead, that we had a 10-sided die, with the numbers 1 to 10 on it. If we roll that die, we would expect the number 1 to occur
of the time. Suppose, instead, that we had a 10-sided die, with the numbers 1 to 10 on it. If we roll that die, we would expect the number 1 to occur 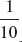 of the time. Going back to our regular die, how often would we expect an even number to occur? Well, there are 3 even numbers, {2, 4, 6}, and 3 odd numbers, {1, 3, 5}. When we roll the die, we would expect an even number to occur
of the time. Going back to our regular die, how often would we expect an even number to occur? Well, there are 3 even numbers, {2, 4, 6}, and 3 odd numbers, {1, 3, 5}. When we roll the die, we would expect an even number to occur  or
or  of the time.
of the time.