Charu C. Aggarwal - Artificial Intelligence A Textbook
Here you can read online Charu C. Aggarwal - Artificial Intelligence A Textbook full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2021, publisher: Springer International Publishing, genre: Computer. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
- Book:Artificial Intelligence A Textbook
- Author:
- Publisher:Springer International Publishing
- Genre:
- Year:2021
- Rating:3 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Artificial Intelligence A Textbook: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Artificial Intelligence A Textbook" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
Artificial Intelligence A Textbook — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Artificial Intelligence A Textbook" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:

This Springer imprint is published by the registered company Springer Nature Switzerland AG
The registered company address is: Gewerbestrasse 11, 6330 Cham, Switzerland
To my wife Lata, my daughter Sayani,
and all my computer science instructors
AI is likely to be either the best or the worst thing that happened to humanity. Stephen Hawking
Artificial intelligence is a field that spans work from multiple communities, including classical logic programming, machine learning, and data mining. Since the founding of the field, there has a clear dichotomy between the deductive reasoning and the inductive learning forms of artificial intelligence. In the deductive reasoning view, one starts with various forms of domain knowledge (which are often stored as knowledge bases), and these forms of domain knowledge are used in order to make inferences. Such methods are often highly interpretable. The domain knowledge can be used in order to create hypotheses, which are then leveraged to make predictions. For example, in a chess game, the domain knowledge about the importance and position of pieces can be used to create a hypothesis about the quality of a position. This hypothesis can be used to predict moves by searching a tree of possible moves up to a specific number of moves. In learning methods, data-driven evidence is used to learn how to make predictions. For example, it is possible to generate data from chess games using self play, and then learn which moves are best for any particular (type of) position. Since the number of possible alternative move sequences in chess is too large to evaluate explicitly, chess programs often use various types of machine learning methods to relate typical patterns of pieces on the board to make predictions from carefully selected sequences. This approach is somewhat similar to how humans make chess moves. In the early years, deductive reasoning methods were more popular, although inductive learning methods have become increasingly popular in recent years. Many books in artificial intelligence tend to focus predominantly on deductive reasoning as a legacy from its dominance during the early years. This book has attempted to strike a balance between deductive reasoning and inductive learning.
The main disadvantage of inductive learning methods is that they are not interpretable, and they often require a lot of data. A key point is that humans do not require a lot of data to learn. For example, a child is often able to learn to recognize a truck with the use of a small number of examples. Although the best solutions to many problems in artificial intelligence integrate methods from both these areas, there is often little discussion of this type of integration. This textbook focuses on giving an integrated view of artificial intelligence, along with a discussion of the advantages of different views of artificial intelligence.
Methods based on deductive reasoning: Chapters discuss deductive reasoning methods. The primary focus areas include search and logic.
Methods based on inductive learning: Learning methods are discussed in Chapters . The topics covered include classification, neural networks, unsupervised learning, probabilistic graphical models, and reinforcement learning.
Methods based on both reasoning and learning: Chapter discuss a number of methods that have aspects of both reasoning and learning. This include techniques like Bayesian networks, knowledge graphs, and neuro-symbolic artificial intelligence.
Throughout this book, a vector or a multidimensional data point is annotated with a bar, such as 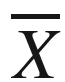 or
or 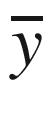 . A vector or multidimensional point may be denoted by either small letters or capital letters, as long as it has a bar. Vector dot products are denoted by centered dots, such as
. A vector or multidimensional point may be denoted by either small letters or capital letters, as long as it has a bar. Vector dot products are denoted by centered dots, such as 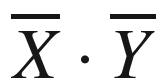 . A matrix is denoted in capital letters without a bar, such as R. Throughout the book, the nd matrix corresponding to the entire training data set is denoted by D, with n data points and d dimensions. The individual data points in D are therefore d-dimensional row vectors, and are often denoted by
. A matrix is denoted in capital letters without a bar, such as R. Throughout the book, the nd matrix corresponding to the entire training data set is denoted by D, with n data points and d dimensions. The individual data points in D are therefore d-dimensional row vectors, and are often denoted by 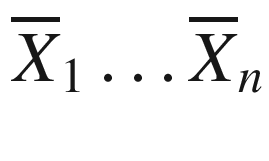 . On the other hand, vectors with one component for each data point are usually n-dimensional column vectors. An example is the n-dimensional column vector
. On the other hand, vectors with one component for each data point are usually n-dimensional column vectors. An example is the n-dimensional column vector 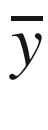 of class variables of n data points. An observed value yi is distinguished from a predicted value
of class variables of n data points. An observed value yi is distinguished from a predicted value 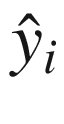
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Artificial Intelligence A Textbook»
Look at similar books to Artificial Intelligence A Textbook. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Artificial Intelligence A Textbook and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.












