
All That Glitters
From the moment the first humans noticed sparkly chunks of rock in the ground, crystals and gemstones have been hunted and prized.
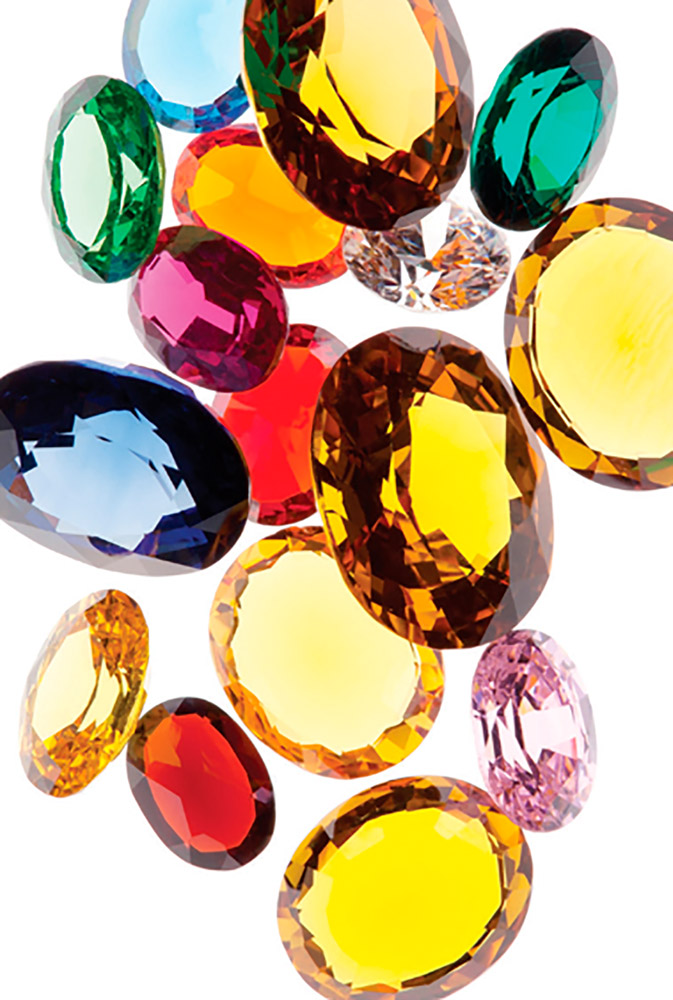

What is a crystal?
Crystals are all around us snowflakes, diamonds, salt, and sugar are all crystals. Rock crystals are minerals: solid substances found in the earth that have formed into geometric shapes. They are solid with straight edges and smooth surfaces.
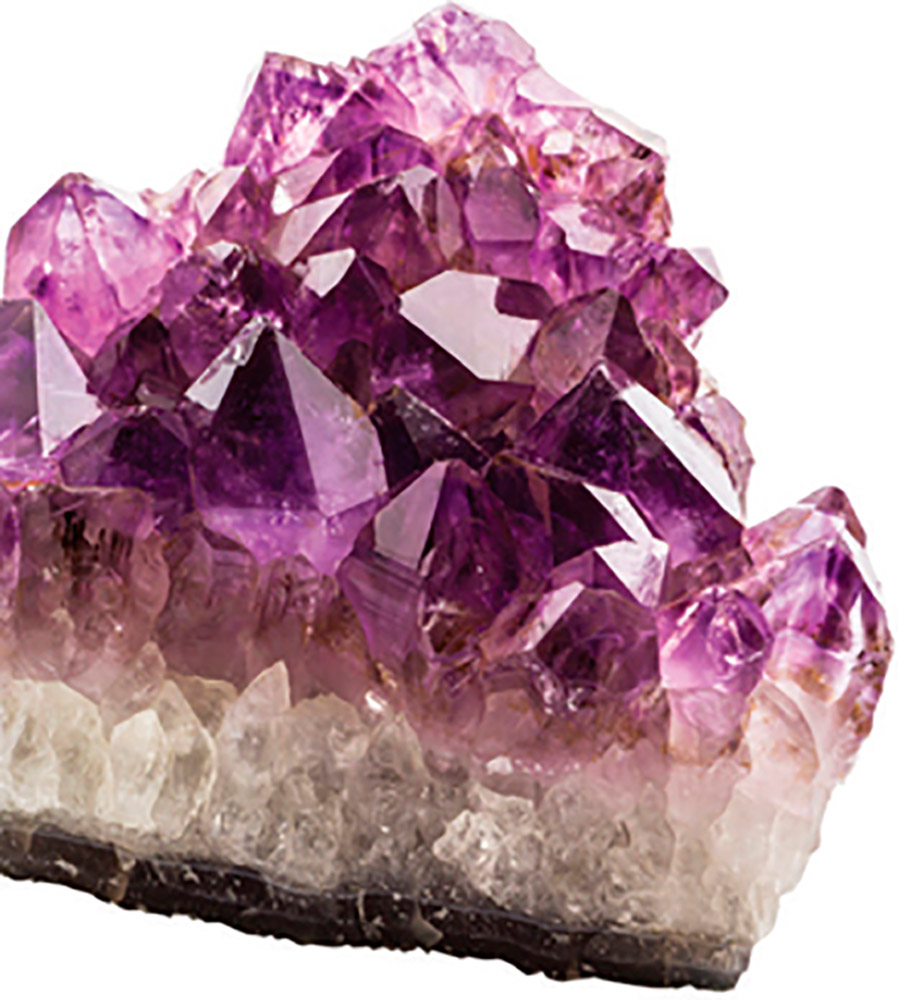

What is a gemstone?
A gemstone is a type of rare, well-formed crystal that has been cut and polished to show off its beautiful, gleaming colours. Gemstones can be inorganic (made from minerals) or organic (made from once-living plants or animals).
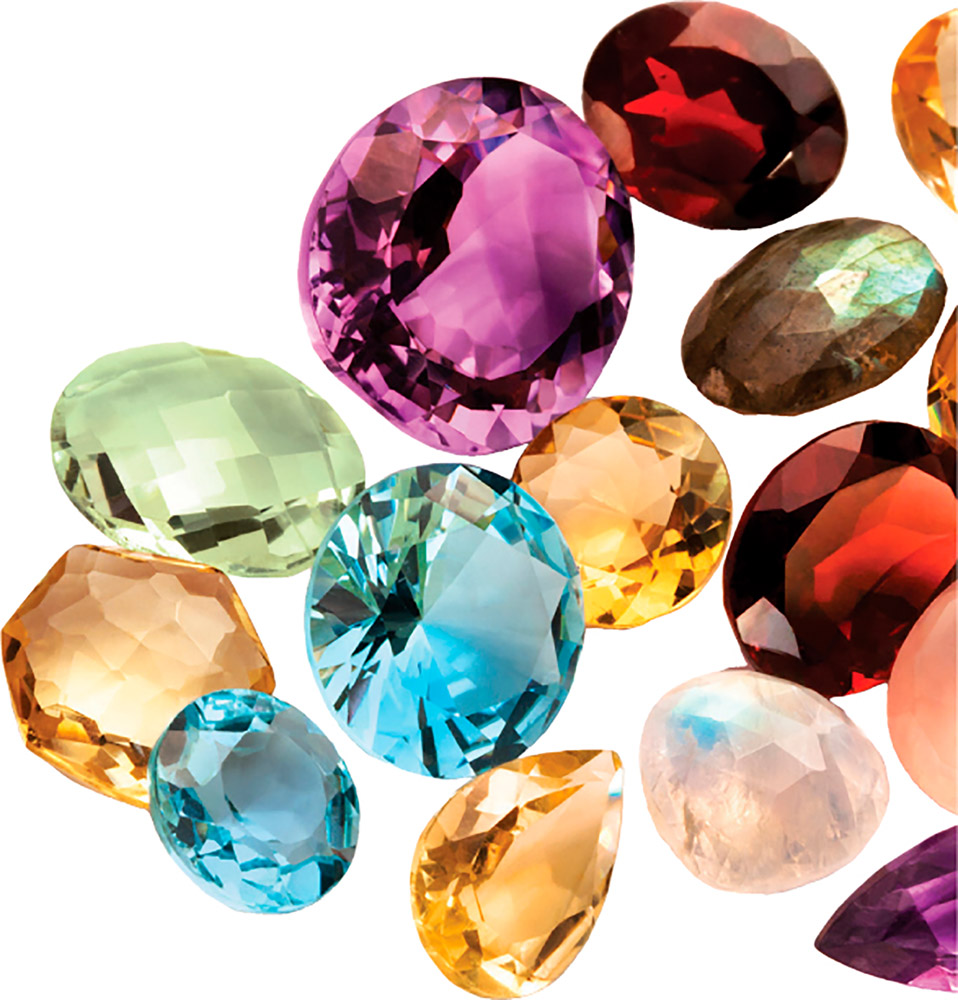

Mineral makeup
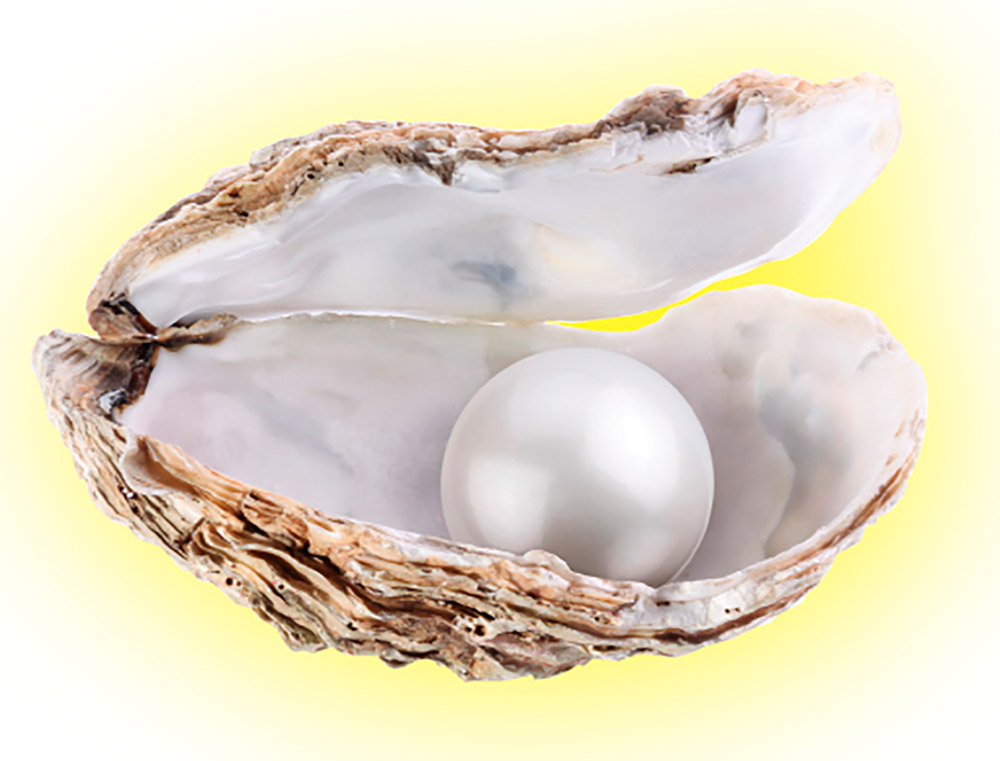
Most gemstones are minerals. As a mineral forms, its atoms arrange themselves in a crystal structure. But other gemstones are formed from organic matter that has hardened over time. Some examples are pearls, found in oysters; amber, made from tree resin; and coral, found as reefs in the sea.

Precious things
When people talk about precious gemstones, they are usually referring to just four types: diamonds, rubies, sapphires, and emeralds. Other stones amethyst, turquoise, agate, jasper, and so on are known as semiprecious stones. The higher the gems quality, hardness, or rarity, the more precious it will be.
Icelike
The word crystal comes from the Greek krystallos, meaning ice. This is because crystals can resemble chunks of ice, in their clear, colourless state.
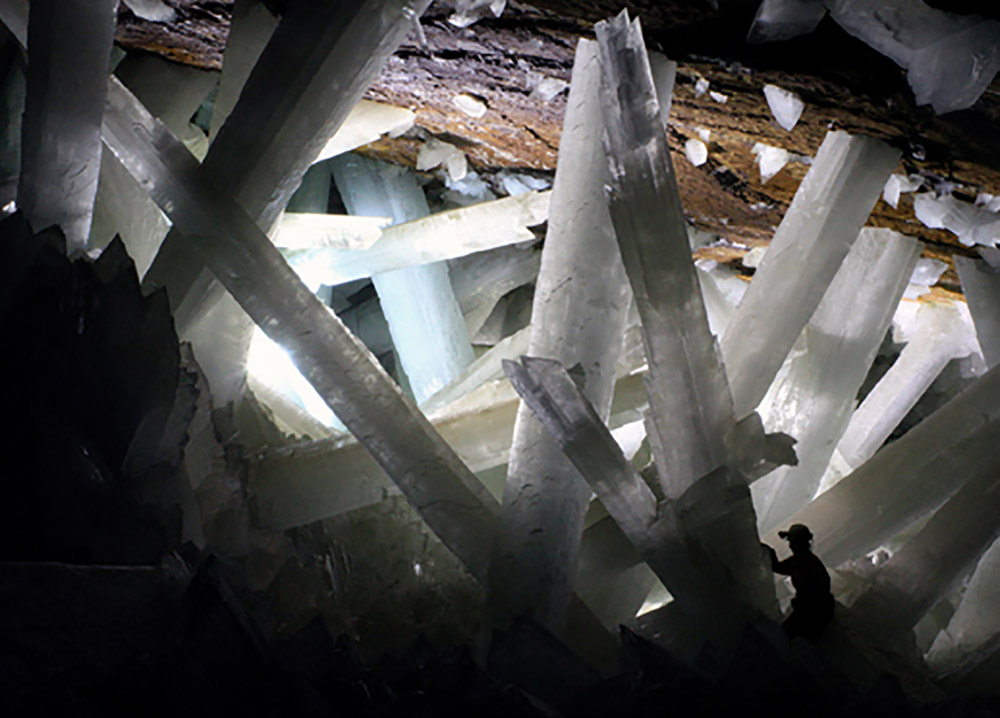

Crystal cave
Discovered in 2000, this magnificent cave in Naica, Mexico, contains some of the most stunning crystals ever found. Theyre also some of the largest: compare them to the person in the bottom right of the photo. The Cave of the Crystals is 300 metres (1,000 feet) underground.
Rock-Solid Facts
People have always looked upon twinkling crystals and dazzling gems with a sense of awe. Discover some fascinating facts behind these special rocks.

Multipurpose
Throughout history, crystals and gemstones have been used by people to create jewellery. They have also been used to decorate objects, such as plates and vases. Some weaponry and armour, such as Roman helmets, used gems and glass jewels to give the impression of opulence. Today, the hardest gemstones, including diamonds and rubies, are also used in industry to make cutting and grinding tools.
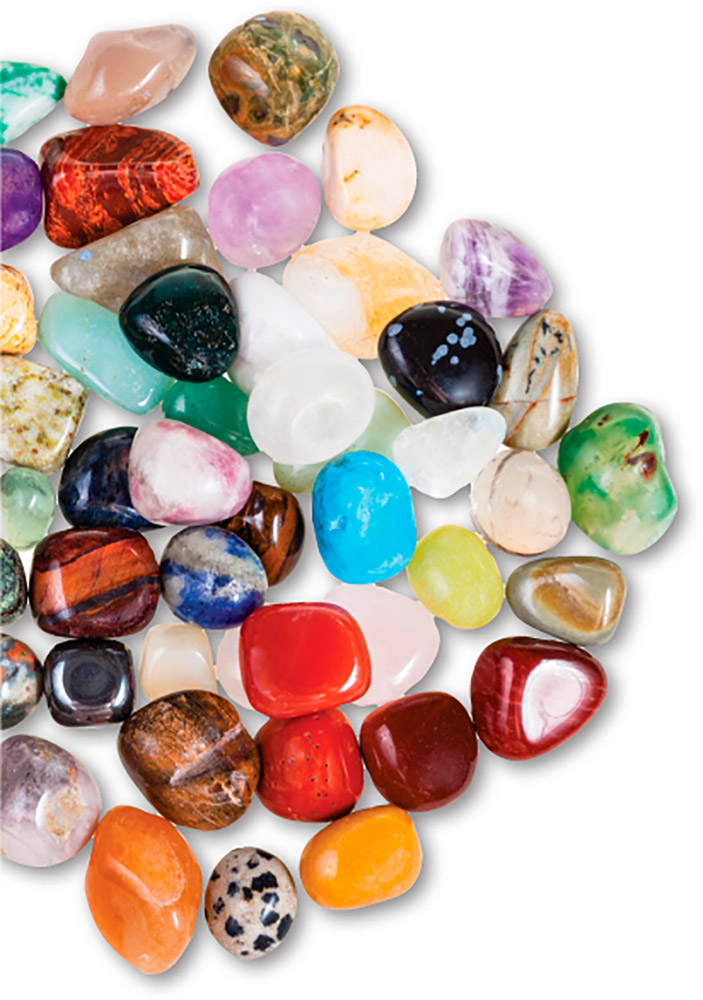

Mineral groups
There are more than 2,000 minerals in the world, 16 of which form gemstones. Some minerals, such as beryl, produce many different sorts of gemstone. The 16 gemstone minerals are:
- Beryl
- Chrysoberyl
- Corundum
- Diamond
- Feldspar
- Garnet
- Jade
- Lazurite
- Olivine
- Opal
- Quartz
- Spinel
- Topaz
- Tourmaline
- Turquoise
- Zircon

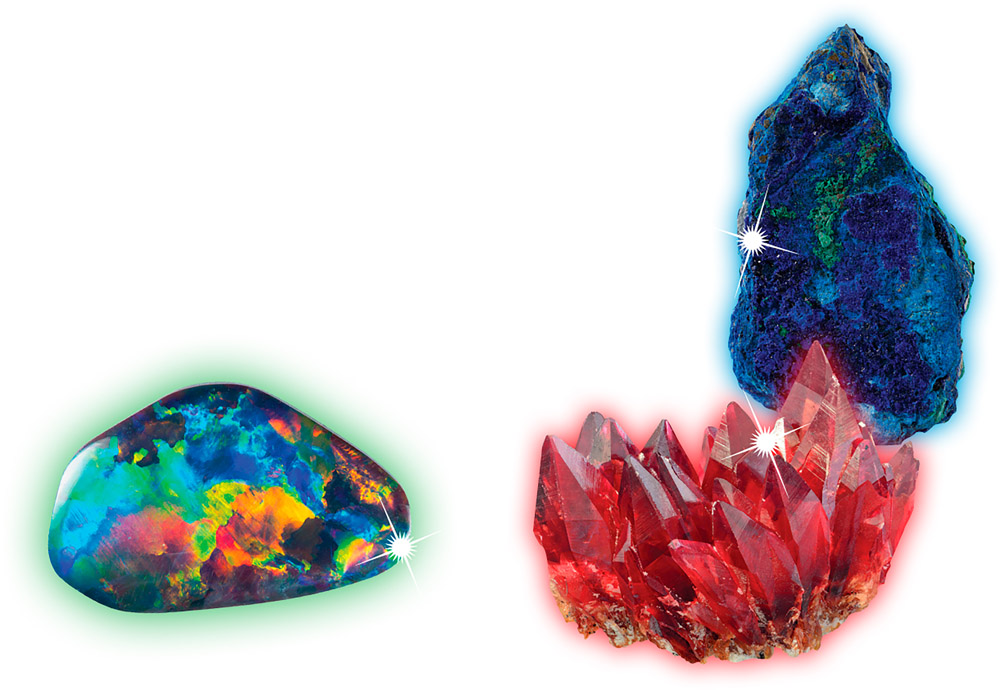
Rainbow of colours
Gemstones are made from many different minerals, and these often create a surprising rainbow of colours. For example, azurite gives a rich blue hue, and manganese gives shades of pink in rhodochrosite. In gemstones such as opal, the structure of the crystals reflects the light in such a way that it seems to flash lots of different colours.
Mohs scale
In 1812, German mineralogist Friedrich Mohs created a scale to measure the hardness of various minerals. The scale featured readily available minerals, with the softest, talc, at number one and the hardest, diamond, at number ten.
Mineral name | Scale number |
|---|
DIAMOND | |
CORUNDUM | |
TOPAZ | |
QUARTZ | |
ORTHOCLASE | |
APATITE | |
FLUORITE | |
CALCITE | |
GYPSUM | |
TALC | |
Gemology: The Science Bit
The study of gemstones is known as gemology. A scientist called a gemologist identifies different gems and classifies them (puts them into groups). In laboratories all over the world, gemologists work to classify and grade the quality of gems.
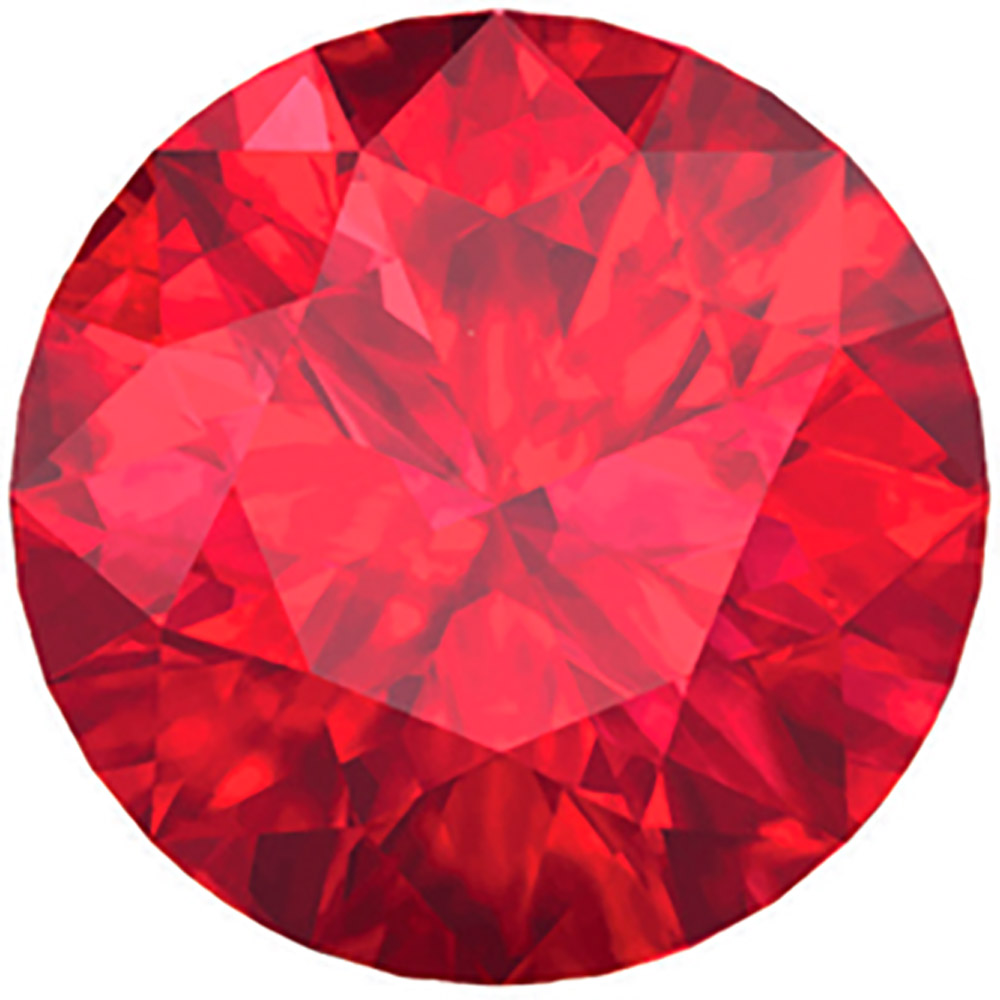

How do we tell them apart?
There are several ways to classify gemstones. As the vast majority of gems are minerals, one method is to use the gemstones mineral type, which is also known as its species. For example, ruby is the red variety of the species corundum. Gems can also be identified from their crystal structure, which is the arrangement of their atoms.
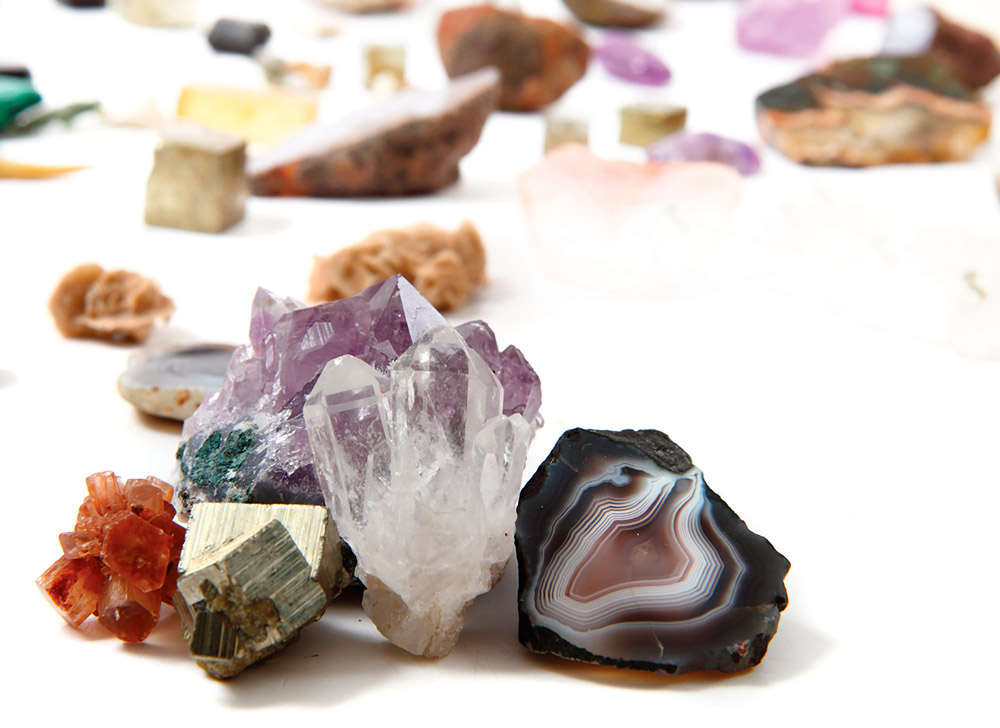

Crystal habit
Gemologists use the term crystal habit, which is the outward shape a gem usually takes. Identifying the habit helps gemologists to recognize the mineral type.
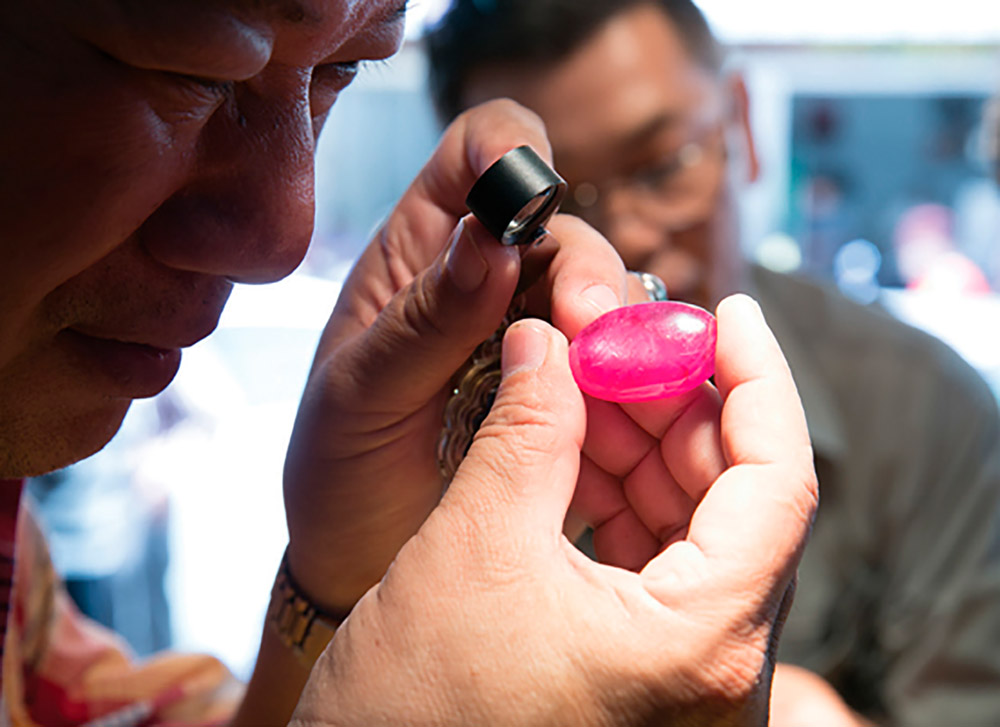

Translucency
Gemstones are also classified by translucency and hardness. Translucency refers to the way in which light is scattered as it passes through the gemstone. Hardness depends on the stones structure. Gemologists can also measure the sparkle of a gemstone, and the structure of the stone itself.
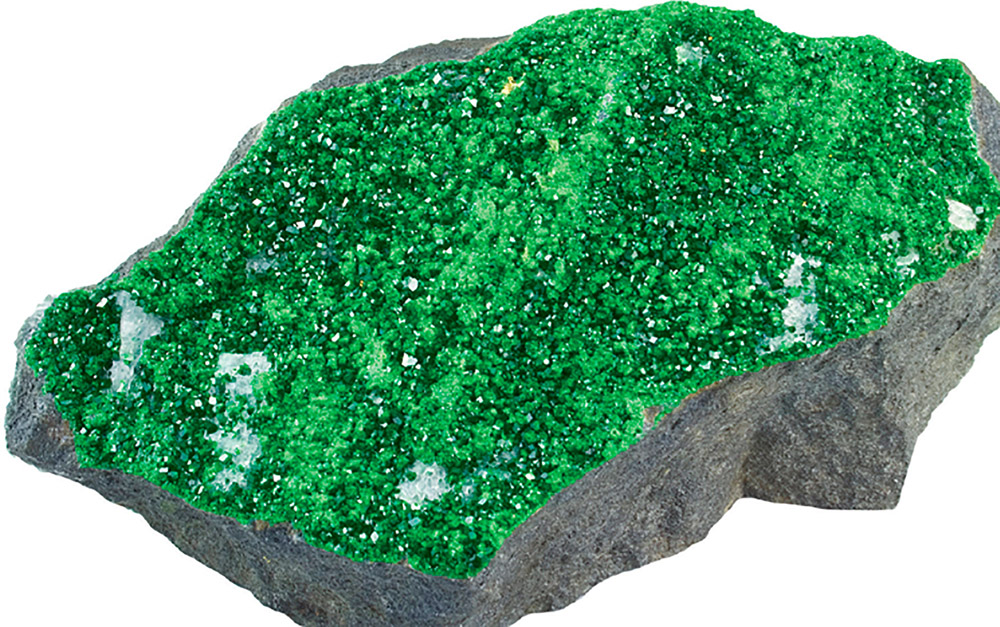

True colours?
Although colour is an easy way to tell one gem from another, it cant be relied on. This is because some stones vary in colour. For example, you may expect garnets to be dark red but sometimes they are green. By looking beyond colour and finding out about the structure of gemstones, youll be able to tell a green garnet from an emerald.
Next page



























