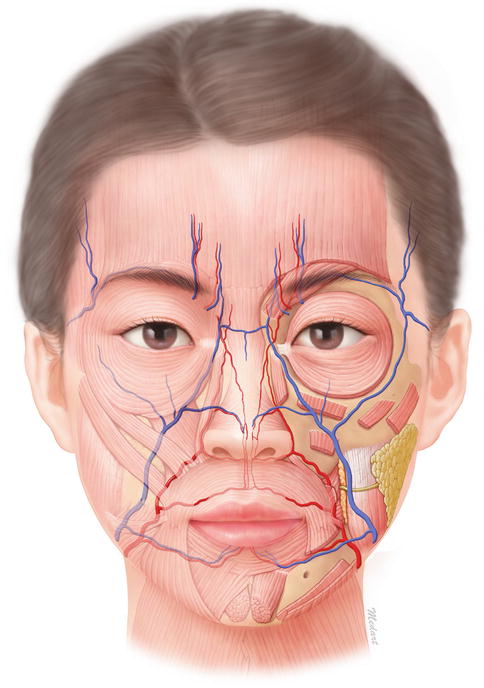
1.1.1 Basic Aesthetic Terminology
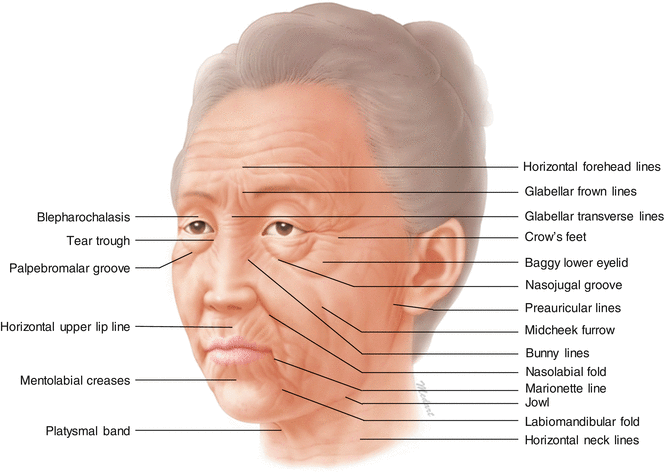
Facial Creases
Facial creases are deep, shallow creases caused by changes in the structural integrity of the skin. It occurs due to loss of skin and muscle fiber elasticity caused by repetitive facial movements and changes in facial expressions. Creases are generally termed wrinkles and lines. Other terms such as furrow, groove, and sulcus are used in the clinical fields.
Skin Folds
Skin folds occur due to sagging, loss of tension, and gravity. Representative skin folds are the nasolabial fold, the labiomandibular fold, etc.
Baggy Lower Eyelids (or Cheek Bags, Malar Bags)
Baggy lower eyelids occur due to a drooping of the adipose tissue underneath the orbicularis oculi m. This should be distinguished from the festoon since the baggy lower eyelid occurs inferior to the orbital margin.
Blepharochalasis
Blepharochalasis occurs due to sagging of the eyelid skin.
Bunny Line
The bunny line is the oblique nose furrows lateral to the nose bridge that is pronounced by various facial expressions. The levator labii superioris alaeque nasi m. below the skin and the medial muscular band of the orbicularis oculi m. participate in the formation of the bunny line.
Commissural Lines
Commissural lines are short, vertical lines appearing on each sides of the mouth corner. Occasionally, deep creases may form starting from the perioral regions.
Crows Feet (Lateral Canthal Wrinkles)
Crows feet are thin, bilateral wrinkles at the lateral sides of the eyes formed by the orbicularis oculi m.
Festoon
Festoon is the bulged appearance of the lower eyelids caused by a sagging of the skin and of the orbicularis oculi m. and by a protrusion of the inferior orbital fat compartment underneath the orbital septum.
Horizontal Forehead Lines (Worry Lines)
Horizontal forehead lines are horizontal lines across the forehead region where the frontalis m. is located.
Glabellar Frown Lines (Glabellar Creases or Lines)
Glabellar frown lines are vertical creases along the glabellar region caused by the corrugator supercilii muscle fibers.
Glabellar Transverse Lines
Glabellar transverse lines are horizontal lines on the radix that are typically produced during facial distortion. They occur perpendicular to the fibers of the procerus m.
Gobbler Neck (Platysmal Bands)
The gobbler neck appears as bilateral vertical skin bands on the neck along the anterior cervical and submental region. This occurs due to sagging of the medial border of the platysma muscle.
Horizontal Neck Lines
Horizontal neck lines are horizontal skin folds on the anterior cervical region. They are produced by a combination of platysmal muscle fibers and sagging neck skin.
Horizontal Upper Lip Lines (Transverse Upper Lip Lines)
Horizontal upper lip lines are 12 horizontal lines located at the philtrum on the upper lip.
Jowl (Jowl Sagging)
Jowl is the protrusion and sagging of the subcutaneous adipose tissue along the mandibular border. The anterior border of the prejowl sulcus clearly signifies the existence of mandibular retaining ligaments.
Oral Commissure
The labial commissure is the region where the upper and lower lips join on each lateral side. The joining point is referred to as the cheilion.
Labiomandibular Fold
The labiomandibular fold spans from the corner of the mouth to the mandibular border and becomes prominent with age. The depressor anguli oris m. (DAO) defines the folds medial and lateral borders. The attachment of the mandibular retaining ligament causes the labiomandibular fold to be located more anteriorly and medially.
Marionette Line
The marionette line is a long, vertical line that proceeds inferiorly from the corner of the mouth. It occurs commonly with age but with unknown causes. It is more pronounced in people with less fat tissues than in those with more fat tissues. This line is also called the disappointment line.
Mentolabial Creases (or Furrows)
Mentolabial creases are horizontal creases (one or more) between the lower lip and the chin (mentum). These creases lie between the orbicularis oris m. and the mentalis m.
Midcheek Furrow (Indian Band)
The midcheek furrow is a downward and lateral band, or furrow, that extends the nasojugal groove from the lateral aspect of the nose to the region superior to the anterior cheek. This band may carry on inferior to the cheek. With age, the cheek and the midface droop inferiorly and medially, and the band forms along the inferior margin of the zygomatic bone at the same height where the zygomatic cutaneous ligament attaches to the skin in this region.
Nasojugal Groove
The nasojugal groove is formed at the border between the lower lid and the cheek and runs inferolaterally from the medial canthus. The nasojugal groove region corresponds with the lower border of the orbicularis oculi m. and becomes more pronounced with the existence of the medial muscular band of the orbicularis oculi m. With age, this groove obliquely continues downward to the midcheek furrow.
Nasolabial Fold (or Nasolabial Groove)
The nasolabial fold starts from the side of the nasal ala and extends obliquely between the upper lip and the cheek. With age, the subcutaneous adipose tissue of the anterior cheek sags, causing the fold to deepen and move downward. The adipose tissue of the anterior cheek cannot descend inferior to the nasolabial fold due to compact attachment of the fascia, the skin, the cutaneous insertions of upper lip elevator muscles, and the zygomaticus major m. into the skin in this area. In addition, the facial area tends to lie underneath the nasolabial fold with variable depths.
Palpebromalar Groove
The palpebromalar groove is the border between the lower lid and the malar region.
Preauricular Lines
Periauricular lines are several vertical skin lines located near the tragion, the ear lobule, and the anterior region of the auricles.