Acute respiratory distress syndrome. A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001164/ Alcamo IE, Krumhardt B. Barrons E-Z Anatomy and Physiology . Hauppauge, NY: Barrons Educational Series; 2010.
Anatomy & Physiology Made Incredibly Easy . 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012. Assessment Made Incredibly Easy . 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012.
Bickley LS. Bates Guide to Physical Examination and History Taking . 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012. Bogart BI, Ort V. Elseviers Integrated Anatomy and Embryology , St.
Louis, MO: Mosby Elsevier; 2007. Caughey AB, Ahsan A, Hopkins L, Vargas J, Yap OW. Blueprints: Clinical Cases in Obstetrics & Gynecology . 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006. Costanzo LS.
BRS Physiology . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2011. Drake RL, Vogl W, Mitchell AWM, Tibbitts RM, Richardson PE,. Grays Atlas of Anatomy . Evans AT. Evans AT.
Manual of Obstetrics . 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. Farquhar SL, Fantasia L. Pulmonary anatomy and physiology and the effects of COPD. 2005;23(3):167-174. Guinan JJ. Guinan JJ.
Olivocochlear efferents: anatomy, physiology, function, and the measurement of efferent effects in humans. Ear Hear . 2006;27(6):589-607. Gulshan S, Goodwin J. Effect of aging on respiratory system physiology and immunology. 2006;1(3):253-260. 2006;1(3):253-260.
Hall BJ, Hall, JC. Sauers Manual of Skin Diseases . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2010. Hall JE. 12th ed. 12th ed.
Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2011. Hickey JV. The Clinical Practice of Neurological and Neurosurgical Nursing. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009. Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Furie B, Shattil SJ.
Hematology . 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2009. Huether SE, Mccance KL. Understanding Pathophysiology . St. St.
Louis, MO: Elsevier Mosby; 2012. Jacob S. Human Anatomy: A Clinically-Orientated Approach . New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone; 2008. Jameson JL, De Groot LJ. 6th ed. 6th ed.
Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2010. Lewis SL. Medical-Surgical Nursing : Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems . 8th ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Mosby; 2011.
Monkhouse WS. Master Medicine: Clinical Anatomy . 2nd ed. New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone; 2007. Netter FH. 5th ed. 5th ed.
Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2010. Parham PC. Immune System . 3rd ed. New York, NY: Garland Science; 2009. Porth CM.
Essentials of Pathophysiology: Concepts of Altered Health States . 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2011. The respiratory system. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Retrieved from http://www.nhlbi.nhi.gov/health/health-topics/topics/hlw/system.html .
Rubin R, Strayer DS, Rubin E, eds. Rubins Pathology: Clinicopathologic Foundations of Medicine . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012. Small intestine disorders. MedlinePlus.
Retrieved from http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/smallintestinedisorders.html . Smeltzer SC, Bare BG, Hinkle JL, Cheever KH. Brunner and Suddarths Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing . 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2010. Standring S.
Grays Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice . 40th ed. New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone; 2008. Stomach disorders. MedlinePlus. Retrieved from http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/stomachdisorders.html .
Tortora, GJ, Derrickson BH. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology . 13th ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons; 2011. Van Putte, C, Regan J, Russo A, Tate P, Stephens T, Seeley R. 10th ed. 10th ed.
New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013. Wahl I. Building Anatomy: An Illustrated Guide to How Structures Work. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2007. Wiener C, Fauci A, Braunwald E, et al, eds. 18th ed. 18th ed.
New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2012.
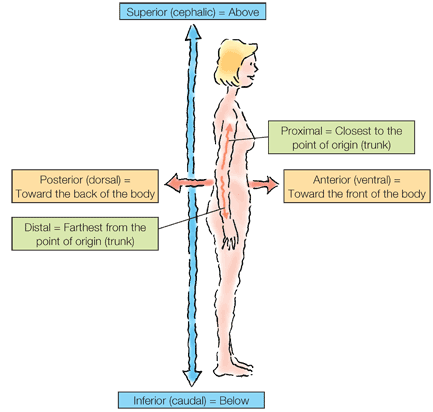
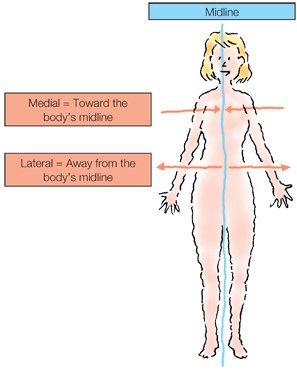
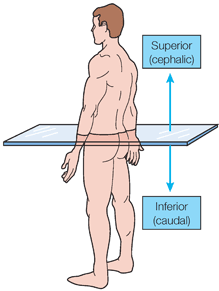
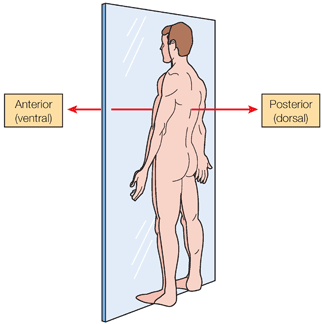
Directional terms Generally, directional terms can be grouped into pairs of opposites.
Reference planes Reference planes are imaginary lines used to section the body and its organs. These lines run longitudinally, horizontally, and on an angle. Median sagittal The median sagittal plane passes through the center of the body, dividing it into two equal right and left halves.
Transverse The transverse, or horizontal, plane is at a right angle to both the median and frontal planes; it divides the body into upper and lower sections.
Frontal The frontal plane, also called the coronal plane , passes at a right angle to the medial plane, dividing the body into front and back portions.
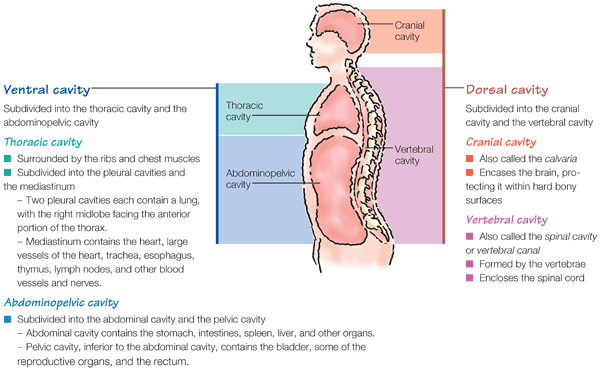
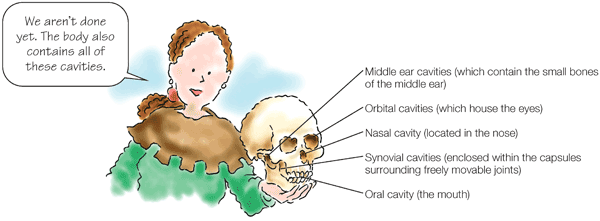
Body cavities Body cavities are spaces within the body that contain internal organs.
Body cavities Body cavities are spaces within the body that contain internal organs.
The dorsal and ventral cavities are the two major closed cavitiescavities without direct openings to the outside of the body.
Body regions
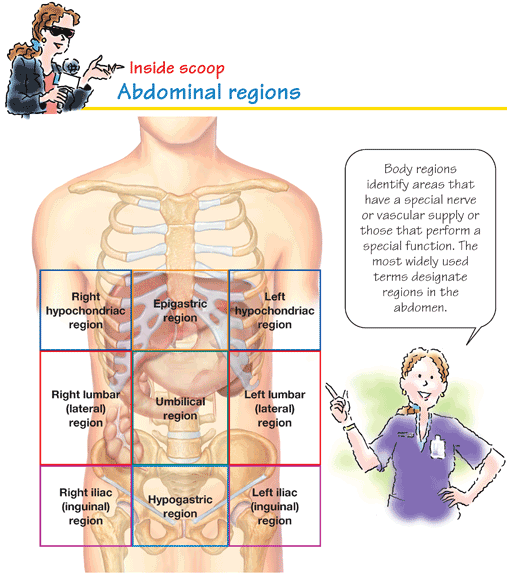
Right and left hypochondriac Contain the diaphragm, portions of the kidneys, the right side of the liver, the spleen, and part of the pancreas Epigastric Contains most of the pancreas and portions of the stomach, liver, inferior vena cava, abdominal aorta, and duodenum Right and left lumbar (lateral) Include portions of the small and large intestines and portions of the kidneys Umbilical Includes sections of the small and large intestines, inferior vena cava, and abdominal aorta Right and left iliac (inguinal) Include portions of the small and large intestines Hypogastric (pubic) Contains a portion of the sigmoid colon, urinary bladder and ureters, and portions of the small intestine Cells are the bodys basic building blocks. Theyre the smallest living components of an organism. The human body consists of millions of cells grouped into highly specialized units that function together throughout the organisms life. Large groups of individual cells form tissues, such as muscle and blood.