Mohamed Elhoseny - Dynamic Wireless Sensor Networks: New Directions for Smart Technologies (Studies in Systems, Decision and Control (165))
Here you can read online Mohamed Elhoseny - Dynamic Wireless Sensor Networks: New Directions for Smart Technologies (Studies in Systems, Decision and Control (165)) full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2018, publisher: Springer, genre: Home and family. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
- Book:Dynamic Wireless Sensor Networks: New Directions for Smart Technologies (Studies in Systems, Decision and Control (165))
- Author:
- Publisher:Springer
- Genre:
- Year:2018
- Rating:5 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
Dynamic Wireless Sensor Networks: New Directions for Smart Technologies (Studies in Systems, Decision and Control (165)): summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Dynamic Wireless Sensor Networks: New Directions for Smart Technologies (Studies in Systems, Decision and Control (165))" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
This book provides a collection of high-quality research works that address broad challenges in both theoretical and applied aspects of dynamic wireless sensor networks (WSNs) for intelligent and smart applications in a variety of environments. It presents the most central concepts associated with Dynamic Wireless Sensor Networks applications, and discusses issues surrounding Wireless Sensor Network Structures for complex and mobile-based applications. The book subsequently discusses several topics related to energy management in dynamic WSNs, and reviews the steps involved in building a secure and trusted data transmission model using the WSN applications of intelligent environments. Lastly, it discusses the applications of WSNs in live data systems such as SCADA systems.
Readers will discover a collection of high-quality research works that address broad challenges in both theoretical and applied aspects of WSNs for intelligent real-life applications. In addition, the book presents original research on the application of a dynamic WSN to solve the problem of energy consumption in a secure WSN during the process of data aggregation and transmission. Written by respected experts in the field, the book will stimulate further efforts in the application of the intelligent WSNs model, helping to solve the problem of data processing in a limited resource WSN-based environment.Mohamed Elhoseny: author's other books
Who wrote Dynamic Wireless Sensor Networks: New Directions for Smart Technologies (Studies in Systems, Decision and Control (165))? Find out the surname, the name of the author of the book and a list of all author's works by series.












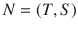 be a wireless sensor network, where
be a wireless sensor network, where 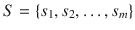 is a set of sensors with a sensing range
is a set of sensors with a sensing range 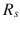 ,
, 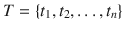 is a set of targets with known locations, m is the number of sensors, and n is the number of targets. Each target is sensed with one or more sensors, e.g. the target
is a set of targets with known locations, m is the number of sensors, and n is the number of targets. Each target is sensed with one or more sensors, e.g. the target  is covered with the sensors
is covered with the sensors 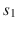 and
and 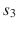 . The collected data are processed by a sink node. A sensor is in the active mode if it acquires or relays data, or both. A sensor in the sleep state when the sensor is not performing any tasks.
. The collected data are processed by a sink node. A sensor is in the active mode if it acquires or relays data, or both. A sensor in the sleep state when the sensor is not performing any tasks.