Lim - Beginning React (incl. Redux and React Hooks)
Here you can read online Lim - Beginning React (incl. Redux and React Hooks) full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2017, genre: Home and family. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
- Book:Beginning React (incl. Redux and React Hooks)
- Author:
- Genre:
- Year:2017
- Rating:5 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Beginning React (incl. Redux and React Hooks): summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Beginning React (incl. Redux and React Hooks)" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
Beginning React (incl. Redux and React Hooks) — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Beginning React (incl. Redux and React Hooks)" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Beginning React Greg Lim Copyright 2020 Greg Lim All rights reserved. Copyright 2020 by Greg Lim All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced in any form or by any electronic or mechanical means including information storage and retrieval systems, without permission in writing from the author. The only exception is by a reviewer, who may quote short excerpts in a review. Second Edition: April 2020
Table of Contents
Preface About this book Developed by Facebook, React is one of the leading frameworks to build efficient web user interfaces. You use small manageable components to build large-scale, data-driven websites without page reloads.
No more wasting time hunting for DOM nodes! In this book, we take you on a fun, hands-on and pragmatic journey to master React from a web development point of view. You'll start building React apps within minutes. Every section is written in a bite-sized manner and straight to the point as I dont want to waste your time (and most certainly mine) on the content you don't need. In the end, you will have what it takes to develop a real-life app. Requirements Basic familiarity with HTML, CSS, Javascript and object-oriented programming Contact and Code Examples The source codes used in this book can be found in my GitHub repository at https://github.com/greglim81 .
Chapter 1: Introduction 1.1 What is React? React is a framework released by Facebook for creating Single Page Applications (SPA).
Chapter 1: Introduction 1.1 What is React? React is a framework released by Facebook for creating Single Page Applications (SPA).
What is a Single Page Application? Most web applications are traditionally server-side applications. The server holds the business logic, stores data, and renders the website to the client. When a client clicks on a link, it sends a request to the server, and the server will handle this request and send back a response with html code which the browser will render and be viewed by the user. The problem here is that with this approach, the server receives a lot of requests. For example, when we go to a website and click on its Home page, we send a request for which the server has to respond. We click on the About page and it sends another request, and the server responds.
We click on Blog and it sends another request and again the server responds. Essentially, traditional websites consist of independent HTML pages and when a user navigates these pages, the browser will request and load different HTML documents. The many requests, response incurs a lot of time and resources spent on these tasks lead to a slow feeling of web pages, whereas the apps on your mobile phone or desktop feel very fast most of the time. React wants to bring this app like feeling to the browser where we do n t always have to load new pages each time there is an action from the user. A user still clicks on various links in a SPA. However, this time, the client handles the requests on its own and will re-render the html page through Javascript, so the server is left out here if no data from the server is needed.
This is much faster as we do n t have to send data over the Internet. The client does n t have to wait for the response, and the server does n t have to render the response. Also, in a SPA, the browser loads one HTML document and when users navigate through the site, they stay on the same page as Javascript unloads and loads different views of the app onto the same page itself. The user gets a feel that she is navigating through pages but is actually on the same HTML page. Facebook newsfeed is a good example. Other examples are Instagram or Twitter where the content gets dynamically refreshed without requiring you to refresh or navigate to a different page.
Manipulating DOM Elements Efficiently Loading and unloading different views of the same page involve querying and manipulating DOM elements. Such DOM operations involve adding children, removing subtrees and can be really slow. This is where React addresses this shortcoming in manipulating DOM elements efficiently. React does this by updating the browser DOM for us. With React, we do not interact with the DOM directly. We instead interact with a virtual DOM which React uses to construct the actual DOM.
The virtual DOM is made up of React elements (which we specify in JSX more about that later) which look similar to HTML elements but are actually Javascript objects. It is much faster to work with Javascript objects than with the DOM API directly. We make changes to the Javascript object (the virtual DOM) and React renders those changes for us as efficiently as possible. Asynchronous Operations In times when we need to get or send data from/to the server, we send a request to the server. But these are mainly restricted to initial loading and necessary server-side operations like database operations. Besides these operations, we will not frequently need to request from the server.
And if we do make server requests, we do it asynchronously, which means we still re-render the page instantly to the user and then wait for the new data to arrive and incorporate it and re-render only the required view when the data arrives; thus providing a fluid experience. Step by Step In this book, I will teach you about React from scratch in step by step fashion. You will build an application where you can input search terms and receive the search results via GitHub RESTful api (fig. 1.1.1). 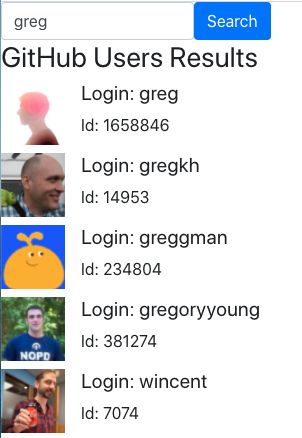 figure 1.1.1 In the end, you will also build a real-world application with full C.R.U.D. 1.1.2).
figure 1.1.1 In the end, you will also build a real-world application with full C.R.U.D. 1.1.2). 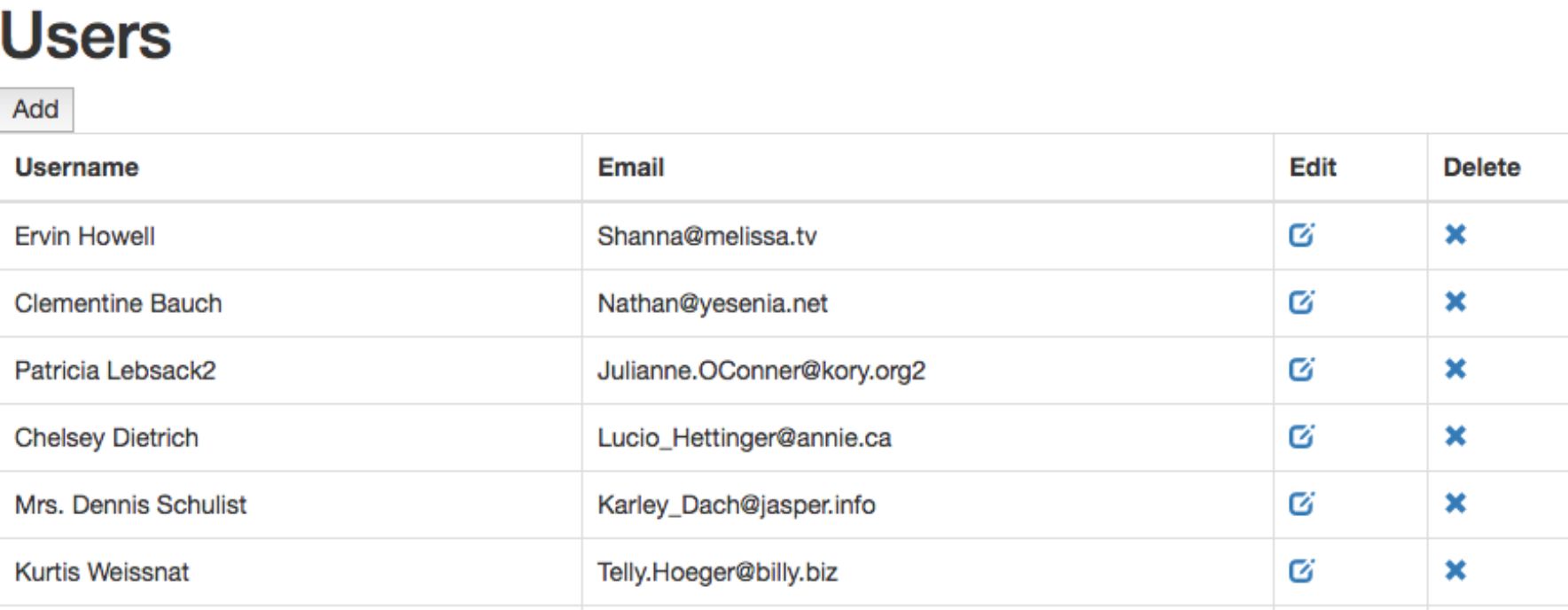 figure 1.1.2 These are the patterns you see on a lot of real-world applications.
figure 1.1.2 These are the patterns you see on a lot of real-world applications.  figure 1.1.2 These are the patterns you see on a lot of real-world applications.
figure 1.1.2 These are the patterns you see on a lot of real-world applications.
In this book, you will learn how to implement these patterns with React. Although this book covers techniques for developing single-page web applications with React, web browsers are not the only place React apps can run. React Native, released in 2015 allows us to develop iOS and Android native apps with React. And in the future, there is React VR, a framework for building interactive virtual reality apps that provides 360-degree experiences. We hope that this book will provide you with a strong base that you can build applications in React even beyond the web browser. Using ES6 In this book, we will be using ES6 syntax for our code.
Both ES5 and ES6 are just Javascript, but ES6 provide more features for example: - const (variable that cannot be changed), - template strings. Instead of console.log(Hello + firstName) , we can concatenate strings by surrounding them with ${}, i.e. console.log(`Hello ${firstName}`) - arrow functions. In ES6, we can create functions without using the function keyword which simplifies the syntax. - In declaring classes, ES6 can leverage on class features, object orientation as well as life cycle hook methods. Note that the ES5 way of declaring classes ( react.createClass ) is deprecated as of React 15.5.
This section is meant to address readers who have a bit of React development experience and are asking the question of whether to use ES6 or ES5. If you dont know what I am referring to, dont worry about it. We will go through the concepts in the course of this book. We will aim to use emerging Javascript whenever possible. 1.2 Thinking in Components A React app is made up of components. For example, if we want to build a storefront module like what we see on Amazon, we can divide it into three components.
Next pageFont size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Beginning React (incl. Redux and React Hooks)»
Look at similar books to Beginning React (incl. Redux and React Hooks). We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Beginning React (incl. Redux and React Hooks) and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.