EXCEL VBA: A BEGINNERS GUIDE RAJAN Contents at a Glance
Acknowledgement I would like to express my gratitude to my friends and family who made their contribution to the successful publication of this book. My special thanks to my family, friends and colleagues. I would like to thank my readers for their constant support and encouragement. Disclaimer This book is an independent publication and it does not affiliate or sponsored by Microsoft Corporation. Dear My Friend, If you are not satisfied with this eBook, could you please return the eBook for a refund within seven days of the date of purchase rather than post a review? If you found any errors in this book, could you please send an email to me instead of posting a review? erajan24@gmail.com I will appreciate your email. Thank you very much! Sincerely Rajan
1) Introduction to Excel VBA
VBA abbreviation is Visual Basic for Applications.
It is not a completely object oriented language instead we can say it as event driven programming language because to run your script you need a host. Microsoft Office comes with inbuilt Visual basic Editor to write your code easily. Using the power of VBA you can easily able to access the COM objects of all Microsoft office. For instance, you can open new word document using excel VBA, you can send the all details of your excel sheet to word document, you can control Microsoft outlook using VBA. But among the Microsoft programs, VBA for Excel is most popular used application because almost all kinds of works are done in Excel when compared to other programs such as Outlook, Power point, Access. So, if you know VBA for excel then you can easily do almost all your stuff without any hassle.
Microsoft Excel by default comes with thousands of inbuilt functions. Even though it has many functions, it does not satisfy all the users requirement. In order to resolve this problem, Microsoft allows user to create their own functions according to their requirement with the help of VBA. For example, if you want to convert the degree to Celsius or Fahrenheit using Excel built in functions is complex, but it is relatively easy to solve this problem by creating your own function using VBA. Visual Basic for Application allow user to create customized User Defined Functions, automating the manual process ,controlling the windows AP.VBA is somewhat closely related to Visual basic but it need a host application to run your code. You cannot able to create a standalone application using VBA.
VBA is built into most of the Microsoft Office Applications to allow the user to meet their requirements. It interacts with other application using the OLE automation technology. Sometime VBA can also be called as Macro. To start writing your script you need to have the Developer tab but by default Developer tab is hidden by Microsoft. You need to activate it. Let us see how to activate the Developer tab.
The screenshots attached in the book is Microsoft Excel 2007 the appearance may look different in other versions but the code will be compatible with all Excel versions. Click on the Excel Office button and choose the Excel options then the dialog box will appear as show in the Fig 1.1.Mark the check box Show Developer tab in the Ribbon and click the ok button then you can able to see the Developer tab added to your Excel as shown in the Fig 1.2 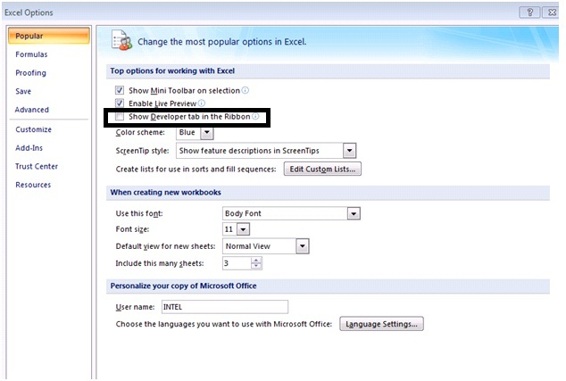 Fig 1.1 Adding the Developer tab to Excel
Fig 1.1 Adding the Developer tab to Excel 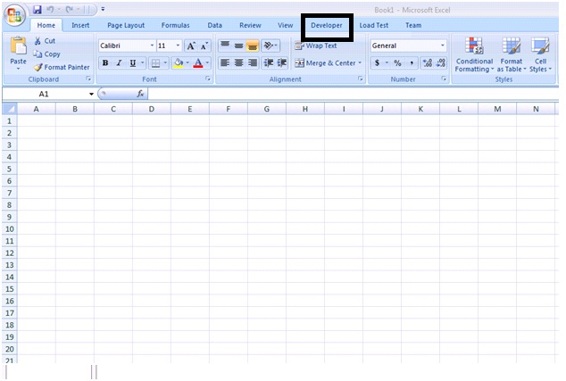 Fig 1.2 After adding the Developer tab to Excel Navigate to the developer tab to explore the options available in the tab.
Fig 1.2 After adding the Developer tab to Excel Navigate to the developer tab to explore the options available in the tab. 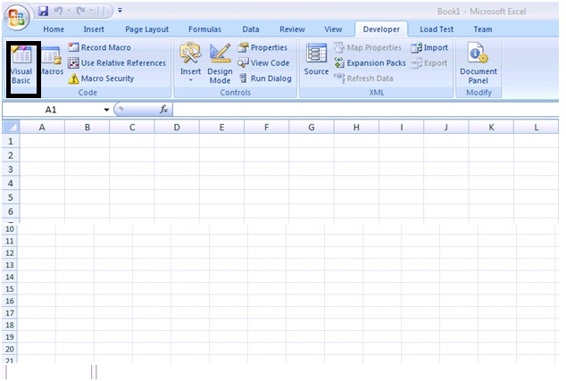 Fig 1.3 Options available in the Developer tab To write your first script we need to open the Visual Basic Editor and to do that click on the Visual Basic button as shown in the Fig 1.3.You can able to see the Visual Basic Editor window appear on the screen.
Fig 1.3 Options available in the Developer tab To write your first script we need to open the Visual Basic Editor and to do that click on the Visual Basic button as shown in the Fig 1.3.You can able to see the Visual Basic Editor window appear on the screen. 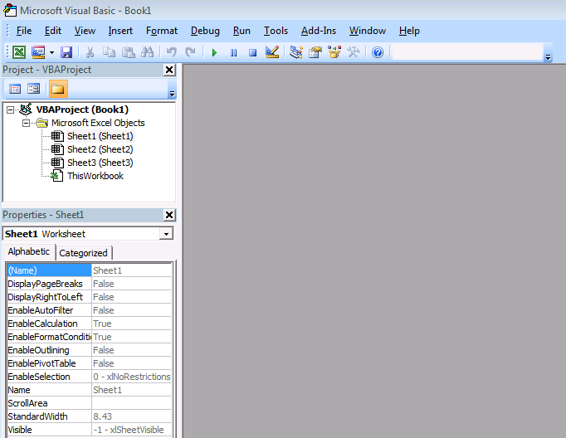 Fig 1.4 Visual Basic Editor Window Till now we are not ready to write our code because we need to insert a module to write our code. To do those in the Visual Basic Editor window click Insert ->Module. After that you can able to see the window similar to the below Fig 1.5
Fig 1.4 Visual Basic Editor Window Till now we are not ready to write our code because we need to insert a module to write our code. To do those in the Visual Basic Editor window click Insert ->Module. After that you can able to see the window similar to the below Fig 1.5 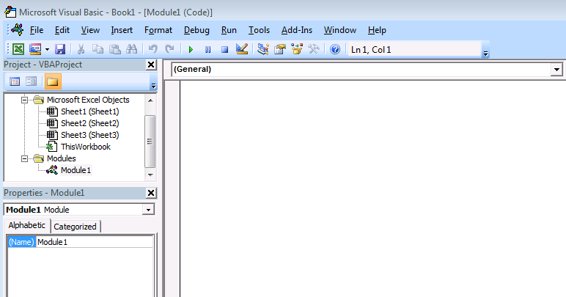 Fig 1.5 After inserting the Module to VB Editor Now we will do simple thing like addition and subtractions.
Fig 1.5 After inserting the Module to VB Editor Now we will do simple thing like addition and subtractions.
Below are the steps we are going to do using the VBA code Step 1: Assigning A1 to 5 Step 2: Assigning B1 to 7 Step 3: Adding A1 and B1 and display its value in the C1 Step 4: Assigning A2 to 10 Step 5: Assigning B2 to 15 Step 6: Subtracting the value A2 from B2 Step 7: Displaying the subtracted value in the C2 It may look somewhat complicate but its very easy once you are comfortable with VBA As I previously mentioned our codes are stored as module in the VBA so first thing we need to do is to create a subroutine named calc. Sub routines are procedures which contain our macro. Below is the syntax for subroutine Sub < Procedure Name >() Your code goes here End Sub Our macro lies within the subroutine named Calc 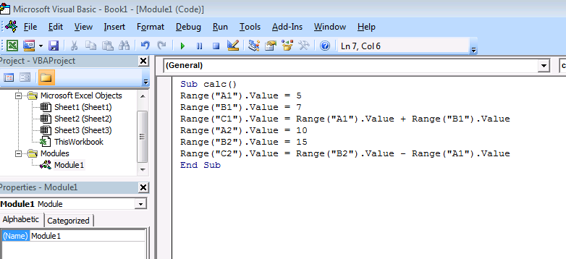 Fig 1.6 Code for addition and subtraction Range(A1 ).value=5 It assigns the value 5 to the cell A1.Be cautious that it will assign the value 5 to the currently active sheet. Suppose if the active sheet of your Excel workbook is Sheet 3 then it will enter the value 5 in the sheet 3 not in the sheet 1 Note:If you want the value 5 to be appear in the sheet 1 then you can specify that properly in your code like the below statement Sheets(1).Range("A1").Value = 5 The above statement enters the value 5 only in the sheet 1 irrespective of which sheet is currently active in your workbook. Like other programming language you can use the Arithmetic operations in VBA. Range("C1").Value = Range("A1").Value + Range("B1").Value This statement first add the value of A1 and B1 assign the total to the value C1 Do the same for subtraction.
Fig 1.6 Code for addition and subtraction Range(A1 ).value=5 It assigns the value 5 to the cell A1.Be cautious that it will assign the value 5 to the currently active sheet. Suppose if the active sheet of your Excel workbook is Sheet 3 then it will enter the value 5 in the sheet 3 not in the sheet 1 Note:If you want the value 5 to be appear in the sheet 1 then you can specify that properly in your code like the below statement Sheets(1).Range("A1").Value = 5 The above statement enters the value 5 only in the sheet 1 irrespective of which sheet is currently active in your workbook. Like other programming language you can use the Arithmetic operations in VBA. Range("C1").Value = Range("A1").Value + Range("B1").Value This statement first add the value of A1 and B1 assign the total to the value C1 Do the same for subtraction.
To run the code Press F5 or Go to Run->Run sub/Userform in the VBA editor window. Output will be displayed in the sheet1 in excel if sheet 1 is active sheet. 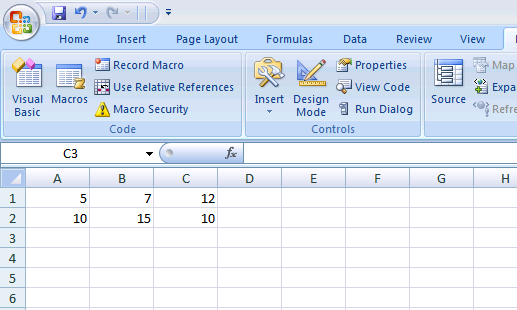 Fig1.7 Output of our code 2) Declaring Variables Variables are the storage location of your values in the computer memory.VBA allow the user to store different type of Data such as Boolean(true or false), string, numbers, double(precision values) etc. VBA has certain rules to accept your variable name. Below are the rules you need to follow for your variable name 1) The length of the variable must be less than 255 characters 2) Space or periods are not allowed 3) Special characters like (#, $, %, &,!) is not acceptable 4) First character must not be numeric How to declare a variable? Variable should be declared with Dim(Optional) statement as prefix and followed by its datatype (optional).If variable dont have a datatype like string, integer then VBA assigned default data type called Variant. Data stored as Variant acts like chameleon and it changes its type according to the value you assigned to the variable.
Fig1.7 Output of our code 2) Declaring Variables Variables are the storage location of your values in the computer memory.VBA allow the user to store different type of Data such as Boolean(true or false), string, numbers, double(precision values) etc. VBA has certain rules to accept your variable name. Below are the rules you need to follow for your variable name 1) The length of the variable must be less than 255 characters 2) Space or periods are not allowed 3) Special characters like (#, $, %, &,!) is not acceptable 4) First character must not be numeric How to declare a variable? Variable should be declared with Dim(Optional) statement as prefix and followed by its datatype (optional).If variable dont have a datatype like string, integer then VBA assigned default data type called Variant. Data stored as Variant acts like chameleon and it changes its type according to the value you assigned to the variable.
Next page








 Fig 1.1 Adding the Developer tab to Excel
Fig 1.1 Adding the Developer tab to Excel  Fig 1.2 After adding the Developer tab to Excel Navigate to the developer tab to explore the options available in the tab.
Fig 1.2 After adding the Developer tab to Excel Navigate to the developer tab to explore the options available in the tab.  Fig 1.3 Options available in the Developer tab To write your first script we need to open the Visual Basic Editor and to do that click on the Visual Basic button as shown in the Fig 1.3.You can able to see the Visual Basic Editor window appear on the screen.
Fig 1.3 Options available in the Developer tab To write your first script we need to open the Visual Basic Editor and to do that click on the Visual Basic button as shown in the Fig 1.3.You can able to see the Visual Basic Editor window appear on the screen.  Fig 1.4 Visual Basic Editor Window Till now we are not ready to write our code because we need to insert a module to write our code. To do those in the Visual Basic Editor window click Insert ->Module. After that you can able to see the window similar to the below Fig 1.5
Fig 1.4 Visual Basic Editor Window Till now we are not ready to write our code because we need to insert a module to write our code. To do those in the Visual Basic Editor window click Insert ->Module. After that you can able to see the window similar to the below Fig 1.5  Fig 1.5 After inserting the Module to VB Editor Now we will do simple thing like addition and subtractions.
Fig 1.5 After inserting the Module to VB Editor Now we will do simple thing like addition and subtractions. Fig 1.6 Code for addition and subtraction Range(A1 ).value=5 It assigns the value 5 to the cell A1.Be cautious that it will assign the value 5 to the currently active sheet. Suppose if the active sheet of your Excel workbook is Sheet 3 then it will enter the value 5 in the sheet 3 not in the sheet 1 Note:If you want the value 5 to be appear in the sheet 1 then you can specify that properly in your code like the below statement Sheets(1).Range("A1").Value = 5 The above statement enters the value 5 only in the sheet 1 irrespective of which sheet is currently active in your workbook. Like other programming language you can use the Arithmetic operations in VBA. Range("C1").Value = Range("A1").Value + Range("B1").Value This statement first add the value of A1 and B1 assign the total to the value C1 Do the same for subtraction.
Fig 1.6 Code for addition and subtraction Range(A1 ).value=5 It assigns the value 5 to the cell A1.Be cautious that it will assign the value 5 to the currently active sheet. Suppose if the active sheet of your Excel workbook is Sheet 3 then it will enter the value 5 in the sheet 3 not in the sheet 1 Note:If you want the value 5 to be appear in the sheet 1 then you can specify that properly in your code like the below statement Sheets(1).Range("A1").Value = 5 The above statement enters the value 5 only in the sheet 1 irrespective of which sheet is currently active in your workbook. Like other programming language you can use the Arithmetic operations in VBA. Range("C1").Value = Range("A1").Value + Range("B1").Value This statement first add the value of A1 and B1 assign the total to the value C1 Do the same for subtraction. Fig1.7 Output of our code 2) Declaring Variables Variables are the storage location of your values in the computer memory.VBA allow the user to store different type of Data such as Boolean(true or false), string, numbers, double(precision values) etc. VBA has certain rules to accept your variable name. Below are the rules you need to follow for your variable name 1) The length of the variable must be less than 255 characters 2) Space or periods are not allowed 3) Special characters like (#, $, %, &,!) is not acceptable 4) First character must not be numeric How to declare a variable? Variable should be declared with Dim(Optional) statement as prefix and followed by its datatype (optional).If variable dont have a datatype like string, integer then VBA assigned default data type called Variant. Data stored as Variant acts like chameleon and it changes its type according to the value you assigned to the variable.
Fig1.7 Output of our code 2) Declaring Variables Variables are the storage location of your values in the computer memory.VBA allow the user to store different type of Data such as Boolean(true or false), string, numbers, double(precision values) etc. VBA has certain rules to accept your variable name. Below are the rules you need to follow for your variable name 1) The length of the variable must be less than 255 characters 2) Space or periods are not allowed 3) Special characters like (#, $, %, &,!) is not acceptable 4) First character must not be numeric How to declare a variable? Variable should be declared with Dim(Optional) statement as prefix and followed by its datatype (optional).If variable dont have a datatype like string, integer then VBA assigned default data type called Variant. Data stored as Variant acts like chameleon and it changes its type according to the value you assigned to the variable.