Plain Tales from the Raj
Tales from the Dark Continent
Tales from the South China Seas
Raj Scrapbook
The Savage Wars of Peace
Thunder and Lightning
Lives of the Indian Princes
A Soldier of the Company
A Glimpse of the Burning Plain
Kiplings Kingdom
A Mountain in Tibet
The Search for Shangri-La
The Buddha and the Sahibs
Soldier Sahibs
Duel in the Snows
Gods Terrorists
Kipling Sahib
The Buddha and Dr Fhrer
Published by Hachette Digital
ISBN: 978-1-408-70388-5
Copyright Charles Allen 2012
Map copyright John Gilkes
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, without the prior permission in writing of the publisher.
Hachette Digital
Hachette Digital
Little, Brown Book Group
100 Victoria Embankment
London, EC4Y 0DY
www.hachette.co.uk

The whole earth is the sepulchre of famous men. They are honoured not only by columns and inscriptions in their own land, but in foreign nations on memorials graven not on stone but in the hearts and minds of men.
Thucydides, History of the Peloponnesian War, 404 BCE
Contents
The King Without Sorrow
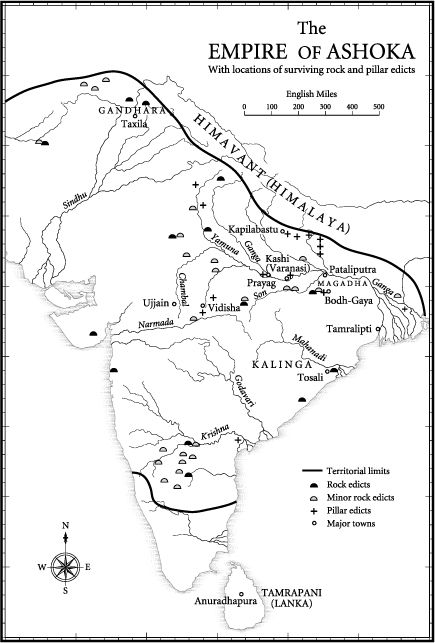
The emperor listed in the ancient Brahmanical Puranas as Ashoka raja, The King Without Sorrow, ruled over a united India some 2250 years ago. In the course of some forty years Ashoka unified the subcontinent under one government, transformed a minor religious sect into a world religion and introduced moral concepts whose impact on Asia can be felt to this day. Ashoka may be said to be Indias founding father, being the first ruler to forge India into a single nation state. As if that were not enough, long before Mahatma Gandhi, Emperor Ashoka espoused non-violence and the utterly novel concept of conquest by moral force alone and he was very probably the first ruler in history to establish a welfare state. Ashoka is also the first in Indias ancient dynasties of kings with a distinctive, identifiable voice and no ordinary voice at that, for what he had to say was and remains absolutely, unequivocally unique as a statement of governing principles.
The words of what might justifiably be called Ashokas Song more prosaically referred to as the Ashokan Rock or Pillar Edicts were inscribed in Indias first written script, Ashoka Brahmi. They were chiselled on hundreds of rock surfaces and on scores of polished pillars of stone throughout the Indian subcontinent, so that his song could be heard loud and clear from Kandahar to the mouths of the Irrawady and from Cape Cormorin at the tip of southern India to the Himalayas. From this heartland that same message spread out in ripples on all sides until it was heard in the furthest corners of Asia.
Only a precious few of these edicts have survived the vicissitudes of time and human violence in readable form: some seven edict rocks, eleven edict pillars, another nineteen more modest sites bearing what are usually referred to as the Minor Rock Edicts and perhaps a dozen more inscriptions in various forms that can be attributed to Ashoka. Together they constitute the earliest surviving written records of Indias ancient history. Yet it is a remarkable and little-known fact that they and the emperor who composed them were all but lost to history for the better part of two thousand years.
The religious tolerance that Emperor Ashoka called for in his seventh Rock Edict (RE 7), where he spoke of his desire that all religions should reside everywhere, lay at the heart of the new thinking that Ashokas religious ministers promoted within the borders of his empire and his missionaries beyond. But even in his own time this message was perceived as a threat by those who believed that they and they alone had the authority to dictate what religious codes people should follow.
British historians and archaeologists working in India in the nineteenth century were quick to blame the eclipse of Buddhism there on the Muslim conquests. For seven centuries zealots did indeed inflict horrendous human and cultural damage on India in the name of Islam, yet the fact is that Buddhism in India was in terminal decline long before Mahmud of Ghazni first crossed the Indus in the year Already by the ninth century Buddhism as practised by its adherents in India had become so esoteric, so isolated from the wider community as to be unable to compete with revitalised, devotional Hinduism as promoted by the ninth-century reformer Adi Shankaracharya and his followers. However, there is another equally important reason for the failure of Buddhism in India one that few followers of the Hindutva nationalist movement (which believes that the only good Indian is a Hindu Indian) are prepared to accept: Brahmanical intolerance, which at times was as unbending in its hatred of heresy and heretics as later Muslim hardliners were in their jihads against unbelief and unbelievers.
Much of the evidence for this Brahmanical oppression comes from Indias Buddhist neighbours in Tibet, Nepal, Burma and Ceylon. However, there are also Brahmanical texts that demonstrate an implacable hostility towards Buddhists and record their persecution at the hands of orthodox Hindu rulers. And there is the evidence of archaeology.
The politicians who in 1991 egged on the mob that destroyed Baburs mosque at Ayodhya on the grounds that it was built over the Hindu warrior-god Ramas fort may be surprised to know that some of the most famous Hindu temples in India almost certainly began as Buddhist structures, often incorporating Buddhist icons, either in the form of images of deities or as lingams. Four likely examples selected simply because they come from the four corners of the subcontinent are the Badrinath shrine in the far north Garhwal Himal, the Jagannath temple at Puri on the east coast, the Ayyappa shrine at Sabarimala in Kerala and the Vithalla shrine at Pandharpur in Western Maharashtra.

The triumph of Brahmanism (the lion) over Buddhism (the elephant), as photographed in 1890. The giant lion is one of a pair that guard the entrance to the great temple of the sun god Surya, a sublime example of Hindu architecture in India. (APAC, British Library)
However, the most striking evidence of Brahmanical hostility towards Buddhism comes in the form of silence: the way in which Indias Buddhist history, extending over large parts of the country and lasting for many centuries, was excised from the historical record. It was by this simple act of omission the historical revisionism of generations of pious Brahman pundits and genealogists that Ashokas Song was silenced, and Emperor Ashoka himself all but erased from Indias history. In its call for religious tolerance, its wish that all living beings should live together in harmony and without violence, Ashokas Song spoke to all. But by promoting the Buddhist heresy throughout the land, Ashoka directly challenged the caste-based authority of the Brahman order. He and his beliefs could not be tolerated.
Religious intolerance knows no frontiers. When the Mughal Emperor Shah Jehan was pulling down Hindu temples in Benares, Puritans in England were busying themselves smashing medieval stained glass and destroying idols in churches up and down the country. Historians who deny or conceal such uncomfortable truths do us no favours. Herein lies part of the reason for writing this book about a long-forgotten emperor whose song was silenced.















