
Imagined Empires
The publisher gratefully acknowledges the generous support of the Ahmanson Foundation Humanities Endowment Fund of the University of California Press Foundation.
Imagined Empires
A HISTORY OF REVOLT IN EGYPT
Zeinab Abul-Magd

UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA PRESS
BERKELEYLOS ANGELESLONDON
University of California Press, one of the most distinguished university presses in the United States, enriches lives around the world by advancing scholarship in the humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences. Its activities are supported by the UC Press Foundation and by philanthropic contributions from individuals and institutions. For more information, visit www.ucpress.edu.
University of California Press
Berkeley and Los Angeles, California
University of California Press, Ltd.
London, England
2013 by The Regents of the University of California
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Abul-Magd, Zeinab, 1976
Imagined empires : a history of revolt in Egypt / Zeinab Abul-Magd.
pagescm
Includes bibliographical references and index.
ISBN 978-0-520-27552-2 (cloth : acid-free paper)
ISBN 978-0-520-27553-9 (paper : acid-free paper)
eISBN 9780520956537
1. EgyptPolitics and government. 2. PeasantsPolitical activityEgyptHistory. 3. Working classPolitical activityEgyptHistory. 4. Government, Resistance toEgyptHistory. 5. RevolutionsEgyptHistory. 6. ImperialismHistory. 7. EgyptColonial influence. 8. Elite (Social sciences)EgyptHistory. I. Title.
DT 82. A 675 2013
962.3dc232013003749
Manufactured in the United States of America
22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
In keeping with a commitment to support environmentally responsible and sustainable printing practices, UC Press has printed this book on Rolland Enviro100, a 100% post-consumer fiber paper that is FSC certified, deinked, processed chlorine-free, and manufactured with renewable biogas energy. It is acid-free and EcoLogo certified.
CONTENTS
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This book was supported by my graduate work in Georgetown Universitys History Department and by grants from Georgetowns Graduate School and Oberlin College. Its production would not have been possible without the invaluable and precious support of many colleagues and friends in the United States and Egypt. First of all, the greatest thanks are due to Judith Tucker, my former advisor at Georgetown University. Late Faruk Tabak of Georgetown thoughtfully helped with earlier stages of writing the manuscript. Many thanks are due to Timothy Mitchell, Khaled Fahmy, and Peter Gran, who were very generous with their time and ideas in discussing earlier versions of the book. Many graduate colleagues have been of indispensable help throughout the years of researching and writing, especially Dina Khalifa, Dina Shehata, Nadya Sabiti, Sara Scalenghe, Mohamed Said Ezz El-Din, Aurelie Perrier, and many others at Georgetowns Center for Contemporary Arab Studies.
I would also like to thank all the great historians and researchers at the National Archives of Egypt whom I met and had fruitful discussions with, especially Emad Hilal, Magdi Guirguis, Nelly Hanna, Gennifer Derr, Shana Minkin, Alan Mikhail, Lisa Pollard, and Will Hanley. At Oberlin College, I have found much support from many colleagues, including Frances Hasso and Sam White. Furthermore, I have to advance many thanks to Max Strasser and Avi Asher-Schapiro, my wonderful students who copyedited the manuscript. Finally, in Upper Egypt, the dear region about which this book was written, I would like to thank all the revolutionary youth of the south and my parents.
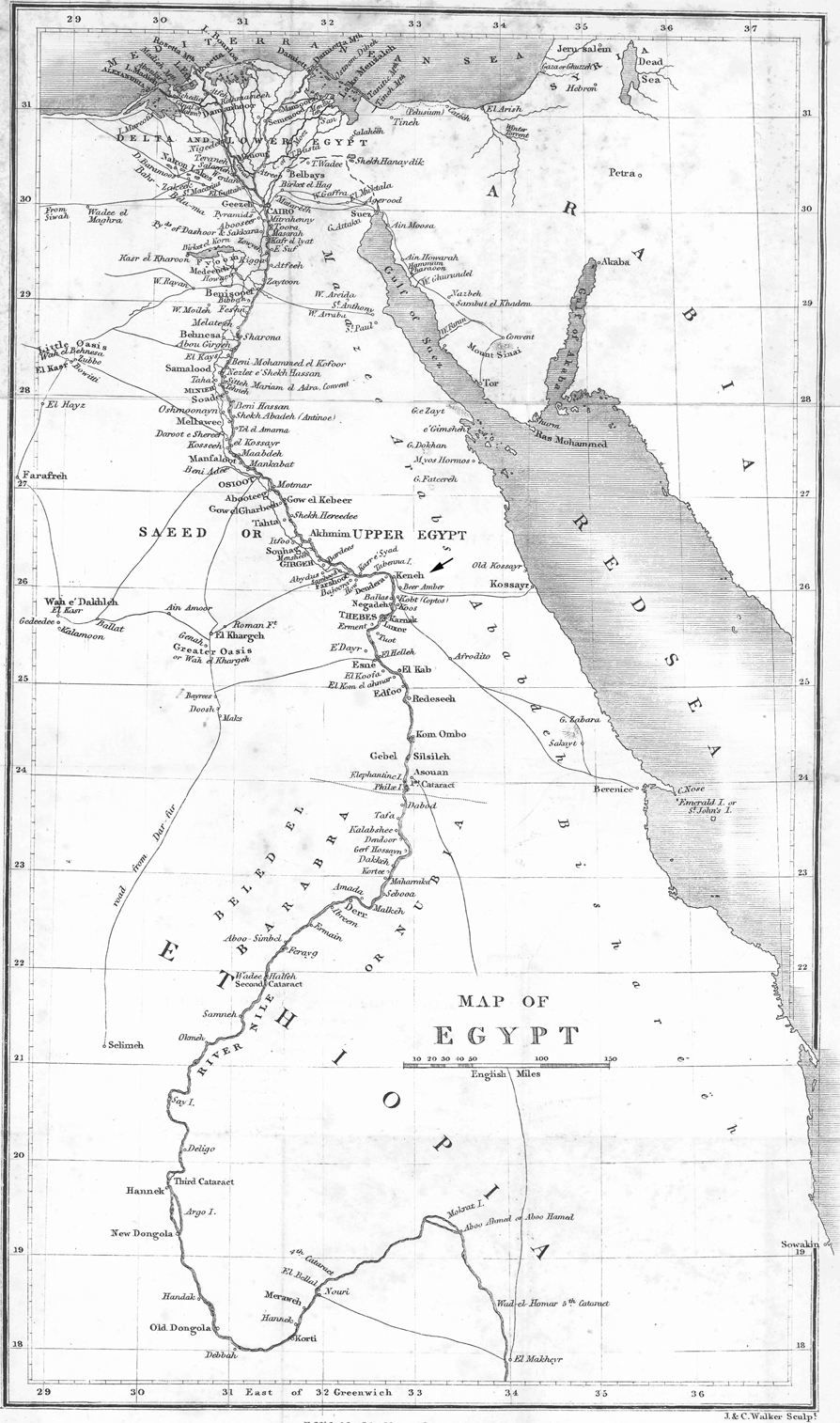
FIGURE 1. Nineteenth-century map of Egypt that shows Qina Province (Keneh) located in the south/Upper Egypt (see arrow).
INTRODUCTION
Imagined Empires, Real Rebels
Empire is almighty. It is an all-encompassing political entity capable of penetrating places big and small, near and far, and establishing full hegemony. The semidivine omnipotence of empire is made manifest not only in its ability to control the high politics of the metropolis but also in its penetration of the daily life of peoples in the remotest placesin the periphery of the periphery of the empire. Wherever it appears, empire is competent, fast, and successful in achieving its goals and altering peoples lives. But that is a myth. Omnipotent empire was imagined. Although empire managed to extend into the farthest places on earth, it failed in that which it thought itself to be most competent, instead leaving behind environmental devastation and revolt. The history of Qina Province, a small place deep in the south of Egypt, over the last five hundred years proves this case.
On the eve of the Egyptian Revolution of 2011, I visited the southern half of the country, Upper Egypt, in order to conduct field research for this book. In the farmlands bordering a small town in Qina Province, I noticed an enormous cylindrical, silver building that looked alien to its surroundings. When I inquired about its contents, I learned that this was a silo for the wheat from the US Agency for International Development (USAID). The controversial American food aid to Egypt, which many analysts believe to be a tool of imperial hegemony through the establishment of grain dependency, had made its way to the farthest reaches of Upper Egypt. I also learned that the informal empire made an appearance in the province in many other ways.
Under Mubaraks overthrown regime, the US presence in Upper Egypt was conspicuously strong, yet failing. Its failure throughout Egypt was a major reason for the eruption of the 2011 revolution. American market reforms, confidently advocated as the most efficient way toward economic development, did not yield results in Upper Egypt, even two decades after their application. The southern provinces, including Qina, were and still are known, to be the most underdeveloped regions throughout the countrys modern history. The UN Development Programmes annual reports on Arab human development place Upper Egypt at the bottom of the ladder of human development, and several World Bank reports allude to the same fact. On the eve of the 2011 revolution, protests against the failed empire spread across the south, especially in Qina Province. The southern provinces were the most rebellious among Egypts regions against the central government in Cairo, which applied the dysfunctional US policies of market reform.
Gangs of bandits known as matarid al-jabal, who take refuge in the mountains surrounding the Nile in the south, have grown to symbolize ruthless crime as well as audacious resistance against the state and its failed free market policies. Many popular TV series and movies present a criminal, yet romantic, image of these bandits. They even make their appearance on Facebook: an opposition group of youth, resenting the authoritarian regime that subjugated itself to American domination, named itself after a memorable proclamation by a legendary southern bandit, Izzat Ali Hanafi. The story of Izzat, whose execution filled the newspapers while I was conducting my archival research in 2006, was made into the most popular Egyptian movie two years later. In a key scene in the film, the angry, outlawed protagonist, or Izzat, says, From today, there is no government. I am the government. ( Min el naharda mafish hakuma. Ana el hakuma. ) This fierce political statement immediately grew popular among youth across Egypt and was quickly adopted as the name of the Facebook opposition group. Eventually, the south, the north, and Cairo all rose to overthrow the US-friendly, neoliberal regime on 25 January 2011.
Next page












