Nurses Assistant (C.N.A.)
Certified Nurse Assistant
Also known as: Nurses aide, Nursing assistant
Description
Nurses assistants care for patients under the supervision of nurses and physicians. They help patients with the activities of daily living such as eating, bathing, dressing and transferring in and out of bed.
Training
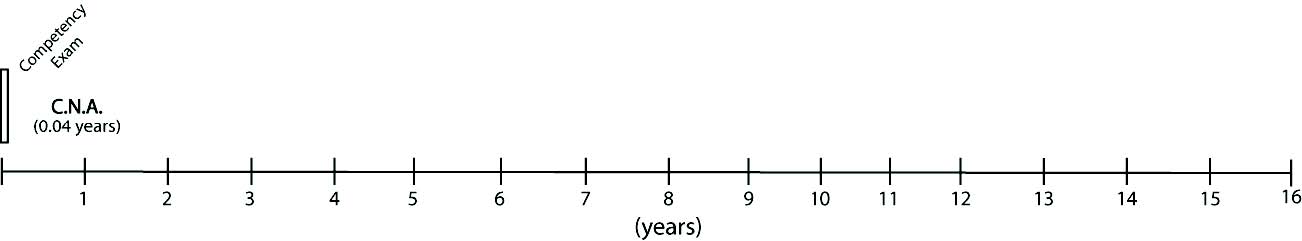
To become a nurses assistant, one must complete a minimum of 75-hours of state-approved training. Some states require up to 150 hours of training. After passing a competency exam nurses assistants become certified (C.N.A.) and are placed on the state registry of nurses aides.
Median Gross Income: $27,141 (106)
Informative Websites
www.nahcacares.org
www.cna-network.org
Phlebotomist (C.P.T. or R.P.T.)
Certified Phlebotomy Technician, Registered Phlebotomy Technician
Description
Phlebotomists collect blood samples from patients via venupuncture. They are trained to use the appropriate collection devices and transport medium for the test(s) ordered.
Training
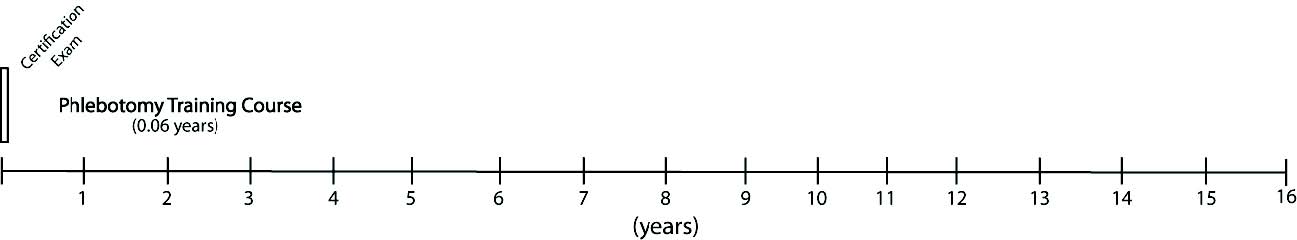
To become a phlebotomist one must complete a phlebotomy training course, which is about 120 hours, or 3 weeks, long. After successfully completing a training course, one may become certified/registered by the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP), the American Medical Technologists (AMT) or the American Society for Phlebotomy Technicians (ASPT).
Median Gross Income: $25,000 (107)
Informative Websites
ww.aspt.org
www.nationalphlebotomy.org
Insertion of a needle into a vein
Emergency Medical Technician (EMT-B, EMT-I/85, EMT-I/99, EMT-P)
EMT-Basic, EMT-Intermediate, EMT-Paramedic
Description
Emergency medical technicians care for and transport the injured and ill to a medical facility. They work closely with firefighters and police officers. EMTs assess patients and provide emergency medical care as per the protocols provided by a physician medical director. On arrival at the emergency department, EMTs report the patients history, their observations on the scene and interventions they provided en route.
The basic level of EMT (EMT-B) is trained to assess patients and manage respiratory, cardiac and trauma emergencies. EMT-Bs perform basic airway management, administer oxygen, give artificial respirations, perform CPR and defibrillate using an AED. EMT-Bs are also trained to take vital signs, perform spinal immobilization, bandage wounds, splint fractures and administer nitrogylcerin, glucose, epinephrine, and albuterol as per protocol.
The 1985 intermediate level EMTs (EMT-I/85) have additional training in IV therapy and multi-lumen airway management.
The 1999 intermediate level EMTs (EMT I/99) have additional training in cardiac monitoring and medication administration.
Paramedics (EMT-P) have the most training among EMTs. They are trained to perform endotracheal intubation, place intravenous lines, and administer a variety of medications as per the medical directors protocol. Paramedics are trained to interpret electrocardiograms and defibrillate patients as per Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) algorithms.
Flight medics care for patients while they are being transported to a medical facility by helicopter. Flight medics are usually paramedics who have several years of experience. Flight nurses also care for patients while they are being transported to a medical facility.
Training
The National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) is a private organization that certifies five levels of emergency medical service providers. Each level of NREMT certification requires the completion of the respective training requirements and passing a cognitive (written) and psychomotor (practical) examination. These examinations meet the National Highway Traffic Safety Administrations (NHTSA) standards.
First Responder ~40 hours of training
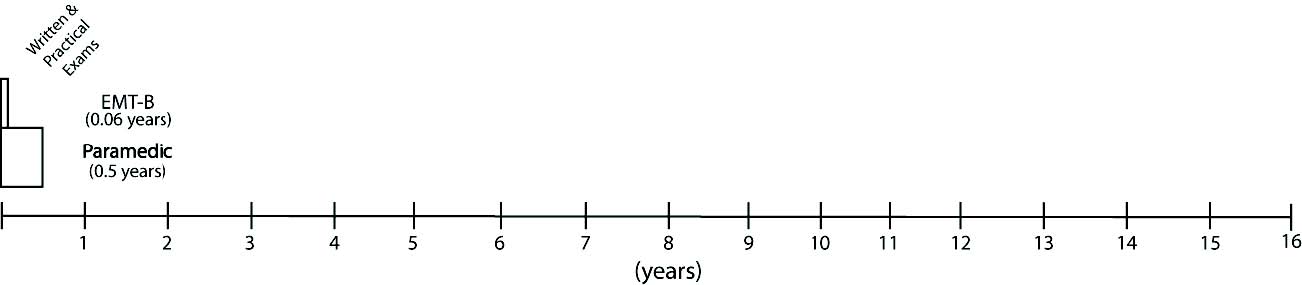
EMT Basic ~110 hours (3 weeks) of training
EMT Intermediate/85 ~200 hours (5 weeks) of training
EMT Intermediate/99 ~400 hours (10 weeks) of training
EMT Paramedic ~1,000 hours (6 months) of training
EMT-B Median Gross Income: $29,040 (108)
EMT-P Median Gross Income: $37,502 (152)
Informative Websites
www.naemt.org
www.nremt.org
Pharmacy Technician (C.Ph.T.)
Certified Pharmacy Technician
Description
Pharmacy technicians assist licensed pharmacists. They receive prescription requests, count tablets and label bottles. Pharmacy technicians may also perform administrative duties and provide customer service. In healthcare facilities, pharmacy technicians may prepare sterile solutions and deliver medications.
Training
There are no standard training requirements for pharmacy technicians. Some states require pharmacy technicians to become licensed and/or registered by passing a state examination. Pharmacy technicians can become certified by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board after passing the Pharmacy Technician Certification Exam (PTCE). One must hold a high school diploma or GED to be eligible to take the PTCE. Formal training programs are available at community and technical colleges. These programs are from 6 months to 2 years in length.
Median Gross Income: $26,600 (110)
Informative Websites
www.ptcb.org
www.nationaltechexam.org
www.ashp.org
www.pharmacytechnician.org
Medical Assistant (C.M.A.)
Certified Medical Assistant
Description
Medical Assistants are specifically trained to work in clinics. They perform administrative tasks such as answering telephones, scheduling appointments, updating medical records, filling out insurance forms, setting up diagnostic tests and arranging for hospital admissions. Medical assistants also perform clinical tasks such as taking vital signs, collecting laboratory specimens, sterilizing medical instruments, removing sutures, changing dressings, preparing patients for examinations and assisting physicians during examinations.
Training
Both one-year certificate programs and two-year associates degree programs exist. The Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP) or the Accrediting Bureau of Health Education Schools (ABHES) accredits training programs. To become certified, one must pass the CMA certification exam administered by the Certifying Board of the American Association of Medical Assistants.
Median Gross Income: $28,300 (127)
Informative Websites
www.aama-ntl.org
Dental Assistant (C.D.A.)
Certified Dental Assistant