Peter Frankopan
The First Crusade: The Call from the East
Disturbing news has emerged from Jerusalem and the city of Constantinople and is now constantly at the forefront of our mind: namely that the race of the Persians, a foreign people and a people rejected by God ... has invaded the lands of the Christians [and has] depopulated them by slaughter and plunder and arson.
Robert of Rheims
An embassy of the emperor of Constantinople came to the synod and implored his lordship the Pope and all the faithful of Christ to bring assistance against the heathen for the defence of this holy church, which had now been nearly annihilated in that region by the infidels who had conquered her as far as the walls of Constantinople. Our Lord Pope called upon many to perform this service, to promise by oaths to journey there by Gods will and to bring the emperor the most faithful assistance against the heathen as very best as they were able.
Bernold of Constance
Kelts assembled from all parts, one after another, with arms and horses and all the other equipment for war. Full of enthusiasm and ardour they thronged every highway, and with these warriors came a host of civilians, outnumbering the sand of the seashore or the stars of heaven, carrying palms and bearing crosses on their shoulders ... like tributaries joining a river from all directions, they streamed towards us in full force.
Anna Komnene
In his essence, the emperor was like a scorpion; for while you have nothing to fear from its face, you do well to avoid injury from its tail.
William of Tyre

BYZANTIUM IN CRISIS
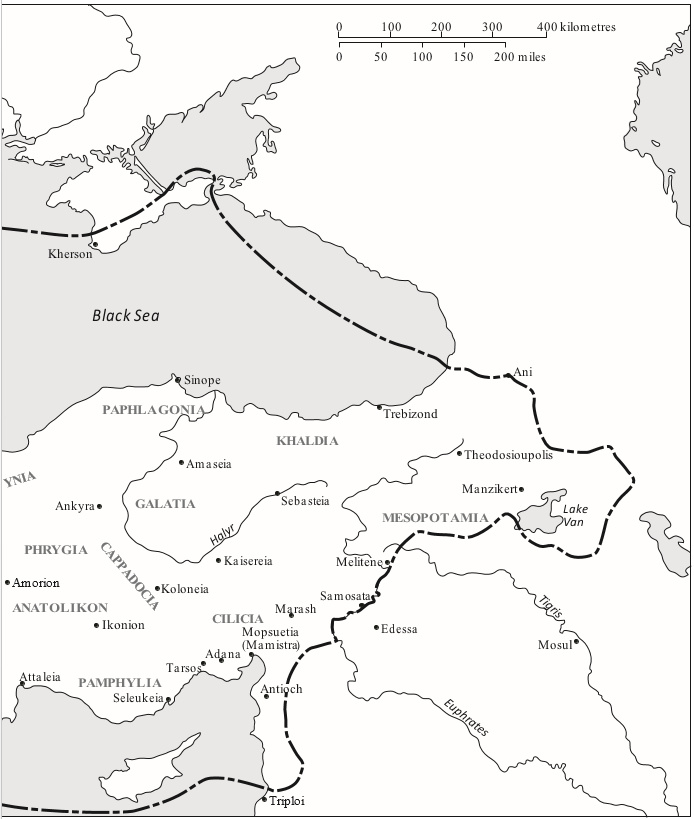
Alp Arslan and Romanos IV after the battle of Manzikert.

BYZANTIUMS GLORY
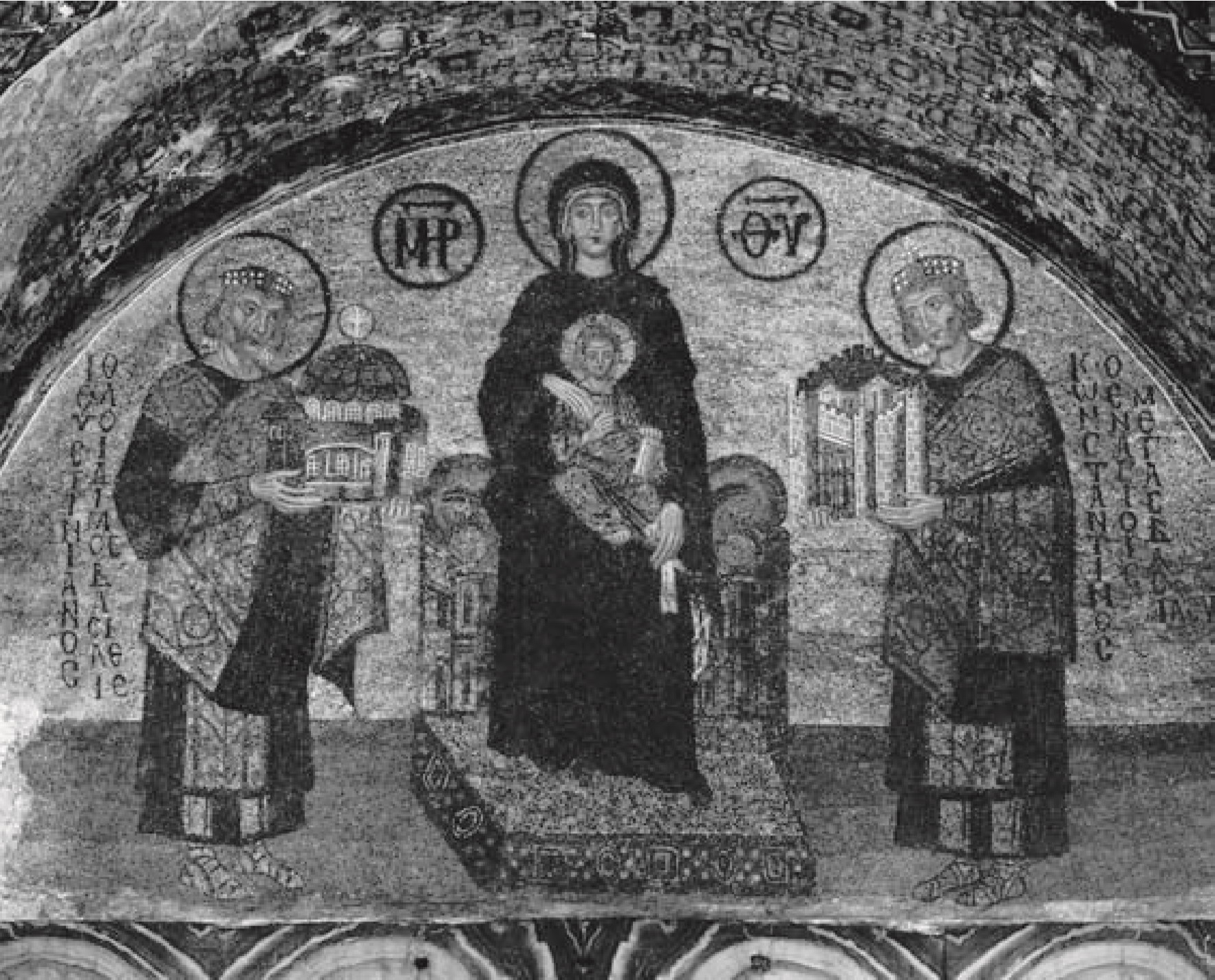
Christ and the Virgin Mary flanked by the emperors Constantine and Justinian. Mosaic in the south vestibule of Hagia Sophia, late tenth century.

Reliquary for wood from the True Cross, c.950.

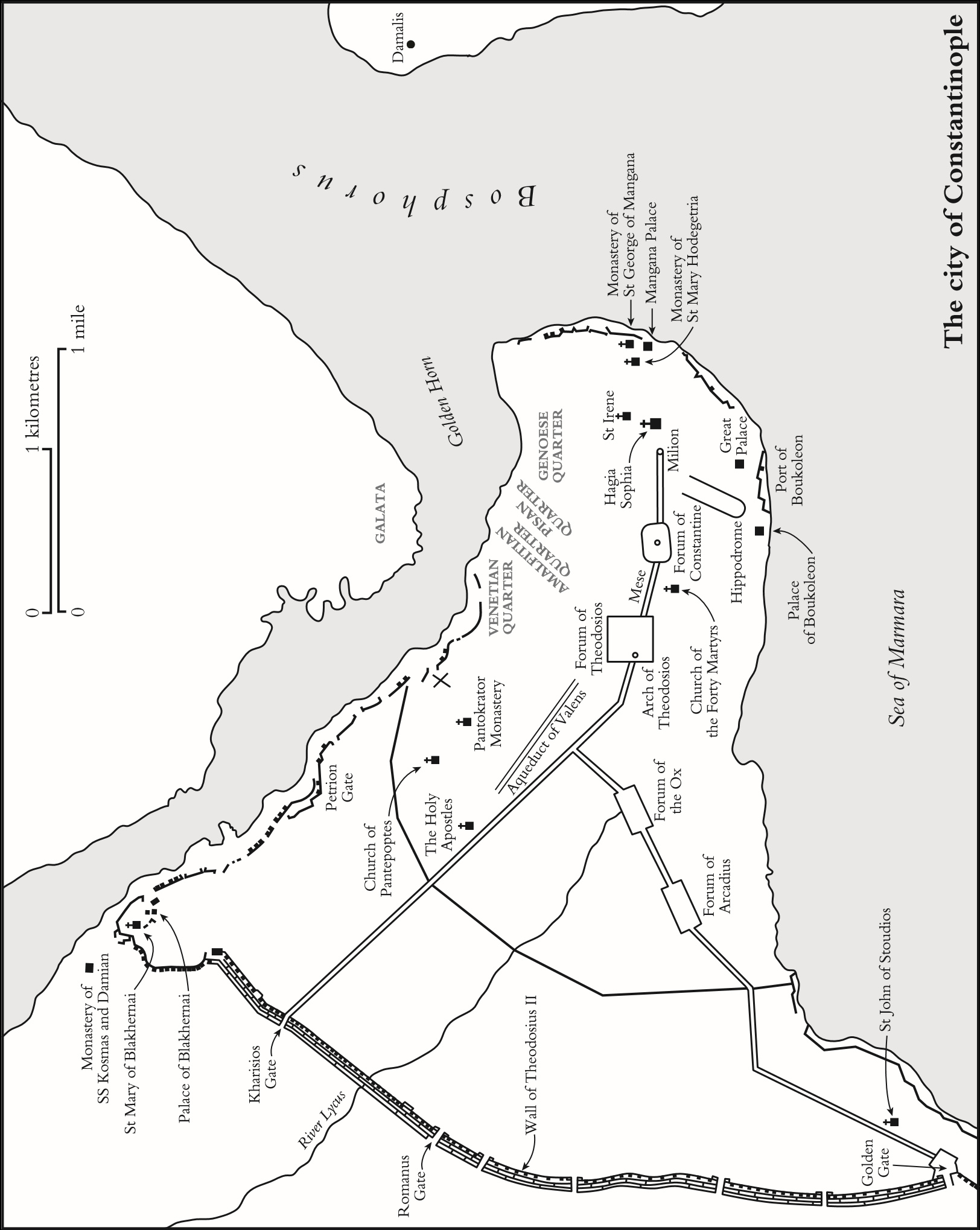
The walls of Constantinople, first built by the emperor Theodosius in the fifth century.

THE CALL FROM THE EAST
The hope of Byzantium: Emperor Alexios I Komnenos.

Coin issued by Alexios, depicting Christ giving a blessing

and the emperor himself.

THE RESPONSE FROM THE WEST
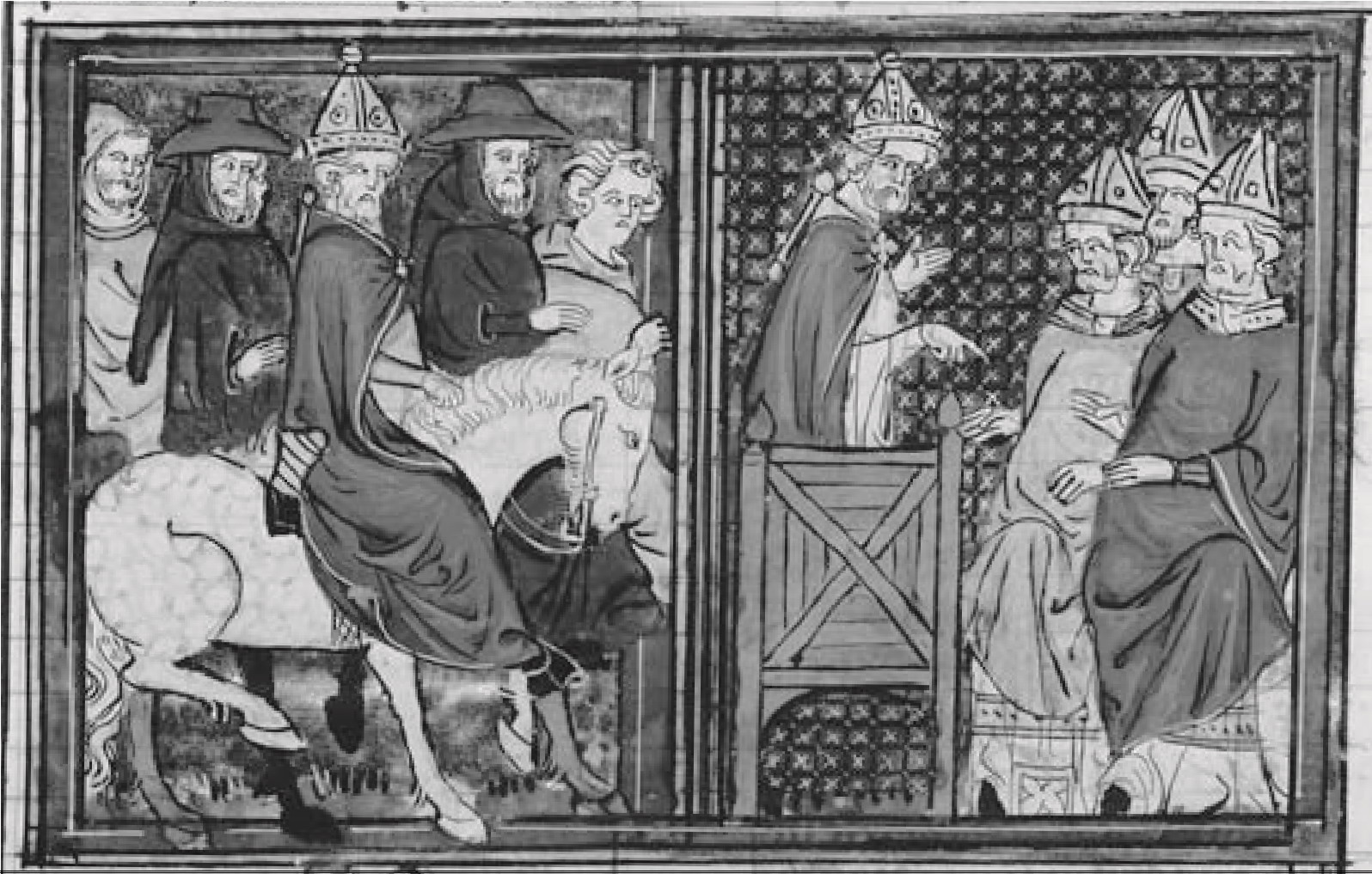
Pope Urban II arrives at the council of Clermont.

Emperor Alexios receives Peter the Hermit.

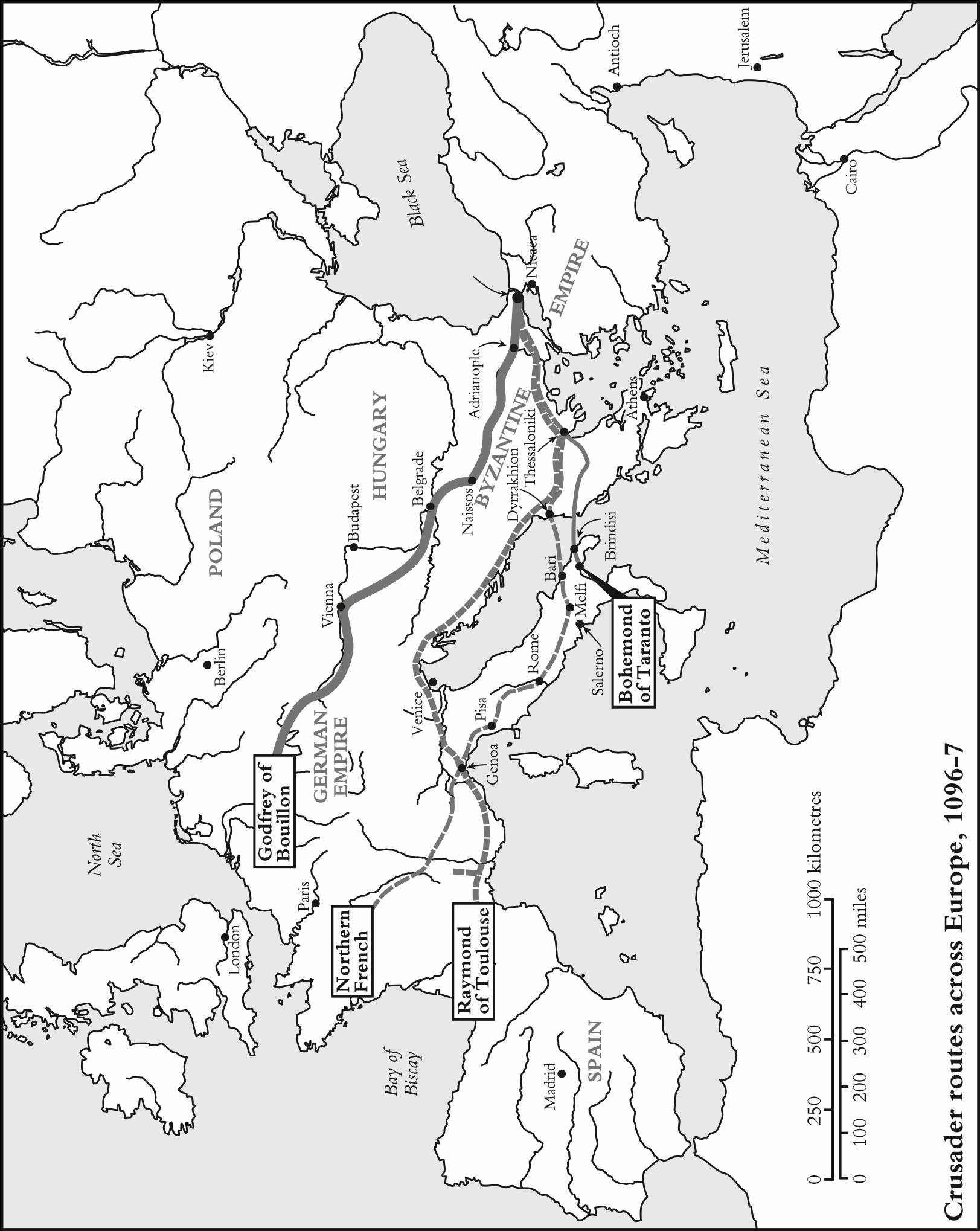
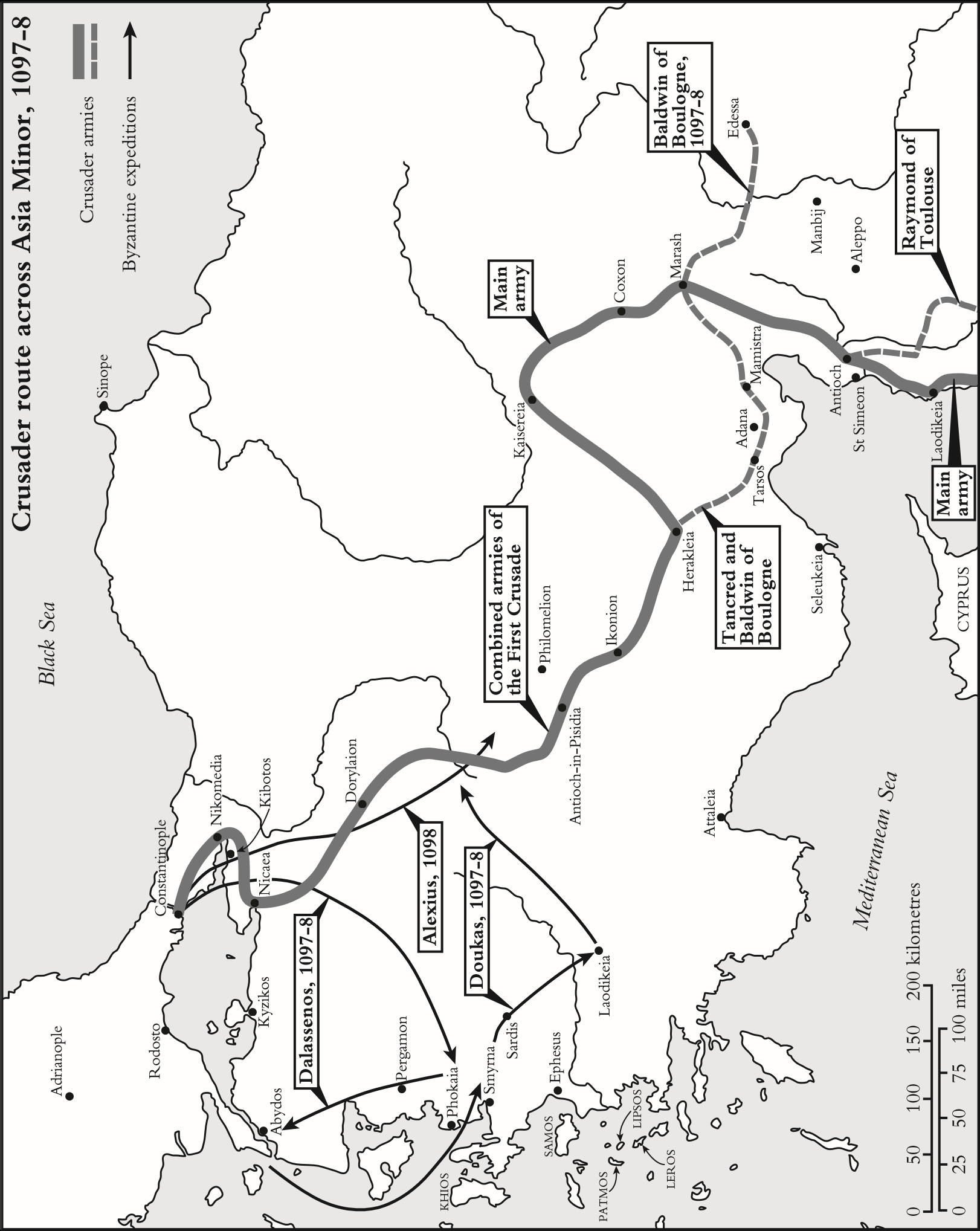
THE EXPEDITION TO THE HOLY LAND
The Crusaders at Nicaea, 1097.

The siege of Antioch, 10978.
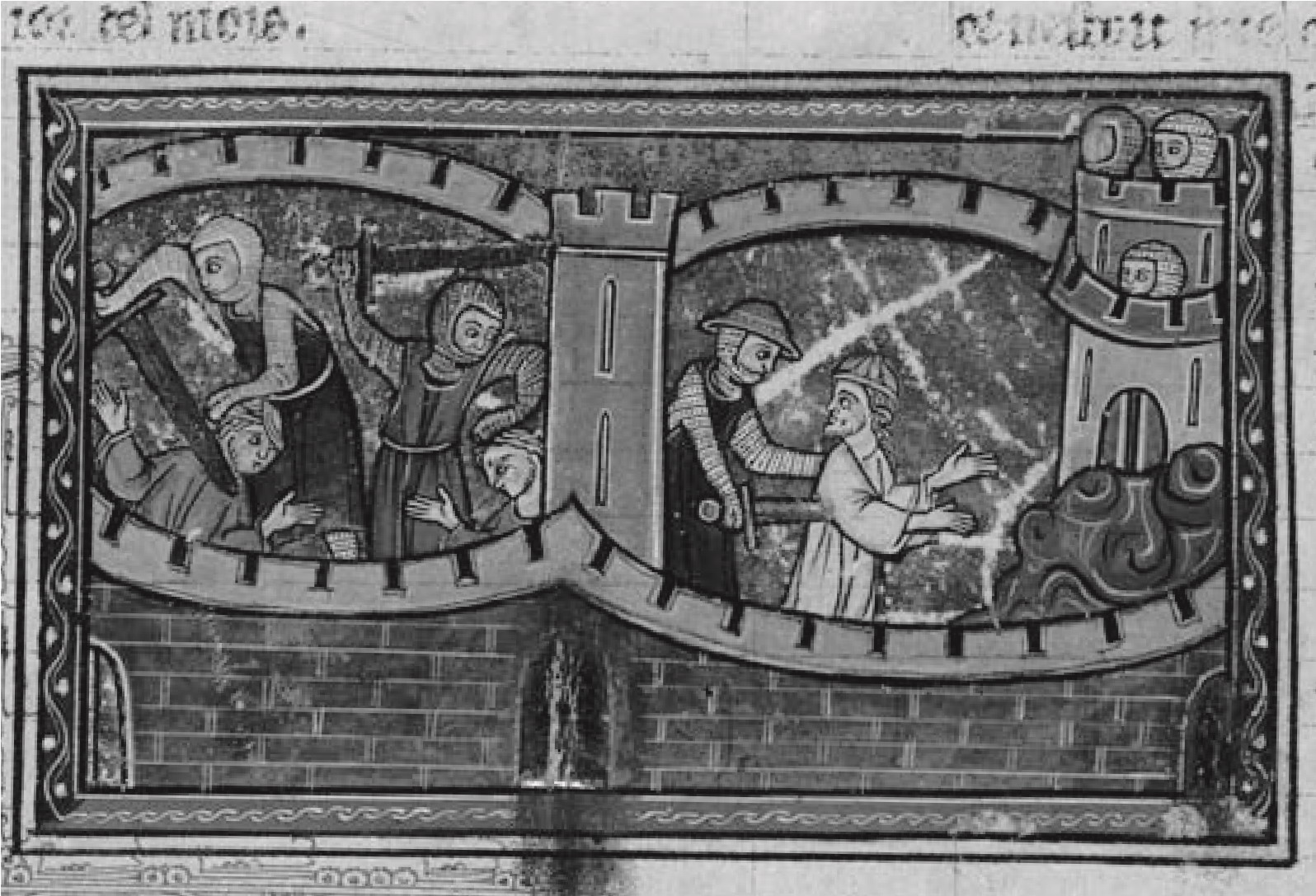

Crusaders massacring the inhabitants of Antioch, 1098.

The siege of Jerusalem, 1099.

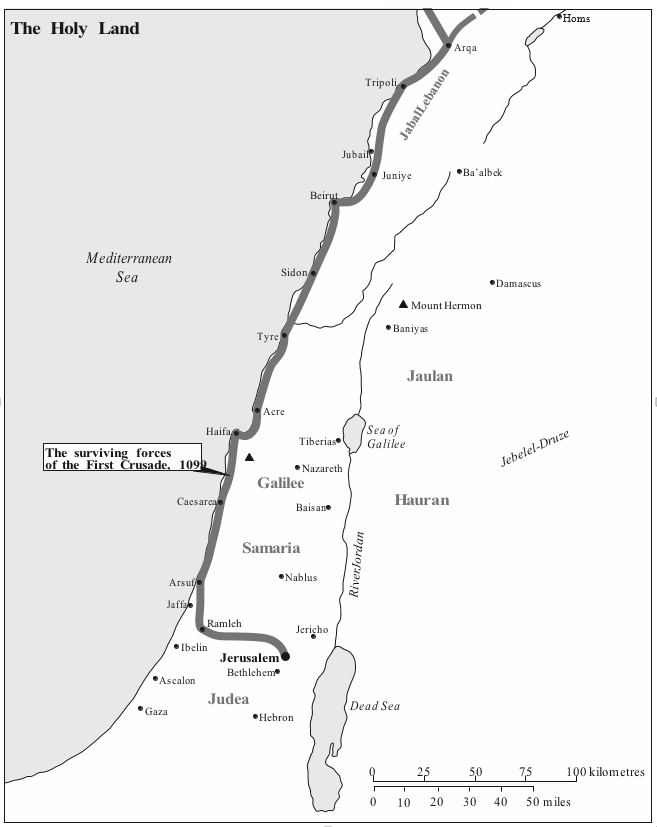
LIBERATING THE HOLY CITY
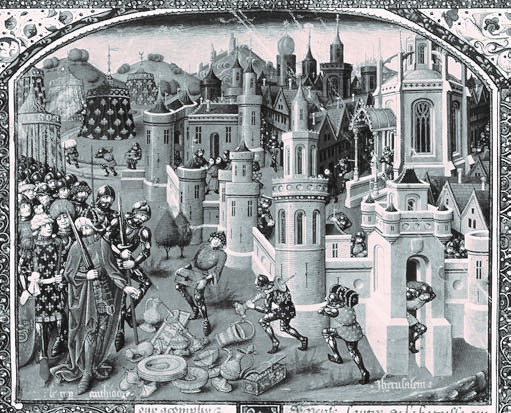
The looting of Jerusalem, 1099.
Preface and Acknowledgements
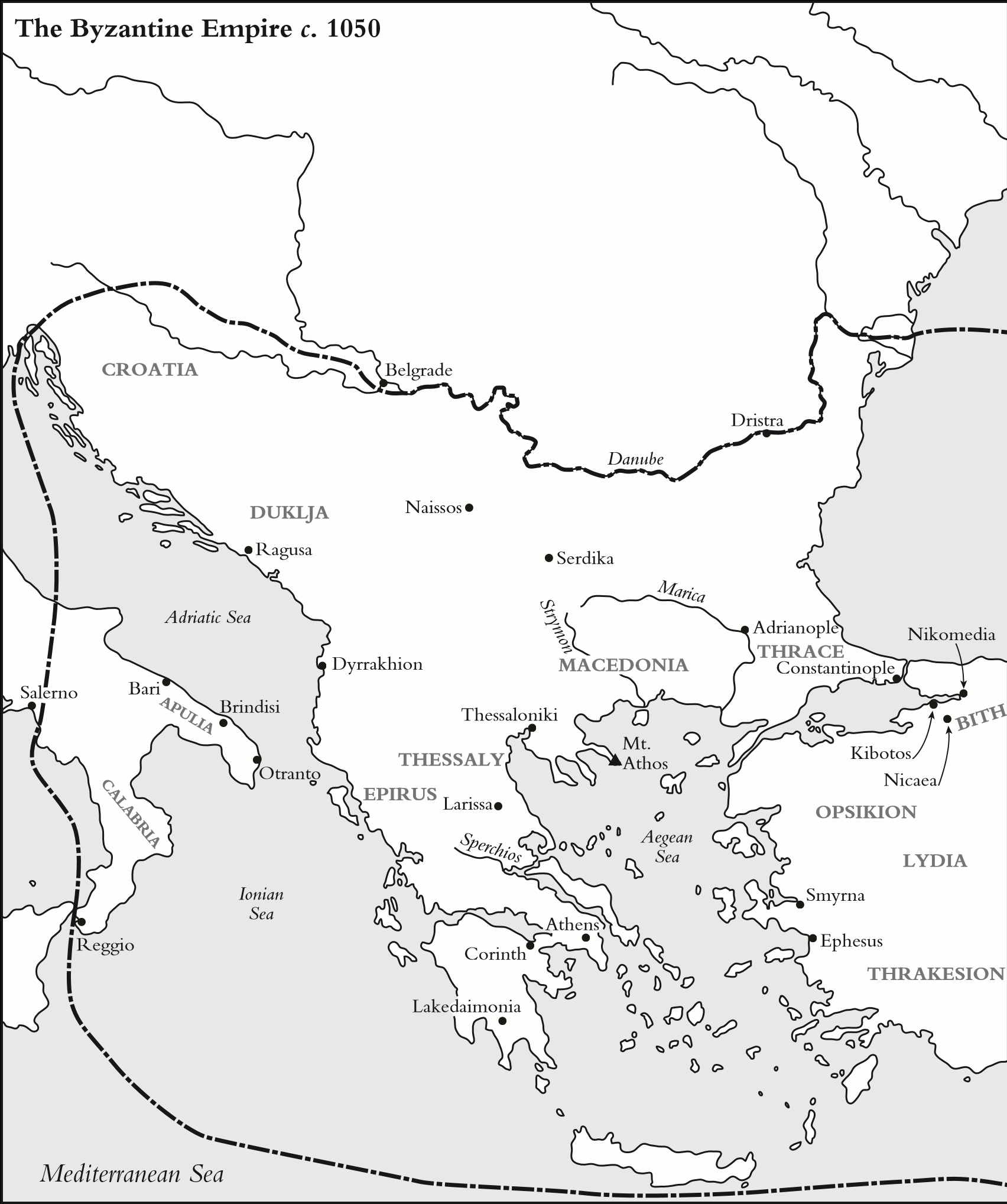
As most undergraduates find, at one point in the course of their studies, the prospect of a lecture starting at 9 a.m. can feel unfair and almost cruel. I remember wearily climbing the stairs of the History Faculty in Cambridge in 1992, having to shake myself awake to take a seat to listen to the first lecture of the term on the paper I had chosen, called Byzantium and its neighbours, 8001200. Five minutes later, I was suddenly alert and transfixed, as though I had just been given a triple espresso. I was hearing about the ruthless Pecheneg steppe nomads and how they would do anything in return for pepper, scarlet silk and strips of Middle Eastern leather; I was wondering about why pagan Bulgar leaders would choose to become Christians in the ninth century; I was hearing about New Rome the imperial city of Constantinople.
The excitement of that first lecture triggered a voracious appetite about the Byzantine Empire and its neighbours. It was a matter of course that I should want to carry on to do postgraduate research, and the only difficulty was choosing a topic. It was the reign of the emperor Alexios I Komnenos that caught my eye, with its wonderfully rich sources and many unanswered questions. It soon became clear, however, that in order to gain any real insight into the Byzantine Empire in the late eleventh and early twelfth centuries, I had to understand the literature of this period, and the Alexiad in particular; then the Greek and Latin sources of southern Italy; then the world of the steppe nomads; then the archaeology and material culture of Constantinople, the Balkans and Asia Minor; then the history of the Crusades, the medieval papacy, the establishment of Latin colonies in the Holy Land ... What had started, innocently enough, with an early morning lecture became a passion; occasionally overwhelming, sometimes frustrating, always exciting.
There are many who deserve thanks for their support and help over the years. The provost and fellows of Worcester College have provided a wonderful and sympathetic home since 1997, outstanding in their generosity and modest in the demands they have made. I owe thanks to Princeton University for awarding me a Stanley J. Seeger Visiting Fellowship, which allowed me a chance to open new avenues of research. The fellows of Harvard are also owed a debt of gratitude for making me a summer fellow at Dumbarton Oaks, where some of the ideas here took shape many moons ago. The staff of the Bodleian Library, above all the Lower Reading Room, and of the History Faculty Library have been wonderfully patient and goodhumoured. The same is true of my many colleagues in Oxford where I have had the great privilege to work alongside some of the finest scholars in the field of Late Antique and Byzantine Studies.





























