Lal - Operational amplifiers and linear integrated circuits
Here you can read online Lal - Operational amplifiers and linear integrated circuits full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2007, publisher: Pearson, genre: Computer. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
Operational amplifiers and linear integrated circuits: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Operational amplifiers and linear integrated circuits" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
Lal: author's other books
Who wrote Operational amplifiers and linear integrated circuits? Find out the surname, the name of the author of the book and a list of all author's works by series.
Operational amplifiers and linear integrated circuits — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Operational amplifiers and linear integrated circuits" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
K. Lal Kishore
Registrar
JNTU, Hyderabad

To
my wife, Gayatri
and
daughters, Kalpana and Pratyusha
I consider it a privilege to write the foreword for this book by Prof. K. Lal Kishore. Since the author has taught this subject for many years, it is apt that such a book be authored by him.
The Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University has often revised their curriculum to maintain currency with the requirements of the industry. Also, the practical aspects of the subject have been increasingly incorporated into the curriculum. This book is an essential text as it fulfils both, theoretical and practical, requirements equally.
K. RAJAGOPAL
VICE-CHANCELLOR
JNTU
HYDERABAD
The fag end of the 20th century saw a technology revolution, after which integrated circuits have come to play an important role in various industries. Although digital circuits are used widely, the role of analog circuits and linear integrated circuits (ICs) is no less important. These topics, therefore, need to be addressed from a students point of view and their applications explained in more detail. In the light of these developments, I felt the need for a textbook on operational amplifiers and linear integrated circuits. Through this book, I have tried to fill the gap in this area and familiarize the students with their design and application.
This book covers operational amplifiers, their applications, other linear integrated circuits like 555 timer, voltage regulator ICs, phase locked loop ICs, waveform generator ICs etc. Importance is given to the explanation of concepts and the working of circuits, so that teachers find it easy to explain the finer points and students are able to understand the same easily. Wherever possible, due importance is given to practical aspects connected with ICs. The book also contains a good number of solved problems. To enable students to prepare for competitive examinations, objective type questions are also given with answers. This textbook meets the requirements of the curriculum of the Indian universities and can also be useful for students of M.Sc. (Electronics), B.Sc. (Electronics), AMIETE, AMIE (Electronics), diploma courses in electronics and many such courses.
While writing this book, I have referred to a number of textbooks written on this subject by both Indian and foreign authors. I am grateful to all the authors and publishers of those books. Though every care has been taken to minimize mistakes, the book may have some errors and omissions. Suggestions on this aspect are welcome.
I am thankful to my family members, my wife Gayatri, and daughters, Kalpana and Pratyusha, for the patience they have shown when I was busy with my book.
K. LAL KISHORE
Objectives:
In this chapter
- Basic and practical considerations of operational amplifiers as well as definitions, and measurement of operational amplifiers are explained.
- Definitions of various parameters, their typical values and units are discussed. They should also get familiar with the internal block schematic and derivations of expressions for different applications of operational amplifiers.
The concept of an Integrated Circuit (IC) was laid in 1958 by Jack St. Clair Kilby of Texas Instruments. The circuit combined basic elements in a single piece of germanium. The device was held together by glue, with gold wires providing interconnections. The first planar (flat) transistor was made by Swiss Physicist Jean Hoemi of Fairchild Semiconductors. This technology became the basis for the present Integrated Circuits where silicon is the semiconductor material used.
In 1959, Robert Noyce of Fairchild constructed an IC, on a thin slice of silicon. This model made mass production of ICs easier.
Integrated circuits are so called because various components of an electronic circuit such as Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs), MOSFETS, resistors, capacitors and so on are integrated or combined together on a single silicon wafer. ICs are also referred to as chips since their actual size is very small.
Largely, based on the application and output response, ICs are classified as (1) Linear Integrated Circuits (Linear ICs), and (2) Digital Integrated Circuits (Digital ICs).
Linear ICs accept analog inputs and deliver analog outputs. Examples of linear ICs are given below.
- Operational Amplifiers (op-amp) 741
- Timer IC 555
- Phase Locked Loop IC 565
- Voltage Regulator IC 723
- Waveform Generator ICs (8038)
Digital ICs accept input in two discrete voltage levels, viz., logic 0 (zero) or logic 1 (+ 5 V). The output is also discrete in two specific voltage levels only. Due to this, noise immunity is better in digital circuits, compared to analog circuits. The noise signal is analog in nature and it also gets processed along with input in analog ICs and (linear ICs), unlike in digital ICs. Examples of digital ICs are given below.
- Logic Gates 7400, 7404
- Multiplexers
- Microprocessor: 8085, 8086, 80486
Classification of ICs is as shown in .
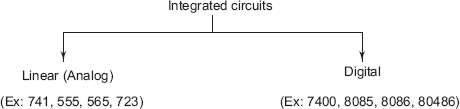
Fig. 1.1 General Classification of ICs
The credit of desiging internal circuit using vacuum tubes goes to George Philbrick. This was in 1948. Originally, operational amplifiers were meant for analog computers to perform mathematical operations like integration, summation, inversion, and so on. The internal circuit is a differential amplifier and cascaded stages and hence the name, operational amplifier. These are also abbreviated as op-amp and popularly called by that name.
The op-amp internal circuit design was further improved by replacing some BJTs with Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFETs). JFETs at the input stage of the op-amp draw very little current. The input can be varied between supply limits because the supply voltage will not fall as very less current is drawn. MOS transistors in the output circuit will also allow voltage to swing closer to supply limits. As both BJTs and JFETs are used, these are called as BiFET op-amps, LF 356, CA 3130 are of this type. With the development of technology, two op-amps sharing the same Vcc have also been fabricated. These are known as Dual op-amp ICs. Similarly four op-amps in the same package of pins have also been fabricated. These are called Quad op-amps: LM 358 is a Dual op-amp, and LM 324 is a Quad op-amp.
Based on their application and features, op-amps are classified as shown in .
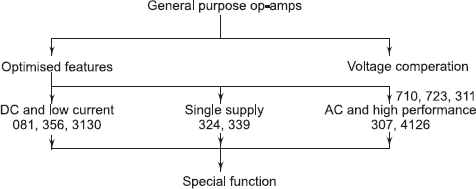
Fig. 1.2 Classification of ICs Based on Features
Some of the special function op-amps are:
- Video/Audio ICs
- Instrumentation applications
- Sonar send/receive modules
- Communication ICs
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Operational amplifiers and linear integrated circuits»
Look at similar books to Operational amplifiers and linear integrated circuits. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Operational amplifiers and linear integrated circuits and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.












