it-ebooks - GeeksForGeeks Computer Network Lecture Notes
Here you can read online it-ebooks - GeeksForGeeks Computer Network Lecture Notes full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2018, publisher: iBooker it-ebooks, genre: Computer. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.

GeeksForGeeks Computer Network Lecture Notes: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "GeeksForGeeks Computer Network Lecture Notes" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
GeeksForGeeks Computer Network Lecture Notes — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "GeeksForGeeks Computer Network Lecture Notes" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
From: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/computer-network-tutorials/
Open system:
A system which is connected to the network and is ready for communication.
Closed system:
A system which is not connected to the network and cant be communicated with.
Computer Network:
It is the interconnection of multiple devices, generally termed as Hosts connected using multiple paths for the purpose of sending/receiving data or media.
There are also multiple devices or mediums which helps in the communication between two different devices which are known as Network devices. Ex: Router, Switch, Hub, Bridge.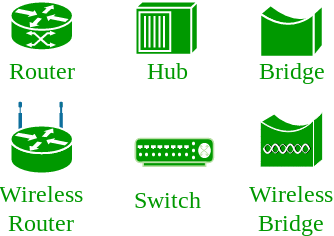
The layout pattern using which devices are interconnected is called as network topology. Such as Bus, Star, Mesh, Ring, Daisy chain.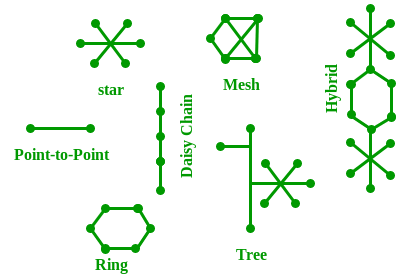
OSI:
OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection. It is a reference model that specifies standards for communications protocols and also the functionalities of each layer.
Protocol:
Protocol is the set of rules or algorthims which define the way how two entities can communicate across the network and there exists different protocol defined at each layer of OSI model. Few of such protocols are TCP, IP, UDP, ARP, DHCP, FTP and so on.
UNIQUE IDENTIFIERS OF NETWORK
Host name:
Each device in the network is associated with a unique device name known as Hostname.
Type hostname in the command prompt and press Enter, this displays the hostname of your machine.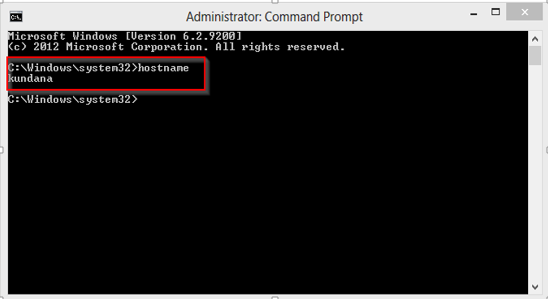
IP Address (Internet Protocol address):
Also know as Logical Address, is the network address of the system across the network.
To identify each device in the world-wide web, Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) assigns IPV4 (Version 4) address as unique identifier for each device on the Internet.
Length of the IP address is : 32-bits. (Hence we have 232 ip addresses available.)
Type ipconfig in the command prompt and press Enter, this gives us the IP address of the device.
MAC Address (Media Access Control address):
Also known as physical address, is the unique identifier of each host and is associated with the NIC (Network Interface Card).
MAC address is assigned to the NIC at the time of manufacturing.
Length of the MAC address is : 12-digit/ 6 bytes/ 48 bits
Type ipconfig/all in the command prompt and press Enter, this gives us the MAC address.
Port:
Port can be referred as logical channel through which data can be sent/received to an application. Any host may have multiple applications running, and each of this application is identified using the port number on which they are running on.
Port number is a 16-bit integer, hence we have 216 ports available which are categorized as shown below:
| Port Types | Range |
|---|---|
| Well known Ports | 0 1023 |
| Registered Ports | 1024 49151 |
| Ephemeral Ports | 49152 65535 |
Number of ports: 65,536
Range: 0 65535
Type netstat -a in the command prompt and press Enter, this lists all the ports being used.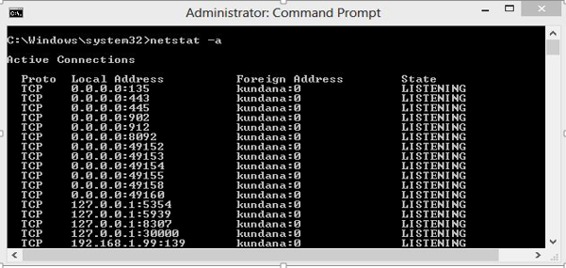
Socket:
The unique combination of IP address and Port number together are termed as Socket.
Few more concepts
DNS Server:
DNS stands for Domain Name system.
DNS is basically a server which translate web addresses or URL (ex: www.google.com) into their corresponding IP addresses. We dont have to remember all the IP addresses of each and every website.
The command nslookup gives you the IP address of the domain you are looking for. This also provides the information of our DNS Server.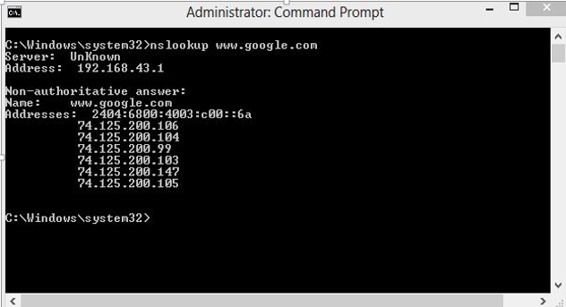
ARP:
ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol.
It is used to convert the IP address to its corresponding Physical Address(i.e.MAC Address).
ARP is used by the Data Link Layer to identify the MAC address of the Receivers machine.
RARP:
RARP stands for Reverse Address Resolution Protocol.
As the name suggest, it provides the IP address of the a device given physical address as input. But RARP has become obsolete since the time DHCP has come into picture.
This article is contributed by Kundana Thiyari. If you like GeeksforGeeks and would like to contribute, you can also write an article using contribute.geeksforgeeks.org or mail your article to contribute@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks.
Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.
A network is two or more devices connected through a link. A link is a communication pathway that transfer data from one device to another. Devices can be a computer, printer or any other device that is capable to send and receive data. For visualization purpose, imagine any link as a line drawn between two points.
For communication to occur, two devices must be connected in some way to the same link at the same time. There are two possible types of connections:
- Point-to-Point Connection
- Multipoint Connection
Point-to-Point Connection :
- A point-to-point connection provides a dedicated link between two devices.
- The entire capacity of the link is reserved for transmission between those two devices.
- Most point-to-point connections use a actual length of wire or cable to connect the two end, but other options such as microwave or satellite links are also possible.
- Point to point network topology is considered to be one of the easiest and most conventional network
topologies. - It is also the simplest to establish and understand.
Example: Point-to-Point connection between remote control and Television for changing the channels.
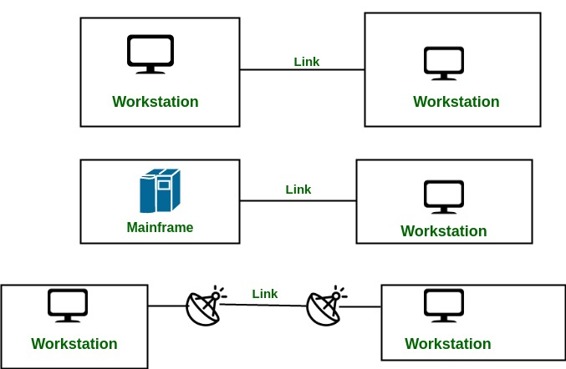
Multipoint Connection :
- It is also called Multidrop configuration. In this connection two or more devices share a single link.
- More than two devices share the link that is the capacity of the channel is shared now. With shared capacity, there can be two possibilities in a Multipoint Line configuration:
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «GeeksForGeeks Computer Network Lecture Notes»
Look at similar books to GeeksForGeeks Computer Network Lecture Notes. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book GeeksForGeeks Computer Network Lecture Notes and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.







