it-ebooks - GeeksForGeeks Operating Systems Lecture Notes
Here you can read online it-ebooks - GeeksForGeeks Operating Systems Lecture Notes full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2018, publisher: iBooker it-ebooks, genre: Computer. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.

GeeksForGeeks Operating Systems Lecture Notes: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "GeeksForGeeks Operating Systems Lecture Notes" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
GeeksForGeeks Operating Systems Lecture Notes — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "GeeksForGeeks Operating Systems Lecture Notes" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
From: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/operating-systems/
An operating system acts as an intermediary between the user of a computer and computer hardware. The purpose of an operating system is to provide an environment in which a user can execute programs in a convenient and efficient manner.
An operating system is software that manages the computer hardware. The hardware must provide appropriate mechanisms to ensure the correct operation of the computer system and to prevent user programs from interfering with the proper operation of the system.
Operating System Definition:
- An operating system is a program that controls the execution of application programs and acts as an interface between the user of a computer and the computer hardware.
- A more common definition is that the operating system is the one program running at all times on the computer (usually called the kernel), with all else being application programs.
- An operating system is concerned with the allocation of resources and services, such as memory, processors, devices and information. The operating system correspondingly includes programs to manage these resources, such as a traffic controller, a scheduler, memory management module, I/O programs, and a file system.
Functions of Operating system Operating system performs three functions:
- Convenience: An OS makes a computer more convenient to use.
- Efficiency: An OS allows the computer system resources to be used in an efficient manner.
- Ability to Evolve: An OS should be constructed in such a way as to permit the effective development, testing and introduction of new system functions without at the same time interfering with service.
Operating system as User Interface
- User
- System and application programs
- Operating system
- Hardware
Every general purpose computer consists of the hardware, operating system, system programs, and application programs. The hardware consists of memory, CPU, ALU, and I/O devices, peripheral device and storage device. System program consists of compilers, loaders, editors, OS etc. The application program consists of business program, database programs.
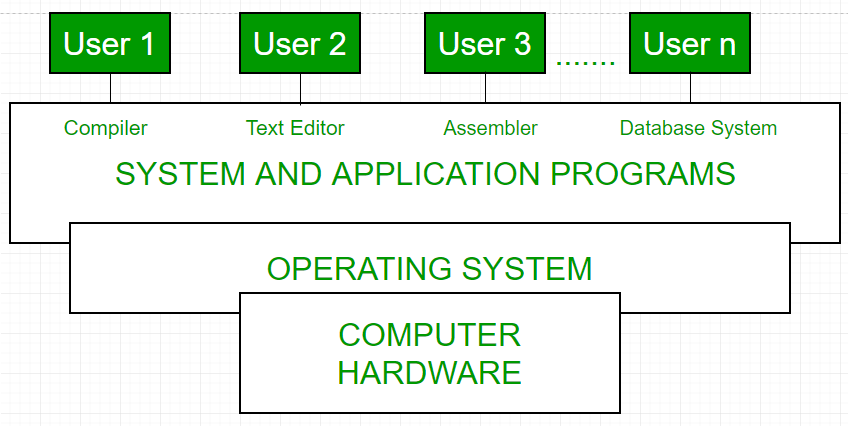
Every computer must have an operating system to run other programs. The operating system and coordinates the use of the hardware among the various system programs and application programs for a various users. It simply provides an environment within which other programs can do useful work.
The operating system is a set of special programs that run on a computer system that allows it to work properly. It performs basic tasks such as recognizing input from the keyboard, keeping track of files and directories on the disk, sending output to the display screen and controlling peripheral devices.
OS is designed to serve two basic purposes:
- It controls the allocation and use of the computing Systems resources among the various user and tasks.
- It provides an interface between the computer hardware and the programmer that simplifies and makes feasible for coding, creation, debugging of application programs.
The Operating system must support the following tasks. The task are:
- Provides the facilities to create, modification of programs and data files using and editor.
- Access to the compiler for translating the user program from high level language to machine language.
- Provide a loader program to move the compiled program code to the computers memory for execution.
- Provide routines that handle the details of I/O programming.
I/O System Management
The module that keeps track of the status of devices is called the I/O traffic controller. Each I/O device has a device handler that resides in a separate process associated with that device.
The I/O subsystem consists of
- A memory Management component that includes buffering caching and spooling.
- A general device driver interface.
Drivers for specific hardware devices.
Assembler
Input to an assembler is an assembly language program. Output is an object program plus information that enables the loader to prepare the object program for execution. At one time, the computer programmer had at his disposal a basic machine that interpreted, through hardware, certain fundamental instructions. He would program this computer by writing a series of ones and Zeros (Machine language), place them into the memory of the machine.
Compiler
The High level languages- examples are FORTRAN, COBAL, ALGOL and PL/I are processed by compilers and interpreters. A compiler is a program that accepts a source program in a high-level language and produces a corresponding object program. An interpreter is a program that appears to execute a source program as if it was machine language. The same name (FORTRAN, COBAL etc.) is often used designate both a compiler and its associated language.
Loader
A Loader is a routine that loads an object program and prepares it for execution. There are various loading schemes: absolute, relocating and direct-linking. In general, the loader must load, relocate and link the object program. Loader is a program that places programs into memory and prepares them for execution. In a simple loading scheme, the assembler outputs the machine language translation of a program on a secondary devices and a loader is places in core. The loader places into memory the machine language version of the users program and transfers control to it. Since the loader program is much smaller than the assembler, those makes more core available to users program.
History of Operating system
Operating system has been evolving through the years. Following Table shows the history of OS.
| Generation | Year | Electronic device used | Types of OS Device |
|---|---|---|---|
| First | 1945-55 | Vaccum Tubes | Plug Boards |
| Secondt | 1955-65 | Transistors | Batch Systems |
| Third | 1965-80 | Integerated Circuits(IC) | Multiprogramming |
| Fourth | Since 1980 | Large Scale Integration | PC |
Types of Operating System
- Batch Operating System- Sequence of jobs in a program on a computer without manual interventions.
- Time sharing operating System- allows many users to share the computer resources.(Max utilization of the resources).
- Distributed operating System- Manages a group of different computers and make appear to be a single computer.
- Network operating system- computers running in different operating system can participate in common network (It is used for security purpose).
- Real time operating system meant applications to fix the deadlines.
Examples of Operating System are
- Windows operating System (GUI based, PC)
- Linux operating System (Personal workstations, ISP,File and print server, Three-tier client/Server)
- MAC Operating System (Macintosh), used for personal computers and work stations.
- Android operating System (used in mobile applications)
References
Operating System Concepts Book
Introduction to Operating System NPTEL
This article is contributed by Aluka Madhavi. If you like GeeksforGeeks and would like to contribute, you can also write an article using contribute.geeksforgeeks.org or mail your article to contribute@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «GeeksForGeeks Operating Systems Lecture Notes»
Look at similar books to GeeksForGeeks Operating Systems Lecture Notes. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book GeeksForGeeks Operating Systems Lecture Notes and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.







