Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany 2017
Chunbao Xu and Fatemeh Ferdosian Conversion of Lignin into Bio-Based Chemicals and Materials Green Chemistry and Sustainable Technology 10.1007/978-3-662-54959-9_1
1. Structure and Properties of Lignin
Abstract
Lignin is a phenolic natural polymer, second only to cellulose. It can be extracted from lignocellulosic biomass through various chemical, physical, mechanical, and enzymatic treatments. The chemical structure and properties of the extracted lignin are mainly depended on the extraction method, vegetal species, location, season, etc. Based on the separation method, several types of lignin, also called technical lignin, could be obtained, including alkali lignin/kraft lignin, lignosulfonate, organosolv lignin, milled wood lignin (MWL), klason lignin, and hydrolytic lignin. The separation conditions can influence the cross-linked structure and molecular weight distributions of the technical lignin products. By far, lignin is mainly regarded waste or by-product streams from paper pulping mills and cellulosic ethanol plants with a limited application for heat and power generation. However, the abundant availability and unique structure of lignin make it a potential feedstock for the synthesis of biochemicals and biopolymers such as surfactants/dispersants, carbon fibers, phenolic resins, epoxy resins, and polyurethane resins, etc.
1.1 Lignin
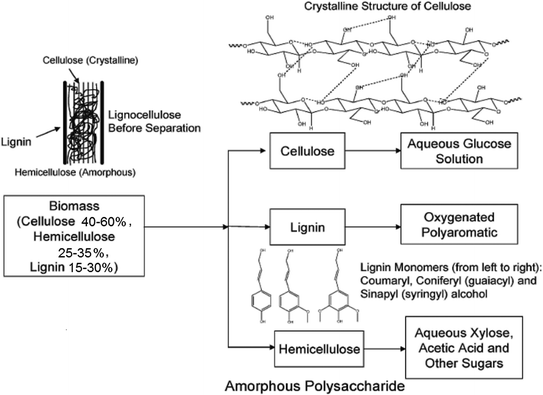
Wood, a heterogeneous, hygroscopic, cellular and anisotropic material, consists of cells, and the cell walls consist mainly of three organic components including cellulose (4060 wt%), hemicelluloses (2535 wt%), and lignin (1530 wt%) (Fig. ]. Currently, the majority of technical lignin is generated in kraft pulping processes, and the annual kraft lignin (KL) generation is estimated to be 50 million tons, present in the form of black liquor that is used mainly in the recovery boilers for heat and power generation in the kraft pulping mills.
Fig. 1.1
Schematic structure of wood cells, reprinted with permission from Ref. [] with modifications. Copyright (2006) American Chemical Society
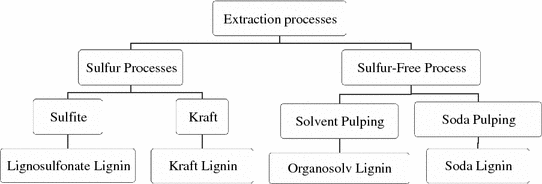
Fig. 1.2
Various lignin extraction processes and their dominant products (modified from Ref. [])
Lignin is the second most abundant natural renewable polymer after cellulose [] have been widely used in exploring the structure of lignin.
Table 1.1
Contents of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin in common lignocellulosic biomass (reprinted with permission from Ref. [])
Lignocellulosic materials | Cellulose (%) | Hemicellulose (%) | Lignin (%) |
|---|
Hardwoods stems | 4055 | 2440 | 1825 |
Softwood stems | 4550 | 2535 | 2535 |
Nut shells | 2530 | 2530 | 3040 |
Corn cobs | | | |
Grasses | 2540 | 3550 | 1030 |
Paper | 8599 | | |
Wheat straw | | | |
Sorted refuse | | | |
Leaves | 1520 | 8085 | |
Cotton seed hairs | 8095 | | |
Newspaper | 4055 | 2540 | 1830 |
Waste papers from chemical pulps | 6070 | 1020 | |
Primary wastewater solids | | NA | 2429 |
Swine waste | 6.0 | | NAa |
Solid cattle manure | 1.64.7 | 1.43.3 | 2.75.7 |
Coastal Bermuda grass | | 35.7 | 6.4 |
Switch grass | | 31.4 | 12.0 |
Copyright (2002) Elsevier
aNot available
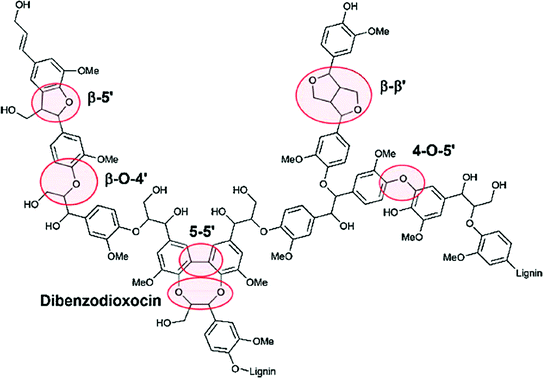
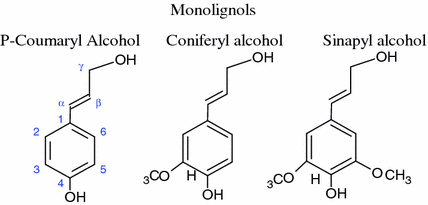
Lignin is a phenolic polymer formed by radical coupling polymerization of three monolignols (Figs. ].
Fig. 1.3
A fraction of lignin model structure, reprinted with permission from Ref. []. Copyright (2013) Royal Society of Chemistry
Fig. 1.4
Structure of three lignin monomers
1.2 Types of Lignin
Technical lignin is conventionally named after the separation (extraction) method, e.g., lignosulfonate lignin, kraft lignin, organosolv lignin, and soda lignin (Fig. ]. In addition, the separation conditions including mechanical action, enzymes, or chemical reagents can influence the crosslinked structure of lignin and formed lignin fragments with different molecular weight distributions.
Some important types of technical lignin are described as follows:
Alkali Lignin/Kraft Lignin
Alkali lignin is isolated from biomass in the presence of NaOH solution at high temperature and pressure. The linkages to polysaccharides are broken and lignin fragments are dissolved in the solvent, forming black liquor. The resulted lignin separated from black liquor with Na2CO3 is called soda lignin. The lignin separated in the presence of Na2SO4 is named kraft lignin [].
Lignosulfonate
Lignosulfonates or sulfonated lignins are water-soluble anionic polyelectrolyte polymers, recovered from the sulfite pulping of wood (brown liquor) [].
Organosolv Lignin
Organosolv pulping is conducted in the presence of an aqueous organic solvent at the temperature ranging from 140 to 220 . In this process, the alpha aryl-ether linkages of lignin are broken down by hydrolytic cleavage and the obtained fragments dissolve in the solvent [].
Milled Wood Lignin (MWL)
The milled wood lignin is obtained from milling wood in a ball-mill for tens of hours and the linkages to polysaccharides are broken mechanically. The fragmented lignin is dissolved in solvents such as 0.2 mol/L NaOH solution followed by extraction with dioxane-water mixture [. Lignin yields were as high as 2467% based on the total amount of lignin present.