1.1 Transfer RNA
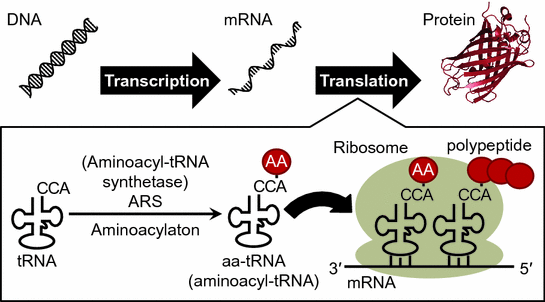
Genetic information is transcribed from DNA into mRNA (messenger RNA) and mRNA is translated into protein, and this process is called as central dogma (Fig. ).
Fig. 1.1
Schematic illustration of central dogma. AA in the red circle indicates amino acid. An image of protein was prepared from crystal structure of GFP ( green fluorescent protein) (PDB ID: 1GFL) (Yang et al. )
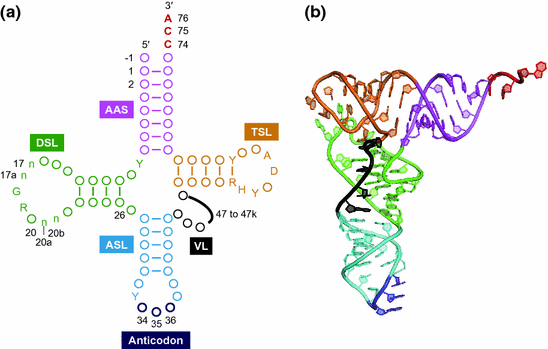
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is one of the most abundant and popular noncoding RNA, which works as an adaptor molecule linking the language of nucleotide to the language of amino acid in the translation step. Canonical tRNA forms cloverleaf secondary structure and L-shaped tertiary structure as shown in Fig. )] and accurate translation of mRNA to protein is essential for living organisms.
Fig. 1.2
Structure of tRNA. a Clover leaf structure of tRNA. Conserved bases are described, circles represent nonconserved bases, and numbers indicate the nucleotide position. Positions 3436 ( dark blue ) are anticodon bases and positions 7476 ( red ) are universally conserved as CCA. The sequences composing the intron and the extra bases presenting in the variable loop (position noted 4747k) are shown as black line . AAS ( magenta ), the amino acid-accepting stem; DSL ( green ), the dihydrouridine stem and loop; ASL ( cyan ), the anticodon stem and loop; VL ( black ); the variable loop, TSL ( orange ); the thymidine stem and loop, Y; pyrimidine, R; purine, H; not G, D; not C. The n bases at position 17, 17a, 20a, and 20b are optional bases not present in all tRNAs. Position 1 bases are found in all cytoplasmic mature tRNA GUGHis from the three biological domains. This figure was adapted from the previous paper (Marck and Grosjean )
Fig. 1.3
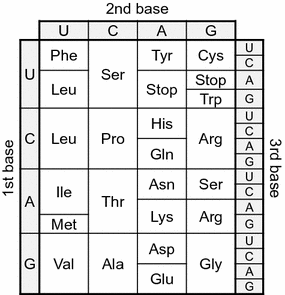
Standard genetic code. All 64 codons were assigned to corresponding amino acids or termination signal (termed as Stop in this figure)
CCA sequence at the 3-end is universally conserved in all three domains, prokaryote, eukaryote, and archaea. During the translation, CCA-3 end interacts with ribosome and translation factors, and these interactions are important for efficient translation. In the aminoacylation step, ARSs strictly recognize the body sequences of substrate tRNAs to charge specific amino acids onto specific tRNAs. In addition, because most ARSs also interact with the universally conserved CCA-3 end of tRNAs (Cavarelli and Moras ) may be usable. However, in this method, it is laborious work that various aminoacyl-nuleotides are prepared by chemical synthesis. If the easy method to prepare various aa-tRNA bearing mutations in the CCA-3 end, it is usable for analyzing the role of CCA-3 end during the translation and engineering the translation machinery.
1.2 Other Noncoding RNAs Than tRNAs
As I mentioned above, tRNA is one of the most abundant and popular noncoding RNA (ncRNA). In addition to tRNA, ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) are also known as popular ncRNA, which constitute a ribosome. There are three kinds of rRNAs (5S, 16S, and 23S rRNAs) in prokaryote, and four kinds of rRNAs (5S, 5.8S, 18S, and 28S rRNA) in eukaryote. Peptidyl transfer reaction, which makes a peptide bond, is catalyzed by 23S rRNA or 28S rRNA. These tRNAs and rRNAs are much abundant and account for about 95% of all RNAs in mammalian cells (Lindberg and Lundeberg ).
The various other ncRNAs than tRNA and rRNA have been identified mainly in mammalian (Esteller ).
The class of small ncRNA includes various RNAs such as snRNAs (small nuclear RNAs), snoRNAs (small nucleolar RNAs), and miRNAs (micro RNAs) (Matera et al. ).
As mentioned above, various small ncRNAs have been identified and the function of those RNAs have been studied. However, it is not easy to discover the small ncRNAs with very low abundance because tRNAs are too much abundant in small RNA fraction (less than 200 nt). To overcome this problem, easy method to remove tRNAs from small RNA fraction is required.
1.3 Aminoacylation Ribozyme Flexizyme
In order to achieve these requirements described in former sections it is necessary (i) to easily prepare the various aa-tRNAs bearing mutations in the CCA-3 end, and (ii) to remove endogenous tRNAs from small RNA fraction. I focused attention on the unique characteristics of flexizymes which were in vitro selected aminoacylation ribozyme (Suga et al. ). First, I briefly summarize how flexizymes have been developed.
A ribozyme which is an RNA having catalytic activity was first discovered in nature in 1980s (Kruger et al. )]. Among them, aminoacylation ribozymes were important because these are candidates as key molecules which link the ancient RNA world with modern protein world.
Fig. 1.4
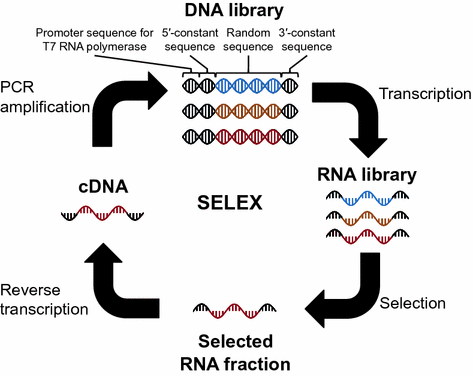
General scheme of SELEX (in vitro selection) of functional RNAs. Black sequences are constant regions including the promoter sequence for T7 RNA polymerase and the 5/3-constant sequences necessary for reverse transcription and PCR amplification. Colored ( blue , orange , and red ) sequences indicate the random region. This figure is adapted from the previous review (Terasaka and Suga )