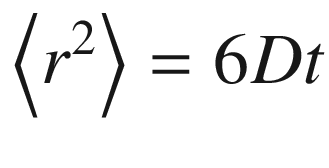1. DW MRI: Techniques, Protocols and Post-processing Aspects
1.1 Introduction
Diffusion is the process of random motion of water molecules in a free medium. For human tissues, water mobility can be assessed in the intracellular, extracellular and intravascular spaces. All media have a different degree of structure and thus pose a variant level of difficulty in water mobility that is called diffusivity. A sequence sensitized to microscopic water mobility by means of strong gradient pulses can be utilized to provide insights in the complexity of the environment which in turn can reveal information related to tissue microarchitecture.
A major requirement in diffusion imaging is to select ultrafast pulse sequences that may freeze macroscopic motion in the form of respiration, peristalsis or patient motion in general. For this reason, Echo Planar Imaging (EPI) sequences modified with the addition of two identical strong diffusion gradients are routinely used to provide diffusion information. The amplitude and duration of the diffusion gradients is represented by the b-value (measured in s/mm2), an index used to control the sensitivity of DWI contrast to water mobility.
1.2 Formal Definition of Diffusion
Molecules are involved in a thermal random motion called the Brownian motion, according to the observation in 1827 by Robert Brown [17731858] of the erratic translation movement of pollen in water, a random movement with no net ensemble displacement. This situation was further studied in 1908 by Paul Langevin [18721946] []. This microscopic movement is due to thermal agitation and occurs for water molecules in a bath of pure water (self-diffusion) or in a viscous liquid medium.
For the free three-dimensional diffusion, considering the Brownian motion under thermal agitation, Albert Einstein derived in 1905 the relation between the mean quadratic displacement, the diffusion coefficient and the diffusion time
t:
In other words, starting from a position
r0 after a time
t the particles reach a standard deviation position located on the surface of a sphere of radius (6
Dt)1/2. The value of the diffusion coefficient
D depends on the temperature
T and the friction
F (that is proportional to the viscosity) of the medium.
In living tissues, diffusion is restricted by many other factors like intracellular metabolites, the presence of cell membranes, the extracellular architecture, the relative size of cells and extracellular compartment. Therefore, the measured diffusion coefficient is called apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC). The apparent diffusion coefficient value is in general reduced if cells expand because of cytotoxic oedema, or when the cell density is more elevated, like in most malignant tissues. The link between the ADC and tissue cellularity seems quite complex and is still under investigation [].
In biological tissue, water diffusion can be spatially restricted by the presence of ordered structures; therefore, diffusion becomes anisotropic where the mathematical description requires a diffusion tensor D to be introduced. However, in abdominal organs like the liver or the pancreas the overwhelming majority of studies deals with the isotropic part of the diffusion tensor, i.e. the average diffusion measured in three orthogonal directions, called the average diffusivity or the mean diffusion. In what follows we shall simply refer to it as the diffusion coefficient.
1.3 Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging
1.3.1 The StejskalTanner Sequence, Image Contrasts, and Basic Image Processing
Following the seminal works on MR and diffusion by Carr and Purcell [). Diffusing spins (moving spins) travelling at least partially along the direction of the diffusion gradients will accumulate a net dephasing and this results into a signal attenuation, while stationary spins will be identically dephased and rephased with no signal loss. The StejskalTanner gradients are generally used within a Spin Echo Echo Planar Imaging (SE-EPI) sequence, allowing to acquire diffusion-weighted images (DWI). The signal of the SE StejskalTanner sequence can be calculated as: