To The Point...
100+ SQL Queries
Jet SQL for Microsoft Office Access
By I.F.S. Harrison with Fish Davis MCSE, MCDBA, MCITP, MCTS ~**~ Published By I.F.S. Harrison Copyright 2013-2019 by I.F.S.Harrison AllRights Reserved NOT FOR RESALE Please Note: This product is not for resaleor redistribution. Any reselling, reproducing, redistributing, orcopying of this book, its pictures, listing description, or titleis strictly prohibited by Local, State, Federal and InternationalIntellectual Copyright laws. Any unauthorized use will be pursuedto the fullest extent of the law.
All copyrights, quotations, websites, orregistered trademarks listed in this book are merely listed asexamples or reference. The author is in no way affiliated with anycompanies, services, websites, quotations, properties or namesmentioned herein, and each individual trademark or copyright listedwithin this book belongs only to the respective owner and are beingused with written permission or under terms of fair use or publicdomain. Any references, prices, policies, and procedures mentionedherein are subject to change without notice. It is the usersresponsibility to ensure that they follow the terms, EULA, and anyother conditions of any software, websites, and any other property,or item mentioned within this guide Microsoft and Access are registeredtrademarks of the Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/orother countries.
Learn the structure of the SELECT statement,used to retrieve data from your database. WHERE The WHERE clause is in SQL used to filterrecords ORDER BY In SQL, ORDER BY is used to sort the resultset GROUP BY AND AGGREGATEFUNCTIONS In SQL, use aggregate functions to return onevalue, calculated from multiple values in a column SUBQUERIES In SQL, a subquery is a query that is nestedinside a SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement, or inside ofanother subquery UPDATE In SQL, use UPDATE to update existing recordsin a table.
DELET E In SQL, use DELETE to delete existing recordsin a table JOINS Examples of how to Join tables in your Accessdatabase using SQL CREATINGTABLES Learn how to create tables using SQL in yourMicrosoft Access databases INSERT Now that your table has been created, learnhow to insert data into those tables using SQL ALTERTABLES In SQL, use ALTER TABLE to add, delete, ormodify columns in an existing table. OTHER SQLQueries TEST YOURSKILLS TEST YOUR SKILLS ANSWERS
INTRODUCTION
The examples that follow use MicrosoftsNorthwind database. Northwind is a sample database that I use inmany SQL courses. The Northwind database stores informationabout a fictitious specialty food companys employees, clients,products, and orders. The Northwind database is available in thesample templates area of the Microsoft Access application.
Northwind can also be found online throughMicrosoft, and is free.
Switching to SQL view in MicrosoftAccess 1. Open the Northwind database. Create a Query in Design View byclicking the Query Design button on the Ribbons Createtab. 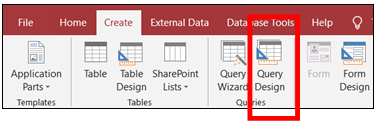 Close the Tables Window ifopened. Click SQL View on the topleft corner of the Design tab.
Close the Tables Window ifopened. Click SQL View on the topleft corner of the Design tab.  To return to SQL View,click the View buttons drop-down arrow, and select SQL View .
To return to SQL View,click the View buttons drop-down arrow, and select SQL View . 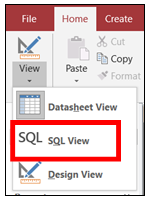
SELECT
The SELECT Syntax SELECT Column1 , Column2,Column3 FROM Table SELECT retrieves all data from the column(s) listed.

SELECT
The SELECT Syntax SELECT Column1 , Column2,Column3 FROM Table SELECT retrieves all data from the column(s) listed.
To retrieve all columns in a table, type anasterisk * after SELECT. To retrieve specific columns, list the columnnames separated by a comma. FROM designates the table(s) from which the data isretrieved. Query: Select all columns, and records, from the Customerstable. 1. In SQL view type the following: SELECT *
FROM Customers NOTE: SQL is not case sensitive, nor does SELECT andFROM need to be on different lines.
SELECT * FROM Customers works just aswell. 2. Click the Run button. 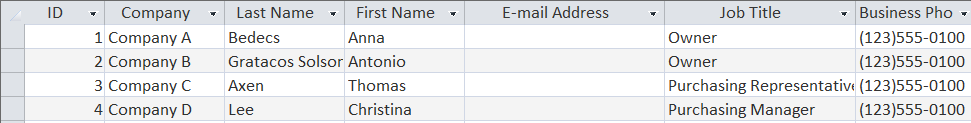 The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 18 columns and 29records. Query : Select all columns, and records,for the Products table.
The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 18 columns and 29records. Query : Select all columns, and records,for the Products table.
SELECT * FROM Products 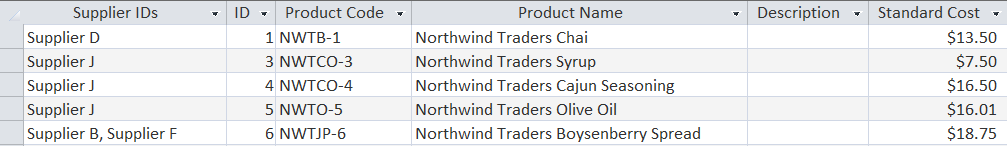 The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 14 columns and 45records. Query: Select the company names, state, and phone numbers for all ofthe customers. SELECT Company,[State/Province], [Business Phone] FROM Customers NOTE: The order of the columns in the record set isdetermined by the order of the columns listed in the SELECTstatement, not the underlying table. The State/Province and Business Phone fieldscontain spaces and special characters, and must be surrounded bysquare brackets in the SQL statement.
The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 14 columns and 45records. Query: Select the company names, state, and phone numbers for all ofthe customers. SELECT Company,[State/Province], [Business Phone] FROM Customers NOTE: The order of the columns in the record set isdetermined by the order of the columns listed in the SELECTstatement, not the underlying table. The State/Province and Business Phone fieldscontain spaces and special characters, and must be surrounded bysquare brackets in the SQL statement. 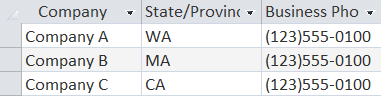 The record set is truncated to savespace.
The record set is truncated to savespace.
The results are 3 columns and 29 records. Query : Select the product name, listprice, and category of product in the Products table. SELECT [Product Name],[List Price], Category FROM Products 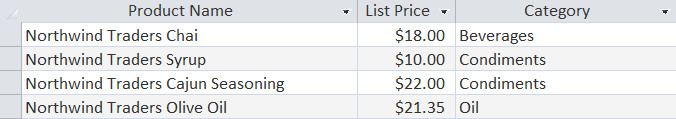 The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 45 records. Query: Using the Employees table, select the first name, last name,city and state of the employees. SELECT [FirstName],[Last Name],City,[State/Province] FROMEmployees
The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 45 records. Query: Using the Employees table, select the first name, last name,city and state of the employees. SELECT [FirstName],[Last Name],City,[State/Province] FROMEmployees 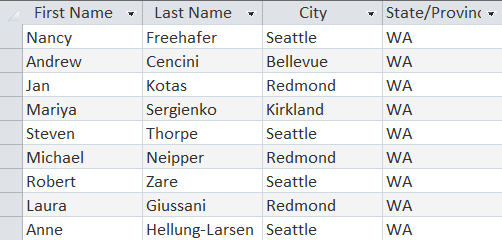 Query: Using the Customers table, select the company, state, firstname, last name and job title of the customers.
Query: Using the Customers table, select the company, state, firstname, last name and job title of the customers.
SELECT Company,[State/Province], [First Name], [Last Name], [Job Title] FROM Customers  The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 29 records.
The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 29 records.
Aliasing Columns
There might be occasions when the field namesare not easily interpreted, or you just want to change the displaytext in your record set. In databases that I work with, I use aone-word naming convention for my fields. For example, strFirstName denotes astring field that holds the first name information. While that is fine for the database, it mightbe confusing for someone looking at the record set.
Next page











 Northwind can also be found online throughMicrosoft, and is free.
Northwind can also be found online throughMicrosoft, and is free.  Close the Tables Window ifopened. Click SQL View on the topleft corner of the Design tab.
Close the Tables Window ifopened. Click SQL View on the topleft corner of the Design tab.  To return to SQL View,click the View buttons drop-down arrow, and select SQL View .
To return to SQL View,click the View buttons drop-down arrow, and select SQL View . 
 The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 18 columns and 29records. Query : Select all columns, and records,for the Products table.
The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 18 columns and 29records. Query : Select all columns, and records,for the Products table. The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 14 columns and 45records. Query: Select the company names, state, and phone numbers for all ofthe customers. SELECT Company,[State/Province], [Business Phone] FROM Customers NOTE: The order of the columns in the record set isdetermined by the order of the columns listed in the SELECTstatement, not the underlying table. The State/Province and Business Phone fieldscontain spaces and special characters, and must be surrounded bysquare brackets in the SQL statement.
The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 14 columns and 45records. Query: Select the company names, state, and phone numbers for all ofthe customers. SELECT Company,[State/Province], [Business Phone] FROM Customers NOTE: The order of the columns in the record set isdetermined by the order of the columns listed in the SELECTstatement, not the underlying table. The State/Province and Business Phone fieldscontain spaces and special characters, and must be surrounded bysquare brackets in the SQL statement.  The record set is truncated to savespace.
The record set is truncated to savespace. The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 45 records. Query: Using the Employees table, select the first name, last name,city and state of the employees. SELECT [FirstName],[Last Name],City,[State/Province] FROMEmployees
The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 45 records. Query: Using the Employees table, select the first name, last name,city and state of the employees. SELECT [FirstName],[Last Name],City,[State/Province] FROMEmployees  Query: Using the Customers table, select the company, state, firstname, last name and job title of the customers.
Query: Using the Customers table, select the company, state, firstname, last name and job title of the customers. The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 29 records.
The record set is truncated to savespace. The results are 29 records.