Preface
Building Information Modelling (BIM), Iheard this term two years back in one of my firms seminars. The man presentingin his late 60s, white beard, blue eyes like most of British man of his age andof course thick British accent which I adore. It was very basic introductorypresentation on Building Information Modelling and how its going to transformAEC (Architecture, Engineering and construction) industry. The conceptfascinated me; it is felt like AEC industry finally found the solution to allits problems. No more heated coordination meeting, no more design changes atthe last moment, no more discovery of clashes after construction started and nomore interdisciplinary coordination headache. But at the same time its allsound too good to be true or become reality. After the presentation I talkedwith the Presenter about my doubt that its just felt like heaven, too perfectand so not really real. He said me nodded in agreement and said its up to usnow to make heaven real.
After that day, life moves as usualProject Deliveries, Coordination meetings, Client Meeting, last minute designchanges and so on, all very real, certainly not heaven. But this BIM refuse toescape my mind, even in day today working I am thinking OK, we can do likethat in BIM environment and it will make our life less miserable. Days goes byand my BIM fever also going up. I started asking question to my Colleagues, myimmediate supervisor, my Project manager, but everybody has different answer,which making me more and more curious.
I was perusing my graduation and time tosubmit my project and for that I have choose a topic and top of my mind was BIM(Building Information Modelling). During research of my Project I realize thatthere are so many literature online and offline about BIM and that also made merealize, how vast the subject itself. But there was one major problem, all thatmaterial is scattered and everyone talking about only one or two aspects ofBIM. There are books from various publications, lots of blogs, market reportsand what not. But for beginner like me, I am looking for a complete and conciseoverview of BIM. Not many details but as single book covering all essentialaspects of BIM, which will help to set my direction and give me sense offulfilment knowledge about the subject. But I could not found it.
Meanwhile I submitted my Graduationproject on BIM Implementations Framework and Hurdles; its got approved andappreciated. After that it made me think that there are so many beginners likeme, who are going to face the problems like me and might, lost their interestin subject. So here I am writing this book for all those beginners, who hasheard of BIM in some way or other but dont know where to start.
This book is for all BIM enthusiast, Engineers,Contractors, Consultants, Designers, Owners and all those are even remotelyconnected to AEC industry. I am not BIM expert or dont have many yearsexperience in the BIM area, but I am BIM enthusiast who is Woking in AECindustry form last seven years and realise what correct implementation of BIMcan do wonders.
In this book I have tried to cover mostof the topic related to BIM in concise manner. As the subject itself is vastmultidisciplinary in nature, this book will act has path finder and help youhave complete glance over a subject in one sitting. This book is for all thosebeginners who share passion for the subjects, but get blown away by vast andscattered information. I hope this book will help to spark an interest insubject and will contribute to make BIM heaven a reality.
This is my first book and I will really appreciateyour feedback and views to make this book better. You write me on Sagar_UB09@yahoo.in
Best of Luck!
Sagar Ub October 2014
Content
Cover
Title Page
Preface
Chapter 1 What is BIM?
Chapter 2 BIM Types and MaturityLevels
Chapter 3 Why BIM?
Chapter 4 Discipline Specific BIM
Chapter 5 Common Myths about BIM
Chapter 6 Getting Started with BIM
Chapter 7 BIM Implementation Framework(Project Specific)
Chapter 8 Major Implementation Hurdles
Chapter 9 BIM Data Exchange Platforms
Chapter 10 BIM Personnel
Chapter 11 Future of BIM
Key terms
References
Chapter 1: What is BIM?
With the UK governmentcalling for the use of Building Information Modelling (BIM) in all itsconstruction projects by 2016, BIM become a buzz word in construction industry.Many construction firms are now investing in BIM technologies during bidding,preconstruction, construction and post construction. BIM exploits the potentialin computer based modelling technologies to provide a new way of designingbuildings and managing design and construction processes.
In worldwide scenariothere continues to be considerable comment about Building Information Modelling(BIM). BIM is a way of approaching the design and documentation of project byutilising 3-D design, physical performance and other information regarding theentire life cycle of the building in the construction information/buildingmodel. It is clear that the use of BIM is increasing. An NBS survey of theconstruction industry conducted between December 2012 and February 2013 foundthat 39 percent of responding were using BIM, which does not sound a lot butit was up from 13 percept in 2010.
What is BIM?
Building InformationModelling (BIM) is described as:
A digitalrepresentation of physical and functional characteristics of a facility. Assuch it serves as a shared knowledge resource for information about a facilityforming a reliable basis for decision during its life cycle from inceptiononward
(As per National BIMStandard Unites States, 2010).
Building InformationModelling (BIM) is the process and practice of virtual design and constructionthroughout its lifecycle. It is platform to share knowledge and communicatebetween projects participants.
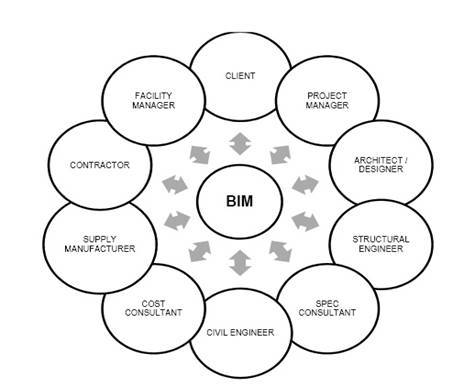
Fig.Data Sharing in BIM
BIM is not just thelatest release of CAD software; it is an entirely new way of looking at thedesign and construction of building. Conventionally, a good deal of design andconstruction work is document-based. Information is communicated and stored viaa variety of drawings and reports that, despite being stored and distributed indigital form, are essentially unstructured and thus of limited use. Not onlyis this information unstructured, it I held in variety for forms and locationsthat are not formally coordinated (information on individual buildingcomponent, for example, are contained on drawings, specification, bills ofquantity, description, etc.). Such an approach has considerable potential fordata conflicts and redundancy as well as risks to data integrity and security.Conversely, by providing an intelligent, digital structure of for projectinformation and ultimately a means by which the information can all be heldcentrally as single model- BIM opens up a wide range of possibilities forimprovements.
BIM is based on digitalmodels of a building that store information about the project (relating toarchitecture, engineering, construction and so on) in a way that enables it tobe shared across and between different design and construction discipline. Notonly that, 3D dynamic modelling software can be used to develop and manipulatethese digital models to refine the design, and also to test and validate itspotential performance across a range of criteria, including build ability,energy performance in-use, whole life cost etc. The potential for all keyproject information to be stored and manipulated in computer is what sets BIMapart form more conventional approaches, and BIM-based design solutions differfrom their traditional counterparts in that they :