MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
HANDBOOK FOR FORMULAS
(GATE, ESE, SSC JE AND OTHER COMPETITIVE EXAMS)
NAVY FEROZ
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FORMULA BOOK
by Navy Publication Pvt Ltd.,
All rights reserved including those of translation into other languages. In accordance with the copyright Act,2012, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise. Any such act or scanning, uploading and electronic sharing of any part of this book without the permission of the publisher constitutes unlawful piracy and theft of the copyright holders intellectual property. If you would like to use material from this book (other than for review purposes), prior written permission must be obtained from the publisher.
ABOUT
Mechanical Engineering Formulas - all subjects formulas with concepts and course outlines are given here. Select your desired course and you can revise all the Formulas within an hour only. When you are a mechanical engineer, you need to know the important formulas during the competitive exams like GATE, ESE and other exams to solve the answers easily using the formula. So, you must know the all-important formulas in the mechanical engineering Subjects. This book is specially prepared for the mechanical engineers.
PREFACE
In order to ignite your preparations for your Exams. This book providing the list of Important formulas for all subject of mechanical engineering, which was quite in demand and useful for all learners. Providing all the formulas in the single book will help the candidates for their preparation.
This combined formula book will help you to learn the all mechanical engineering formulas for GATE, ESE, SSC JE and other mechanical engineering exams.
TABLE OF CONTENT
SI MULTIPLES
Metric System
VALUE | EXPONENT | SYMBOL | PREFIX |
1 000 000 000 000 | | T | tera |
1 000 0S00 000 | 10 | G | giga |
1 000 000 | 10 | M | mega |
1 000 | 10 | k | kilo |
| 10 | h | hecto |
| 10 | da | deca |
0.1 | -1 | d | deci |
0.01 | -2 | c | centi |
0.001 | -3 | m | milli |
0.000 001 | -6 | micro |
0.000 000 001 | -9 | n | nano |
0.000 000 000 001 | -12 | p | pico |
Conversion Chart for Metric Units
To Convert | To Milli- | To Centi- | To Deci- | To Metre, Gram, Litre | To Deca- | To Hecto- | To Kilo- |
Kilo- | x 10 | x 10 | x 10 | x 10 | x 10 | x 10 |
Hecto- | x 10 | x 10 | x 10 | x 10 | x 10 | x 10 -1 |
Deca- | x 10 | x 10 | x 10 | x 10 | x 10 -1 | x 10 -2 |
Metre, Gram, Litre | x 10 | x 10 | x 10 | x 10 -1 | x 10 -2 | x 10 -3 |
Deci- | x 10 | x 10 | x 10 -1 | x 10 -2 | x 10 -3 | x 10 -4 |
Centi- | x 10 | x 10 -1 | x 10 -2 | x 10 -3 | x 10 -4 | x 10 -5 |
Milli- | x 10 -1 | x 10 -2 | x 10 -3 | x 10 -4 | x 10 -5 | x 10 -6 |
BASIC UNITS (DISTANCE, AREA, VOLUME, MASS, DENSITY)
BASIC UNITS
SI | IMPERIAL |
DISTANCE 1 metre (1 m) = 10 decimetres (10 dm) =100 centimetres (100 cm) =1000 millimetres (1000 mm) 1 decametre (1 dam) = 10 m 1 hectometre (1 hm) = 100 m 1 kilometre (1 km) = 1000 m | 12in.=1ft 3 ft = 1yd 5280 ft = 1 mile 1760 yd = 1 mile |
Conversions:
1 in. = 25.4 mm
1 ft = 30.48 cm
1 mile = 1.61 km
1 yd = 0.914 m
1 m = 3.28 ft
AREA
1 sq metre (1 m) = 10 000 cm = 1 000 000 mm 1 sq hectometre (1 hm) = 10 000 m = 1 hectare (1 ha) 1 sq km (1 km) = 1 000 000 m | 1 ft = 144 in. 1 yd = 9 ft 1 sq mile = 640 acre = 1 section |
Conversions:
1 in. = 6.45 cm =645 mm
1 m = 10.8 ft
1 acre = 0.405 ha
1 sq mile = 2.59 km
SI | IMPERIAL |
VOLUME 1 m = 1000000 cm = 1 x 10 mm 1 dm = 1 litre 1 litre = 1000 cm 1 mL = 1cm 1 m = 1000 litres | 1ft = 1728 in. 1 yd = 27 ft 1(liquid) U.S. gallon = 231 in. = 4 ( liquid) quarts 1 U.S. barrel (bbl) = 42 U.S. gal. 1 imperial gallon = 1.2 U.S. gal. |
Conversions:
1 in. = 16.4 cm
1 m = 35.3 ft
1 litre = 61 in.
1 U.S. gal. = 3.78 litres
1 U.S. bbl. = 159 litres
1 litre/s = 15.9 U.S. gal/min
Mass and Weight
1 kilogram (1 kg) = 1000 grams 1000 kg = 1 tonne | 2000 lb = 1 ton (short) 1 long ton = 2240 lb |
Conversions:
1 kg (on Earth) results in a weight of 2.2 lb
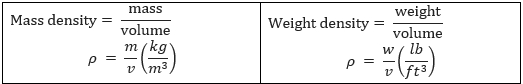
Density
Conversions:
S.I | IMPERIAL |
RELATIVE DENSITY In SI R.D. is a comparison of mass density to a standard. For solids and liquids the standard is fresh water. | In Imperial the corresponding quantity is specific gravity ; for solids and liquids a comparison of weight density to that of water. |